Abstract
Background
Among Neotropical fishes, the family Characidae is highly diverse and speciose and its taxonomy is not completely resolved. In Chile, the family is represented by five species, all within the genus Cheirodon, of which C. pisciculus, C. galusdae, C. kiliani, and C. australe are endemic, while C. interruptus is introduced. We compared chromosomal markers in order to appreciate the taxonomy and evolution of these trans-Andean fishes.
Results
The specimens were photographed in stereomicroscope to observe the ventral protrusive teeth and cusps for morphological analysis and species identification. All of the species analysed had equally diploid chromosome number 2n = 50, with karyotypes dominated by high number of acrocentric chromosomes as compared to those of other members of Cheirodontinae. The distribution of heterochromatin was inconspicuous and was similar in all the species. The number of active NORs (nucleolus organizer regions) was polymorphic, with the greater number of them in C. kiliani and C. galusdae. The location of 5S and 18S rDNA ranged in number and position, showing two sites in different chromosomes. The fluorescent in situ hybridization with telomeric probe did not reveal interstitial sites in all analysed species.
Conclusions
The comparative analysis of karyotypes and morphological markers revealed a biogeographic pattern of distribution, with the species that occur in the southern region forming one group and those in central and northern Chile forming another.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Although South America is typically megadiverse in biodiversity, the hydrogeography of Chile and its natural isolation due to the Andean cordillera makes an exception. These patterns have influenced the evolutionary history of its fish fauna, which is highly endemic and inconspicuous in morphology and coloration what makes them difficult to distinguish [28]. Among the diverse fishes of the Neotropical region, the family Characidae is one of the most complex groups in terms of its taxonomy [13]. In Chile, the family is represented by a single genus, namely Cheirodon [6, 27]. Its species are morphologically similar, which makes it difficult to distinguish them [21].
Five species of Cheirodon occur in Chile, they are distributed allopatrically in a North to South direction: C. pisciculus (Girard, 1855), C. galusdae [4], C. kiliani [3], and C. australe (Campos, 1992) are endemic to Chile [3], whereas C. interruptus (Jenyns, 1842) is native to the Atlantic basins of Argentina, Uruguay, and Brazil (Malabarba 2003). It may have been introduced to Chile in the 1960s along with the larvae of Pejerrey, Odontesthes bonariensis (Valenciennes, 1835) [1, 3]. In fact, the first records of C. interruptus in Chile were from Peñuelas Lake, an artificial lake where O. bonariensis was likely first reared [20].
The Chilean Cheirodon species have already been the subject of morphological and molecular analyses [3, 14, 21], to define their phylogenetic relationships. These analyses tended to group geographically distant species, such as Ch. australe and Ch. interruptus (the introduced species) together [3, 14, 21]. In addition, some of the morphological characters used in those analyses can vary inter- and intra-specifically, which may lead to erroneous identification of Cheirodon populations [13]. Furthermore, the DNA sequence analyses used in Chilean Cheirodon did not include Ch. pisciculus nor Ch. galusdae, respectively, [14], so the phylogenetic relationships between the trans-Andean species remain unclear.
Due to the difficulties in sampling as well as their small size making difficult to obtain chromosomes, there is no cytogenetic information about the Cheirodon except the 2n and karyotypes of the Cheirodontinae genera Odontostilbe and Serrapinnus only [22, 25, 30]. These data may be used to generate cytotaxonomic information and detect evolutionary relationships to better understand the diversity of the genus Cheirodon [2]. Accordingly, in order to infer the taxonomy and evolution of the trans-Andean Characidae, in the present work we elucidated the conventional and molecular cytogenetic characteristics of its five species and contrast them with available morphological, molecular and cytogenetic data for the group.
Methods
Biological materials and sampling areas
A total of 15 individuals were collected for each one of the following species in different areas: Ch. interruptus (Estero Marga-Marga, Viña del Mar, V region, Chile, coordinates 19H 0263800.90 UTM E–6342166.09 UTM S), Ch. pisciculus (Río Angostura, Hospital, Metropolitan region, Chile, coordinates 19H 0338122.17 UTM E–6250729.69 UTM S), Ch. galusdae (Río Andalién, Concepción, VIII região, Chile, coordinates 18H 0682055.00 UTM E–5925386.00 UTM S), Ch. kiliani (Rio Calle-Calle, Antilhue, XIV region, Chile, coordinates 18H 0674363.00 UTM E–5592270.00 UTM S) and Ch. australe (Lagoa La Poza, desembocadura Lago Llanquihue, Puerto Varas, X região, Chile, coordinates 18G 0679651.18 UTM E–5428179.56 UTM S). The capture of the specimens was authorised by the Subsecretaría de Pesca y Acuicultura del Gobierno de Chile (SUBPESCA) and by the Servicio Nacional de Pesca y Acuicultura del Gobierno de Chile (SERNAPESCA), Authorization No. 740.
