Abstract
Background
The Dharamshala region of Kangra valley, India is one of the fastest developing Himalayan city which is prone to landslide events almost around the year. The development is going on a fast pace which calls for the need of landslide susceptibility zonation studies in order to generate maps that can be used by planners and engineers to implement the projects at safer locations. A landslide inventory was developed for Dharamshala with help of the field observations. Based on field investigations and satellite image studies eight casual factors viz. lithology, soil, slope, aspect, fault buffer, drainage buffer, road buffer and land cover were selected to represent the landslide problems of the study area. The research presents the comparative assessment of geographic information system based landslide susceptibility maps using analytical hierarchy process and frequency ratio method. The maps generated have been validated and evaluated for checking the consistency in spatial classification of susceptibility zones using prediction rate curve, landslide density and error matrix methods.
Results
The results of analytical hierarchy process (AHP) shows that maximum factor weightage results from lithology and soil i.e. 0.35 and 0.25. The frequency ratios of the factor classes indicate a strong correlation of Dharamsala Group of rock (value is 1.28) with the landslides which also agrees with the results from the AHP method where in the same lithology has the maximum weightage i.e. 0.71. The landslide susceptibility zonation maps from the statistical frequency ratio and heuristic analytical hierarchy process method were classified in to five classes: very low susceptibility, low susceptibility, medium susceptibility, high susceptibility and very high susceptibility. The landslide density distribution in each susceptibility class shows agreement with the field conditions. The prediction rate curve was used for assessing the future landslide prediction efficiency of the susceptibility maps generated. The prediction curves resulted the area under curve values which are 76.77% for analytical hierarchy process and 73.38% for frequency ratio method. The final evaluation of the susceptibility maps was based on the error matrix approach to calculate the area distributed among the susceptibility zones of each map. This technique resulted in assessing the spatial differences and agreement between both the susceptibility maps. The evaluation results show 70% overall spatial similarity between the resultant landslide susceptibility maps.
Conclusions
Hence it can be concluded that, the landslide susceptibility map (LSM) generated from the AHP and frequency ratio method have yielded good results as the 100% landslide data falls in the high susceptibility and very high susceptibility classes of both the maps. Also, the spatial agreement of almost 70% between the resultant maps increases the reliability on the results in the present study. Therefore, the LSM generated from AHP method with 76.77% landslide prediction efficiency can be used for planning future developmental sites by the area administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Landslides are the down slope movement of debris, rocks or earth material under the force of gravity (Cruden, 1991). Destructive mass movements such as landslides are considered as a major geological hazard around the globe. The Landslide activities in India are mostly associated with its the northern most states such as Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim and West-Bengal which are located in the Himalayan foothills with dynamic tectonic and climatic variations (Sarkar et al. 1995; Chauhan et al. 2010) and also towards the southern India the Nilgiri range and the Western Ghats are prone to landslides instead of hard rocks and tectonic stability (Kaur et al. 2017). According to the Geological survey of India almost 15% of the land area in India is exposed to the landslide events (Onagh et al. 2012) and is the worst affected country by landslides in Asia after China (Guha-Sapir et al., 2012; Binh Thai et al. 2016). The tendency towards the landslide is caused by various factors such as the steepness of slopes, the tectonic conditions of the study area, prolonged rainfall episodes with their return periods, topography and the inherent properties of the slope material, Anbalagan (1992). The mitigation measures for landslides require the identification of existing landslides in an area for spatial prediction of future events by studying the prevailing causal factors (Rai et al. 2014) for which a standard tool known as landslide susceptibility mapping is used around the world by various researchers (Guzzetti et al., 1999; Van Westen et al. 2008). Fell et al. 2008 considered the landslide susceptibility for identification of landslide prone sites and their relation to the set of causal factors in that area. The landslide susceptibility mapping generally involves two methods (I) qualitative which is based on expert knowledge and the landslide inventory development (Saha et al., 2002) such as analytical hierarchy process (AHP) used by many researchers (Komac 2006; Ghosh