Representative individuals of different morphological types (two males and two females for each specie) were anesthetised, labelled, and preserved in absolute ethanol for taxonomic identification. The specimens were photographed using a Leica M205C Stereomicroscope to observe the ventral protrusive teeth and cusps. The analysed material was deposited in the Department of Zoology of the Universidade Federal de Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, under vouchers UFRGS 22295 (Ch. interruptus), UFRGS 22296 (Ch. galusdae), UFRGS 22297 (Ch. pisciculus), UFRGS 22298 (Ch. kiliani), and UFRGS 22299 and UFRGS 22300 (Ch. australe).
Chromosome preparations
Chromosome preparations were obtained from fin tissue regenerated for three days for animals acclimated at 20 °C in aquarium. The regeneration occurs in situ, therefore, does not require special incubation conditions (20 °C), more than those that do the fish to remain activefollowing the protocol of [29]. This technique was employed here due to the small size of the animals (< 3.0 cm). To obtain the number, size, and morphology of chromosomes, the slides were stained with Giemsa diluted in 5% phosphate buffer (KH2 PO4 + Na2 HPO4) pH 6.8 for 10 min and then washed in running water and air dried. To visualize heterochromatic regions, we used the C-band technique by Sumner [23], adaptated by Lui et al. [12]. The nucleolus organizer regions (Ag-NORs) were visualised according to [8].
Fluorescence in situ hybridisation (FISH) was utilised to detect chromosomal location of rDNA (18S and 5S) sites and telomeric sequences, according to the protocol of Pinkel et al. [18], under high stringency (2.5 ng/μL probe, 50% formamide, 2× SSC, and 10% dextran sulphate). The 18S rDNA probe was amplified from the DNA of Prochilodus argenteus (Spix & Agassiz, 1829) [7], using the primers NS1 5′-GTAGT CATATGCTTGTCTC-3′ and NS8 5’-TCCGCAGGTTC ACCTACGGA-3′ [31]. The 5S probe was obtained from DNA amplification of Leporinus elongatus (Valenciennes, 1850), using the primers A 5’-TACGCCCGATCTCGTCCGATC-3′ and B 5’-GCTGGTATGGCCGTAGC-3′ [15]. The telomere probe (TTAGGG) n was amplified using the primers (TTAGGG)5 and (CCCTAA)5, in the absence of a DNA template, according to [9]. The chromosome mapping of the 18S probe was achieved using the Kit Biotin Nick Translation (Roche), and the 5S and telomeric mappings were performed using Kit Dig Nick Translation (Roche), following the manufacturer’s recommendations. Signal detection was performed with digoxigenin conjugated to rhodamine (18S probe) and streptavidin conjugated to FITC (5S and Telomeric probes) (Roche Applied Science).
All analyses used mitotic chromosomes subjected to sequential treatment to optimize the use of the chromosome material. The treatments were applied in order of increasing invasiveness: Giemsa stain, double-color FISH with 18S and 5S rDNA probes, C-bands and silver staining of nucleoli organizing regions (Ag-NORs).
Karyotype analysis
Conventional chromosome preparations were observed under optical microscope, Olympus® BX41. FISH metaphases were analysed using an epifluorescence microscope with appropriate filters. Images were captured using a camera, CCD DP71 12 mp, with the software DP controller (Olympus). At least 10 specimens, five from males and five from females, were analysed for each species. Adobe Photoshop v. CC (2015) software was used to karyotype arrange and Easy Idio v. 1.0 software was used to construct ideograms. Chromosomes were classified following Levan et al. [11] and karyotypes organised in decreasing order of size.
Results
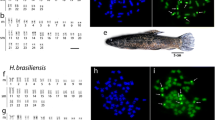
The adaptation of the technique used by [29] produced high-quality metaphases from regenerated fin tissue of different species of Cheirodon. The representatives of each species were returned to their localities of origin, except those deposited in museum. All species under study possessed the diploid chromosome number 2n = 50 and karyotypes varying subtly in proportion among metacentric (m), submetacentric (sm), subtelomeric (st) and acrocentric (a) chromosomes (Table 1, Fig. 1).
Karyotypes of Cheirodon species occurring in Chile. (a) Ch. interruptus, (b) Ch. pisciculus, (c) Ch. galusdae, (d) Ch. kiliani, and (e) Ch. australe arrangend from Giemsa-stained chromosomes. Chromosomes were grouped as metacentric (m), submetacentric (sm), subtelocentric (st), and acrocentric (a). Bar equal 10 μm
Specie-specific variation was observed for FISH marker patterns of the 18S and 5S rDNA sites, which were located into different acrocentric chromosomes or in synteny on the same chromosome. The 18S site patterns was associated with the cytotaxonomic groupings.
The 18S signals were observed in the long arms (q) and the 5S in the short arms (p), except in the pairs 16, 21, and 25 in Ch. austral, in which the 5S region was located in the q arm (Fig. 2). Intraspecific variation was observed too with presence or absence of markers in one or two chromosomes in the same pair, especially in Ch. australe, the most polymorphic specie for these markers (Fig. 2, Fig. 4).
Karyotypes of Cheirodon species occurring in Chile, arranged from chromosomes after double FISH with 18S (Greenred) and 5S (green) probes (Red). (a) Ch. interruptus, (b) Ch. pisciculus, (c) Ch. galusdae, (d) Ch. kiliani, and (e) Ch. australe. Chromosomes after silver staining (white box) and chromosome pairs of other individuals of the same species with FISH rDNA probes (black box). Bar equal 10 μm
In addition, the Ag-NORs enabled us to detect the activity level of the NORs. The highest levels of relative activity were found in C. galusdae and C. kiliani (Fig. 2). In these species, the location of the 18S rDNA is polymorphic with 2 pairs of chromosomes carrying these sequences, one of them being syntenic with 5S rDNA (Fig. 2c and d).
FISH with the (TTAGGG) n probe revealed only telomeric positive sites (Fig. 3a). The C-band pattern was very poor and similar in terms of quantity and distribution in karyotypes of different species (Fig. 3b). Heteromorphic sex chromosomes were not identified in the studied species at the level of analysis applied.
The ideograms allowed us to summarise and compare the general similarities and differences in the karyotypes of the five species as compared to their geographical distribution. The ideograms (Fig. 4) allowed us to summarise and compare the general similarities and differences in the karyotypes of the five species as compared to their geographical distribution. Moreover, these data are complementing with the shape of teeth and number of ventral procurrent rays, morphological characters used for the identification of the species.
Geographic regions of Chile (left), ideograms (middle) and photographs of teeth and caudal peduncle region (right) of Cheirodon species occurring in Chile. (a) Ch. interruptus from Estero Marga-Marga; V region, (b) Ch. pisciculus from Angostura River; Metropolitan region, (c) Ch. galusdae from Andalién River; VIII region, (d) Ch. kiliani from Calle-Calle River; XIV region and (e) Ch. australe from La Poza Lake; X region, base level Llanquihue Lake. Ideograms show 18S and 5S rDNA gene location. Mid-marks represent rDNA sites that may be present or absent, in the same individual (heteromorphism) or in different individuals (polymorphism). In the photographs of teeth bar: 500 μm, and in those of peduncle region bar: 2 mm
Discussion
The karyotype of the five species under study had invariably the same 2n = 50, dominated by acrocentric chromosomes. Karyotypes were probably differentiated from other Characidae due to multiple inversions and/or chromosomal translocations. This very similar pattern (karyotype structures) is consistent with the monophyletic status hypothesized for the Chilean Cheirodon [3, 4, 13, 14]. This finding supports the comparative and evolutionary analyses of the Chilean Cheirodon, as well as phylogenetically related groups that occur on the other side of the Andean cordillera.
The karyotype macrostructure revealed differences between particular species. This differentiation was accompanied by their endemism in regions or particular watersheds. An ancient period of reproductive isolation compatible with the hypothesis of fluctuation as was suggested to explain the phylogeography of a widespread Chilean catfish Trichomycterus areolatus [26] may explain the observed patterns,. Much of the genetic variation found in the endemic fishes of the Atlantic forest along the Brazilian coast may be explained by the population structure promoted by the ancient drainage systems of the Pleistocene [24]. Groups of fishes such as the Characidium genus underwent allopatric speciation. In these species, sex chromosome differentiation was associated with the hydrographic basins in which they evolved [19].