et al. 2011; Kayastha et al. 2012; Wu et al. 2016; Kumar and Anabalgan 2016; Achour et al. 2017) (II) quantitative methods including bivariate and multivariate modeling methods for statistical evaluation of landslides occurrences (Yin and Yan 1988; Kumar et al. 1993; Anbalagan and Singh 1996; Dai and Lee, 2002; Saha et al. 2005; Lee and Sambath 2006; Mathew et al. 2007; Dahal et al. 2008; Singh et al. 2008; Pradhan and Lee 2010; Rozos et al. 2011; Yalcin et al. 2011; Ghosh et al. 2011; Kayastha et al. 2013; Bijukchhen et al. 2013; Anbalagan et al., 2015; Rawat et al. 2015; Sharma and Mahajan 2018; Chen et al. 2016). In India landslide susceptibility mapping for Gharwal and Kumaun region of Uttarakhand has been carried out by Pachauri and Pant 1992; Gupta et al. 1999; Anabalgan et al., 2008; Anbalagan et al., 2015; Kumar and Anabalgan, 2016 whereas, Sarkar and Kanungo, 2004; Sarkar et al. 2013; Ghosh et al. 2011 have mapped the landslides of Darjeeling Himalaya for statistical correlation with the causal factors. For dealing with the landslide hazard and its risk imposed on various elements, it is necessary to evaluate the correlation of probable causative factors with the landslide location’s characteristics. The qualitative methods such as AHP subjectively help to rank the causal factors leading to classification of an area based on the priority scale whereas, the quantitative methods (bivariate or multivariate statistical analysis) use the observed landslide data for asserting the spatial relationship of the problem with the prevailing geo-environmental parameters (J. Corominas et al. 2014). For generating a reliable spatial information regarding a natural hazard, remote sensing data and the geographic information system (GIS) are very powerful tools (Tofani et al. 2013). The application of GIS is useful in processing the digital elevation models for extracting information such as: slope angle, aspect, drainage network etc. and to integrate the various thematic layers for generating susceptibility, hazard or risk maps. In the state of Himachal Pradesh (H.P.) attempts have been made for landslide susceptibility zoning of the landslide prone areas such as district Chamba, Bilaspur and Parwanoo (Sharma and Mehta 2012; Sharma and Kumar 2008) whereas studies related to the use of statistical modeling methods for susceptibility mapping are lacking for important areas of this hilly state such as Kangra Valley which rests at the Himalayan foothills and experiences number of landslide episodes in various parts every year. Some parts of district Kangra, Himachal Pradesh such as Dharamshala region is the fastest growing tourism hub which has been announced as one of the smart cities of India. The Dharamshala region is characterized by steeply dipping slopes with number of drainages cutting across its weak and weathered lithology. The district Kangra, H.P. is tectonically very active and has experienced number of moderate and major earthquakes in past such as 1905 Kangra earthquake (Ms 7.8) which devastated this region badly (Ghosh and Mahajan 2011). Later on, from 1968 to 1986 the Dharamshala region of district Kangra which is sandwiched between longitudinal Main Boundary Thrust (MBT) in the north and Drini Thrust in the south, experienced three moderate earthquakes having magnitude varying between Ms 4.9 to Ms 5.7 (Kumar and Mahajan 1991; Mahajan and Kumar 1994). The tectonic emplacement and the northward movement of Indian landmass keep the Dharamshala region of H.P. under continuous stress conditions making it tectonically and geomorphologically dynamic. Mahajan and Virdi (2000) have studied the landslide sites of Dharamshala region using the field based mapping methods and identified 25 major landslides for correlating with factors such as slope angle, relief, drainage network etc. Sharma et al. (2015) have documented a major landslide event (Tirah lines Landslide) reported as a result of very high rainfall in the month of August 2013 which destroyed almost 10 multistoried buildings in army cantonment area of Dharamshala. Looking at the past record of the landslide studies and the structural complexity in the Dharamshala region it becomes important to statistically analyze the factors playing major role in causing slope instability and in order to minimize their societal impacts by developing landslide hazard or susceptibility zonation maps. This study involves the landslide susceptibility mapping (LSM) of Dharamshala region using heuristic judgment based analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and statistical frequency ratio (FR) method followed by the comparison of susceptibility maps for prediction efficiency of future landslide events. The resulting LSMs have been evaluated by the use of landslide density analysis and error matrix technique in order to check the concordance between the susceptibility class area distributions from heuristic and statistical methods. The evaluation of the LSMs has determined the total agreement and the spatial difference between the maps generated. The results can be useful for landslide risk assessment studies and for planners in implementing developmental projects.