Chilean Cheirodon form two different groups according to their karyotype macrostructure, corresponding also with the groups based in their dental cusps which were analysed by [3].. A slight variation in the karyotypes is associated with the presence and/or absence of p arms in one of the pairs of small chromosomes. In fact, Ch. australe and Ch. kiliani, which are found in the south, share the same karyotypes composed of 8 m + 6sm + 4st + 32a and the same FN = 68. However, Ch. galusdae, Ch. pisciculus, and the introduced species Ch. interruptus, which are distributed in the north, possess the same karyotypes composed 6 m + 6sm + 4st + 34a chromosomes and FN = 66. This differences may be attributed to pericentric inversions, given that the 2n is the same. Nevertheless, there are no remnants of telomeric sequences evidenced by FISH in the pericentromeric regions of their karyotypes. The data support the hypothesis that these chromosomal rearregements are ancient events associated with the speciation of Cheirodon, which probably occurred prior to the formation of the Andean cordillera during the Tertiary Period and was likely influenced by sea-level fluctuation.
These patterns, revealed by the cytogenetic analysis of all species of Cheirodon occurring in Chile, suggest that differences were associated with the geographic distribution of species. Morphological [3] and molecular [14] studies on Cheirodon tended to group species as Ch. australe and Ch. interruptus together, even though they are found in different geographic regions. We consider that this incongruence between the cytogenetic, morphological and molecular data reflects a lack of morphological characters for each of these species, being all of them differentiated mainly by the combination of the same characters, perhaps, by local adaptations [21]. In addition, the absence of chilean Cheirodon species in previous phylogenetic analyses makes it difficult to reach correct conclusions [14, 21].
The variations and polymorphisms that our data indicated, especially the activity and localisation of major ribosomal cluster (18S rDNA) and 5S rDNA chromosome mapping, suggest that all these populations demonstrate a dynamic variation in karyotype microstructure. Many teleost fishes (72% of species) possess just one chromosome pair bearing NORs as reviewed by Gornung [5]. Thus, the rDNA polymorphisms here observed, suggest that karyotype diversification in the Chilean Cheirodon species was produced by more than pericentric inversions; probably transpositions of ribosomal regions between non-homologous chromosomes also occurred. Since inversions and translocations change the order of the loci in the chromosomes, these rearrangements can reduce the genetic flow between populations by reducing fertility in 50% of the gametes of the heterozygous hybrids [10].
Similar karyotypes and some chromosomal homologies were found between species of Cheirodon and other genera of Cheirodontinae, such as Serrapinus and Odontostilbe [13]. For example, the first pair of large metacentric chromosomes present in karyotypes of five species of Chilean Cheirodon appears to be a characid chromosome marker [16].
Alternatively, the greatest karyotype differences among Serrapinus, Odontostilbe, and Cheirodon refers to number and size of a chromosomes, 2n. The karyotypes of the Cheirodon species analysed have 2n = 50 and FN = 66 to 68. In contrast, Odontostilbe and Serrapinus have a 2n = 52 and FN = 79 to 104 for Serrapinus and FN = 89 to 101 for Odontostilbe [17, 22, 25, 30]. Therefore, the karyotypes of species described in this study, with large number of acrocentric chromosomes varying in relative size, seems to be a particular pattern for the representatives of the genus Cheirodon.
However, karyotypes of Ch. australe and Ch. kiliani had one more metacentric chromosome pair and fewer acrocentric chromosomes than that of the other species of the Chilean Cheirodon. This evidence suggests that karyotypes of Cheirodon occurring in the north could be derived from those of southern species by pericentric inversion of a smaller pair of metacentric chromosomes (probably No. four), generating a small acrocentric pair (Fig. 5). This hypothesis is consistent with the observations of [3], who also proposed that the northern species of Cheirodon were derived from the southern species based on a comparison of their dental cusps.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the five species studied have very similar karyotypes, including the introduced species from the east side of the Andean cordillera, Ch. interruptus. This finding is consistent with new theories about the recent, rapid emergence of the Andean cordillera which, after slow initial growth over a period of tens of millions of years, then underwent fast changes over periods of one to four million years of 1.5 km or more new emergence [34]. Thus, the isolation caused by the Andean cordillera could be relatively recent or even incomplete with regard to some watersheds, especially in the southern Patagonia region. Sea-level fluctuation may have been more effective for reproductive isolation among Chilean Cheirodon. These two events mentioned have contributed to allopatric speciation revealed by differentkaryotypeof these species.