Study area and geological setting
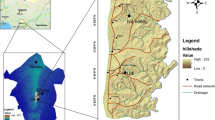
The study area covers a rectangle of 39.7 sq. km (32°12′ and 32° 15′ and N- 76°17′ and 76° 23′ E) as shown in Fig. 1 with an elevation between 899 m to 2523 m a.m.s.l. The geomorphology of the study area is dominated with hills and mountains dissected by number of drainages which are locally known as khad. The main khad flowing are Charan khad at the southern edge, Banoi khad in the middle and the Gaj khad at the northern edge of the study area which are the main tributaries of river Beas in the district Kangra of Himachal Pradesh. Dharamshala region comes under wet temperate zone with mean annual temperature remain between 19 ± 0.5 °C and the annual precipitation 2900 ± 639 mm (Jaswal et al. 2014). Geologically the southern part of the area falls in the Outer Himalaya comprising the Siwalik (boulder conglomerate exposures), Dharamsala group and Murree formation (Sandstone, Claystone and mudstone) which is separated by Main Boundary Thrust (MBT) from the northern part of the study area comprising of Lesser Himalayan rocks (Dharamkot Limestone and Chail Formation having low grade metamorphic such as slates) as shown in Fig. 2. Most of the settlements and the road excavation are in the Outer Himalayan rocks of the study area which are weak and have led to many slope instability conditions in the past. Weak lithology such as weathered sandstone, claystone along with unplanned construction activities or excavations of slopes for development projects and the heavy rainfall in this area often lead to landslides especially in the monsoon season. The slopes of Dharamshala region are steeply dipping up to > 41° with upper 5 m to 10 m cover of fluvial deposits or the debris cover which is easily prone to sliding under adverse conditions.
Geological Map of Dharamshala region showing lithology and structure exposed (Source- Mahajan and Virdi 2000)
Methods
The present analysis was carried out in three steps: data collection, database generation (thematic maps) and modeling for landslide susceptibility mapping (LSM). Firstly, the study area has been investigated for the prevailing landslide conditions for which a landslide inventory (Fig. 3) was developed through field surveys and available satellite imageries. Thirty nine landslide locations were mapped in the total study area of 39.7 km2. For the correlation of spatial distributions of the prevailing landslide with the chosen eight causal factors, various thematic maps were developed. With help of ASTERGDEM of 30 m resolution (source- USGS website) the drainage buffer, slope angle and the aspect maps have been produced whereas the geology, soil and fault buffer maps were prepared with the help of previous published maps (Mahajan and Virdi, 2000) and the land cover and road buffer maps were extracted with help of Google earth imagery. All the prepared thematic maps were rasterized at grid size of 30 × 30 with total pixel count for the study area 44,165 for using in the GIS based modeling methods (AHP and FR). In the analytical hierarchy process (AHP) method field survey based judgments and the data from previous literature have helped in assigning weightage (heuristic) to the causal factors and the factor classes whereas in the frequency ratio (FR) method, the ratio of landslide percentage in a factor class and the percentage area of that factor class gave the weightages (statistical). Both the modeling methods (analytical hierarchy process and frequency ratio) have resulted in landslide susceptibility index (LSI) maps which were reclassed using fivefold classification for zoning the landslide prone area which is very low susceptibility (VLS), low susceptibility (LS), medium susceptibility (MS), high susceptibility (HS) and very high susceptibility (VHS). Both the landslide susceptibility zonation maps (LSZM) were validated using the landslide density distribution method and the prediction curve success rates. The evaluations of the resulting landslide susceptibility maps are based on spatial area distribution match between the susceptibility classes for which the error matrix method has been used. The evaluations represent the concordance and the disagreement of class area distribution from the use of heuristic judgements and the objective datasets.
Analytical hierarchy process (AHP)
Analytical hierarchy process is the decision making for a complex problem by arranging the elements of that problem in a hierarchy. It is a semi-qualitative process in which the weightages to the elements are assigned based on the expert’s judgment and the weightage values vary from 1 to 9 (Saaty, 1980, Saaty and Vargas 2001, Saaty, 2005). The standard scale for using AHP method has been given in Table 1, according to which factor classes and the factors are assigned rating with respect to each other. Value 1 is assigned to the class with least influence and value 9 is assigned to the class with maximum influence. After the weightage assignment the factor maps are reclassed and integrated in GIS.
For checking the consistency of the comparison matrix prepared by rating factors and factor classes against one another, consistency ratio (CR) is used and the CR value below 0. 1 is considered acceptable (Ayalew et al. 2004).
Where CI is the consistency index calculated as:
Where n is the order of the matrix and Ʌ max is the major value of the matrix.
Random index (RI) is the consistency of the randomly generated pair wise matrix and is dependent on the size of the matrix as given in Table 2.
Frequency ratio (FR)
Frequency ratio modeling is based on correlation of landslides in an area with the natural and anthropogenic causal factors in that area. Mathematically, it is the ratio of the percentage of the factor class (y) and the percentage of the landslides (x) in that class (Lee and Talib, 2005; Pradhan, 2010). The correlation factor for FR i.e. x/y (between the landslides and the factors) vary between < 1 to > 1. If the FR value is > 1 then the there exists a high correlation between landslide occurrence and the factor class and if the FR is < 1 then the correlation is weak. All the thematic maps are reclassed according to the FR values for each factor class and then integrated in GIS for generating the landslide susceptibility index (LSI) map.
Landslide inventory
For the preparation of landslide inventory field surveys have been carried out to demarcate the GPS location and the nature of landslides. The vector points of the noted locations were verified using the Google earth imagery and then imported in GIS for applying the heuristic and statistical models. The inventory data was split into training (75%) and testing (25%) groups as shown in Fig. 3 for using in modeling and validation phase respectively. Thirty nine landslides with varying size were demarcated out of which the largest landslide covers an area of 0.103 km2. In total all the landslides cover 1.1 km2 which is 2.7% of the total study area (39.7 km2) and the 75% training data of the total inventory landslide area covers 0.81 km2. Table 3 shows the location and the type of lithology the landslides belong to. Most of the mapped landslides have got activated in the monsoon season (July to September) in form of debris flow mostly. Some of the landslides show mudflow or earth flow type of mass movement which is due to low strength of material and water logging during the monsoons. Figure 4 shows some of the past landslides of the Dharamshala that have caused notable destruction.
There exists no set rules for considering the trigger factors in landslide susceptibility mapping, rather the study area characteristics and the data availability guide the choice of thematic layers to be used (Ayalew and Yamagishi, 2005). Based on the study area characteristics, eight parameters discussed below have been considered as the major causal factors for landslides in the Dharamshala region and their thematic maps as shown in Fig. 5 have been prepared at grid size of 30 × 30 with pixel count of 44,165 in each map for modeling in GIS.
-
1.
Distance from drainage (Drainage buffer): The Dharamshala region has a dense drainage network as shown in the location map (Fig. 1) and some of the landslides mapped during the field survey were found in the vicinity of local drainages. To find the distribution of landslides with respect to the drainages flowing in the study area, a drainage buffer map or distance from the drainage map was prepared at proximity of 100 m, 500 m and 1000 m.
-
2.
Distance from fault (Fault buffer): The emplacement of faults in the study area has been found affecting the slope stability as many landslides were found near to the major faults in this region. To find the effect of faults on the mass movement activity a fault buffer map was prepared with three classes showing the proximity of 1000 m, 2000 m and 3000 m.
-
3.
Distance from road (Road buffer): In hilly areas slope excavation for road widening is a common practice which greatly influences the slope stability and similar has been found for the present study area where landslides associated with the slope excavation are common. Considering it one of the main causal factors a road buffer map was prepared with buffer zones of 200 m, 800 m, 1500 m and 2500 m.
-
4.
Lithology: Lithology of an area is closely related to the landslide occurrence as the strength of the emplaced lithology influences the slope stability. In Dharamshala region the lithology is grouped in to four classes which are Dharamsala Group (sandstone, claystone and mudstone), Siwalik Group (boulder conglomerates), Dharamkot Limestone and Chail formation (Schist, Quartzite and Gneissic rocks). According to the landslide inventory data all the landslides are located in the weak lithology of Dharamsala Group of rocks.
-
5.
Soil: This parameter includes the overlying cover on the lithology which has a varying thickness in the present study area and has been grouped into three classes: debris, clay soil and compact alluvial deposits.
-
6.
Land cover: The study area has been divided into four classes: forest cover, settlement on low to moderate slopes, sparsely vegetated area and settlement on steep slopes.
-
7.
Slope angle: The slope map was extracted from the DEM (30 m resolution) and classified into five classes: 0° - 5°, 6° - 15°, 16° - 25°, 26° - 35° and ≥ 35°. These classes represent the slope inclinations throughout the Dharamshala area.
-
8.