References
Arratia G. Comentario sobre la introducción de peces exóticos en aguas continentales de Chile. Ciencias For, vol. 1; 1978. p. 21–30.
Artoni RF, Castro JP, Jacobina UP, et al. Inferring diversity and evolution in fish by means of integrative molecular cytogenetics. Sci World J. 2015;2015:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/365787.
Campos H. Sistemática del gênero Cheirodon (Pisces: Characidae) en Chile con descripción de una nueva espécie. Análisis de Multivarianza. Stud Neotrop Fauna Environ. 1982;17:129–62.
Eigenmann CH. The freshwater fishes of Chile. Mem Nat Acad Sci. 1928;22:1–63.
Gornung E. Twenty years of physical mapping of major ribosomal rna genes across the teleosts: a review of research. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2013;141:90–102. https://doi.org/10.1159/000354832.
Habit E, Dyer B, Vila I. Estado de conocimiento de los peces dulceacuícolas de Chile. Gayana (Concepción); 2006. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-65382006000100016.
Hatanaka T, Galetti PM. Mapping of the 18S and 5S ribosomal RNA genes in the fish Prochilodus argenteus Agassiz, 1829 (Characiformes, Prochilodontidae). Genetica. 2004;122:239–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-004-2039-y.
Howell WM, Black DA. Controlled silver-staining of nucleolus organizer regions with a protective colloidal developer: a 1-step method. Experientia. 1980;36:1014–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01953855.
Ijdo JW, Wells RA, Baldini A, Reeders ST. Improved telomere detection using a telomere repeat probe (TTAGGG) n generated by PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991;19:4780.
King M. Chromosomal rearrangements as post-mating isolating mechanisms. In: Species evolution. Cambridge: The role of chromosome change. Cambridge University Press; 1993. p. 72–91.
Levan A, Fredga K, Sandberg AA. Nomenclature for Centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas. 1964;52:201–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1601-5223.1964.TB01953.X.
Lui RL, Blanco DR, Moreira-Filho O, Margarido VP. Propidium iodide for making heterochromatin more evident in the C-banding technique. Biotech Histochem. 2012;87:433–8. https://doi.org/10.3109/10520295.2012.696700.
Malabarba L. Monophyly of the Cheirodontinae, characters and major clades (Ostariophysi: Characidae). In: Malabarba LR, Reis RE, Vari RP, et al., editors. Phylogeny and classification of Neotropical fishes. Porto Alegre: EDIPUCRS; 1998. p. 193–234.
Mariguela TC, Ortí G, Avelino GS, et al. Composition and interrelationships of a large Neotropical freshwater fish group, the subfamily Cheirodontinae (Characiformes: Characidae): a case study based on mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol. 2013;68:23–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2013.03.011.
Martins C, Galetti PM. Chromosomal localization of 5S rDNA genes in Leporinus fish (anostomidae, characiformes). Chromosom Res. 1999;7:363–7. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009216030316.
Morelli S, Bertollo LAC, Foresti F, et al. Cytogenetic considerations on the genus Astyanax (Pisces, Characidae). I. Karyotypic variability. Caryologia. 1983;36:235–44. https://doi.org/10.1080/00087114.1983.10797664.
Peres M, Wellington A, Bertollo LAC, Moreira-Filho O. Karyotypic characterization of two species of the genus Serrapinnus (Characiformes, Characidae), with the description of a structural polymorphism in S. Heterodon. Caryologia. 2007;60:319–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/00087114.2007.10797954.
Pinkel D, Straume T, Gray JW. Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986;83:2934–8.
Pucci MB, Barbosa P, Nogaroto V, et al. Population differentiation and speciation in the genus Characidium (Characiformes: Crenuchidae): effects of reproductive and chromosomal barriers. Biol J Linn Soc. 2014;111:541–53. https://doi.org/10.1111/bij.12218.
Riegel H. Observaciones sobre la fauna ictiológica de las aguas dulces chilenas. In: Actas y Trabajos, Primer Congreso Sudamericano Zoología I; 1960. p. 141–4.
Salas D, Véliz D, Scott S. Diferenciación morfológica en especies del género Cheirodon (Ostariophysi: Characidae) mediante morfometría tradicional y geométrica. Gayana (Concepción), vol. 76; 2012. p. 142–52. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-65382012000300007.