Aspect: After the slope extraction slope aspects were extracted using GIS tool and was grouped into nine classes: flat (− 1), N (0° – 22.5° and 337.5° - 360°), NE (22.5° – 67.5°), E (67.5° -112.5°), SE (112.5° – 157.5°), S (157.5° – 202.5°), SW (202.5° – 247.5°), W (247.5° – 292.5°) and NW (292.5° – 337.5°).
As described in the section 2.1 and 2.2 analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and the frequency ratio (FR) methods were applied on the causal factors and the factor classes for assigning weightages of influence and the frequency ratio for finding correlation with the prevailing landslide conditions of the study area. The results have been presented in Table 4 (AHP) and Table 5 (FR) of section 3 respectively.
Results and discussion
In order to combine all the factor maps reclassed with their weightage values using AHP and frequency ratio (FR) values, the map algebra tool was used which resulted the two-landslide susceptibility index (LSI) maps from both the models. The results of AHP comparison matrix in the Table 4 show that maximum factor weightage results from lithology and soil i.e. 0.35 and 0.25 respectively followed by the weightages of land cover (0.14), drainage (0.07) and slope (0.06) whereas factors such as road, fault and aspect show a little influence on the landslide occurrences. Figure 6b shows the landslide susceptibility zonation (LSZ) map resulted from the heuristic analytical hierarchy process (AHP) method which has been classified using fivefold classification: very low, low, medium, high and very high. Table 5 showing the frequency ratios of the factor classes indicates a strong correlation of Dharamsala Group of rock (FR value is 1.28) with the landslides which also agrees with the results from the AHP method where in the lithology factor the maximum weightage has been given to the Dharamsala Group i.e. 0.71. Among the land cover classes, the settlements on steep angled slopes have the maximum FR value 6.51 indicating major concentration of landslide sites in this class as 32.7% of the landslide area alone falls in this class which covers only 5.04% of the total map area, which indicates an impact of anthropogenic activities on and near steep sloping areas. Among the classes for the slope factor, classes with 16° - 25° and 26° - 35° slope angles (moderate and steep slopes) show maximum FR values 1.48 and 1.35 respectively and collectively include more than 60% of the landslide area. Among the aspects the north-east class with 18.84% landslide area and the north aspect with 8.89% landslide area show maximum FR values 1.34 and 1.10 which indicates more exploitation of north facing slopes or high subsurface moisture conditions due to less sun exposure of northern slopes which makes them unstable. Nonetheless the south facing slopes (SW aspect with 14.76% landslide area) have also shown a high correlation FR value but the maximum FR values for northern slopes are an interesting parameter showing high anthropogenic interference. The debris soil hosts all the inventory landslides (100%) and gives the maximum correlation value 1.33 which is indicative of a shallow nature of maximum mass movements here on the steep slopes. The debris layer composes the weathered lithology from the Dharamsala Group (mudstone, sandstone, claystone) and the overlying fluvial deposits. The drainages have shown a higher correlation (FR = 1.01) at 500 m proximity with 62.96% landslide area whereas for the faults the proximity of 1000 m with 80.17% landslide area and 2000 m seem critical in term of FR values 1.16 and 0.75 respectively. The road buffer factor shows high landslide activity associated within 200 m proximity (FR = 1.51) with more than 50% of the landslide area, which indicated direct impact of slope excavation for road widening in the hilly areas. The resulting Fig. 6a shows landslide susceptibility zonation (LSZ) map from the statistical frequency ratio (FR) method with classes: very low susceptibility (VLS), low susceptibility (LS), medium susceptibility (MS), high susceptibility (HS) and very high susceptibility (VHS). Therefore, a five-fold classification scheme was followed based on natural break classifier option in GIS, which maximizes the variance between the susceptibility classes and represents a clear trend of class index value distribution. The classifications of resulting landslide susceptibility index maps were carried out in such a way so that 20% of the LSZ map area using AHP and FR includes 97% and 76% of the landslides respectively. Table 6 shows the distribution of landslides in various susceptibility classes from heuristic and the statistical methods applied, which shows 18.48 km2 area in high susceptibility class and 4.31 km2 area in very high susceptibility class using AHP method whereas using the statistical method (FR) 9.3 km2 and 13.07 km2 falls under high and very high susceptibility class respectively.
Comparative assessments of LSZ maps from AHP and FR
For checking the reliability of the LSZ maps and comparing their performance for future landslide prediction spatially, various techniques have been proposed like agreed area analysis, prediction rate curve, landslide density distribution etc. (Kayastha et al. 2013; Gupta et al. 2008). In the present study landslide density in the susceptibility zones, prediction rate curves and the error matrix method have been used for assessment and the evaluation of LSZ maps (heuristic and statistical) with respect to each other. Table 6 shows the landslide density distribution among the susceptibility classes which was computed using the ratio of the landslide area in a susceptibility class to the area of that susceptibility class. The density should increase from the low to very high susceptibility class (Gupta et al. 2008) which is true for the present study. In case of AHP method the high (HS) and very high susceptibility (VHS) class have density value 0.022 and 0.095 respectively whereas, for the FR method the HS and VHS class have density value 0.004 and 0.059 respectively. Therefore, the susceptibility of various zones in both the maps matched the inventory data distribution noted from the field studies and also both the LSZ maps show a reliable similarity with varying values of landslide density distribution.
The validation of the susceptibility maps from AHP and FR technique was carried out using the prediction rate curve which computed the cumulative percentage of landslide occurrences (testing data) in both susceptibility zonation maps (Sarkar et al. 2013) which is shown in Fig. 7. The prediction curves were analyzed using area under curve (AUC) values which indicate the model fitness for landslide prediction in which value below 0.5 refers low accuracy level whereas value from 0.5 to 1 refers higher accuracy of the models used. In this study both the model heuristic (AHP) and statistical (FR) have shown AUC value above 0.5, where AHP method gave 76.77% (0.76) AUC and the FR method gave 73.38% (0.73) AUC. These results show that both the methods have given a good prediction rate for estimating the future landslide probabilities spatially.
Evaluation of susceptibility zonation maps
Both comparison method: landslide density distribution and prediction rate curve have shown that AHP and FR techniques gave interpretations on a positive side but there exists difference in the results of both the LSZ maps generated i.e. the area of each susceptibility class varies in the maps from AHP and FR method. The spatial differences between the susceptibility classes can help to evaluate the LSMs and can state that, how the choices of subjective and objective judgements in heuristic and statistical methods respectively influence our results. To analyze the spatial difference among landslide susceptibility classes an error matrix method was used (Gupta et al., 2008; Kayastha et al. 2012) which is presented in Table 7. Using the combination of AHP-FR maps error matrix was tabulated showing a high degree match between areas of VLS, LS and MS zones of both the LSZ maps which indicates a similarity of 16.95 km2 area in total which constitutes 42.6% of the total map areas. In case of high susceptibility zone (HS) and very high susceptibility (VHS) zone the difference in the areas is more i.e. for AHP 4.32 km2 area is covered in VHS zone whereas for FR map 13.07 km2 area is covered in VHS zone but, in total more than 55% of both the map’s susceptibility classes show spatial agreement. These differences in the areas of HS and VHS class can be due to difference of the methods used for susceptibility mapping where in the AHP method subjective judgment approach was used for determining the factor weightages whereas in the FR method a bivariate statistical approach was used to compute weights of each class separately. This evaluation has also helped to analyze the agreement of area distribution (pixels or km2) in the resulting LSMs which ascertains the consistency of causal factors used in the study whereas, the disagreement of area distribution refers to the difference of techniques used. Nonetheless, 100% of the observed landslide area falls in the high susceptibility and very high susceptibility classes which shows good prediction rate of both LSZ maps.
Conclusions
The findings in this study point out the following conclusions:
-
1)
The work shows a comparative study of GIS based heuristic and statistical models for landslide susceptibility zonation of Dharamshala region of Himachal Pradesh, India. The lithology and the land cover factors have shown maximum contribution toward landslide occurrence based on the computed weightage values using AHP and FR models. The anthropogenic interferences in this hilly terrain have caused huge impact on the slopes and the condition is worsened as the internal properties of the lithology and the overlying debris material are weak due to which instability of slopes is triggered. Maximum landslide locations were mapped in close proximity of the roads and the local drainages.
-
2)
The landslide susceptibility zonation maps from both the methods have been classified into five zones: very low susceptibility (VLS), low susceptibility (LS), medium susceptibility (MS), high susceptibility (HS) and very high susceptibility (VHS). Both the LSZ maps show a good model fitness for predicting future landslide locations based on prediction rate curve method. Landslide density distribution increases from low to very high susceptibility class of both the LSZ maps which represents an agreement with the field conditions of the study area. Such results have inferred a statistical similarity between both the resultant susceptibility maps.