Santi-Rampazzo AP, Nishiyama PB, Ferreira PEB, Martins-Santos IC. Cytogenetic analysis and description of the sexual chromosome determination system ZZ/ZW of species of the fish genus Serrapinnus (Characidae, Cheirodontinae). Genet Mol Res. 2007;6:504–9.
Sumner AT. A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp Cell Res. 1972;75:304–6.
Thomaz AT, Malabarba LR, Bonatto SL, Knowles LL. Testing the effect of palaeodrainages versus habitat stability on genetic divergence in riverine systems: study of a Neotropical fish of the Brazilian coastal Atlantic Forest. J Biogeogr. 2015;42:2389–401. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.12597.
Troy WP, Pacheco ÉB, Oliveira C, Miyazawa CS. Caracterização do Número Cromossômico em Espécies de Odontostilbe e Serrapinnus (Characidae: Cheirodontinae) da Bacia do Rio Paraguai, Brasil. Publ UEPG Ciencias Biol e da Saude. 2011;16:057–61. https://doi.org/10.5212/Publ.Biologicas.v.16i1.0007.
Unmack PJ, Bennin AP, Habit EM, et al. Impact of ocean barriers, topography, and glaciation on the phylogeography of the catfish Trichomycterus areolatus (Teleostei: Trichomycteridae) in Chile. Biol J Linn Soc. 2009;97:876–92. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.2009.01224.x.
Vila I, Habit E. Current situation of the fish fauna in the Mediterranean region of Andean rivers systems in Chile. FISHMED Fishes Mediterr Environ. 2015;2:19.
Vila I, Pardo R. Diversidad de Espécies. Peces Límnicos. In: CONAMA, editor. Biodiversidad de Chile: Patrimonio y desafíos. Ocho Libros Editores; 2008. p. 302–7.
Völker M, Ráb P. Direct chromosome preparation from regenerating fin tissue. In: Ozouf-Costaz C, Pisano E, Foresti F, LFA T, editors. Fish cytogenetic techniques. Enfield: CRC Press; 2015. p. 37–41.
Wasko AP, Gobbo CAC, Martins C, Galetti PM Jr. A ZZ/ZW sex chromosome system in Cheirodontinae fish. Chromosom Sci. 2001;5:145–8.
White TJ, Bruns S, Lee S, Taylor J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ, editors. PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. New York: Academic Press; 1990. p. 315–22.
Acknowledgements
To Editor for English revision and editing this manuscript. The Subsecretaria de Pesca y Acuicultura del Gobierno de Chile (SUBPESCA) and Servicio Nacional de Pesca y Acuicultura del Gobierno de Chile (SERNAPESCA), for fish collectin permits. To Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) / Organization of American States (OEA) by scholarship to MAS.
Funding
This work was supported by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq, http://cnpq.br; Research Grants) RFA, Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES, http://www.capes.gov.br; Social Demand Scholarship) MAS; JPC.
Availability of data and materials
The biological material was deposited in the Department of Zoology of the Universidade Federal de Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, under vouchers UFRGS 22295 (Ch. interruptus), UFRGS 22296 (Ch. galusdae), UFRGS 22297 (Ch. pisciculus), UFRGS 22298 (Ch. kiliani), and UFRGS 22299 and UFRGS 22300 (Ch. australe).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: RFA, OMF, LRM. Performed the experiments: MAS, JC. Analyzed the data: MAS, MHS, MCA. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: RFA, LW. Wrote the paper: MAS. Reviewing the manuscript: RFA, OMF, LRM. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The work was authorized by the Subsecreataria de Pesca y Acuicultura del Gobierno de Chile (SUBPESCA) and by the Servicio Nacional de Pesca y Acuicultura del Gobierno de Chile (SERNAPESCA), Authorization No. 740. All procedures were made according to international protocols for animal testing and authorized by the Ethic Committee in Animal Experimentation (protocol number 4509/08) of Universidade Estadual de Ponta Grossa. The fish individuals were transported to the laboratory and anaesthetized with clove oil before processing.
Consent for publication
We have read and understood your journal’s policies, and we believe that neither the manuscript nor the study violates any of these. Thus, all authors agree to the submission and publication of this manuscript in Revista Chilena de Historia Natural.
Competing interests
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Soto, M.Á., Castro, J.P., Walker, L.I. et al. Evolution of trans-Andean endemic fishes of the genus Cheirodon (Teleostei: Characidae) are associated with chromosomal rearrangements. Rev. Chil. de Hist. Nat. 91, 8 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40693-018-0078-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40693-018-0078-5