-
3)
The LSMs prepared have been evaluated to check the consistency of area distribution among the susceptibility classes from AHP and FR technique. The evaluation of the susceptibility maps was based on the error matrix method which resulted into differences and the similarities of area (km2) assigned to each susceptibility zone. The results have shown a good consistency in the spatial area distribution in very low, low and medium susceptibility classes of LSZ maps which count for 42.6% of the susceptibility map areas. For the high and very high susceptibility classes the spatial area distribution in both the LSZ maps varies to some extent but this difference factor is hindered as both these classes HS and VHS include 100% landslide affected area in each resulting LSZ map. The spatial difference of susceptibility classes can be attributed to the variance of procedure [subjective (AHP) and objective (FR)] in weighting the factors and their classes whereas, the spatial similarity of the susceptibility zones may have occurred due to the use of similar causal factors and the landslide inventory data for both the modeling methods.
-
4)
The results from the final map evaluations indicate that the 100% landslide data falls in the high susceptibility (HS) and very high susceptibility (VHS) classes and the spatial agreement between both the resultant maps as evaluated from error matrix method (Table 7) is more than 70%. Therefore, the maps landslide susceptibility maps generated can prove to be reliable and helpful in the landslide risk assessment for Dharamshala region and can guide planners for implementing developmental projects at safer locations.
Abbreviations
- Asia-Pac:
-
Pacific
- Comput Geosci:
-
Computers and geoscience
- Comput Intel Sys.:
-
Computational intelligence research
- Curr. Sci.:
-
Current science
- Eng. Geol.:
-
Engineering geology
- Environ:
-
Environment
- Environ:
-
Environmental
- Geoenviron:
-
Geoenvironmental
- Geol. Soc.:
-
Geological society
- Geophys.:
-
Geophysical
- Int J Appl Obs Geoinf.:
-
International journal applied observation and Geoinformation
- J Geosci:
-
Journal of geoscience
- J Sci Ind Res:
-
Journal of scientific and industrial research
- J:
-
Journal
- Jour. Him. Geol.:
-
Journal of Himalayan Geology
- Jour.:
-
Journal
- Mt Res Dev:
-
Mountain research development
- Nat:
-
natural
- rem sens:
-
Remote sensing
- Sci.:
-
Science
- Spat. Inf. Res.:
-
Spatial information research
- Theor. Appl. Climatol:
-
Theoretical
References
Achour, Y., A. Boumezbeur, R. Hadji, A. Chouabbi, V. Cavaleiro, and E.A. Bendaoud. 2017. Landslide susceptibility mapping using analytic hierarchy process and information value methods along a highway road section in Constantine, Algeria. Arabian Journal of Geosciences 10: 194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-2980-6.
Anabalgan, R., D. Chakraborty, and A. Kohli. 2008. Landslide hazard zonation mapping on meso scale for systematic planning in mountainous terrain. Journal of Scientific and Industrial Research 67: 486–497.
Anbalagan, R. 1992. Landslide hazard evaluation and zonation mapping in mountainous terrain. Engineering Geology 32 (4): 269–277.
Anbalagan, R., R. Kumar, K. Lakshmanan, S. Parida, and S. Neethu. 2015. Landslide hazard zonation mapping using frequency ratio and fuzzy logic approach, a case study of Lachung Valley, Sikkim. Geoenvironmental Disasters 2 (1): 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40677-014-0009-y.
Anbalagan, R., and B. Singh. 1996. Landslide hazard and risk assessment mapping of mountainous terrains—A case study from Kumaun Himalaya, India. Engineering Geology 43 (4): 237–246.
Ayalew, L., and H. Yamagishi. 2005. The application of GIS based logistic regression for landslide susceptibility mapping in the Kakuda-Yahiko mountains Central Japan. Geomorphology 65 (1): 15–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2004.06.010.
Ayalew, L., H. Yamagishi, and N. Ugawa. 2004. Landslide susceptibility mapping using GIS based weighted linear combination, the case in Tsugawa area of Agano river, Niigata Perfecture, Japan. Landslides 1: 73–81.
Bijukchhen, P., P. Kayastha, and M.R. Dhital. 2013. A comparative evaluation of heuristic and bivariate statistical modelling for landslide susceptibility mappings in Ghumri-Dhad Khola, East Nepal. Arabian Journal of Geosciences 6: 2727–2743. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-0569-7.
Chauhan, S., M. Sharma, and M.K. Arora. 2010. Landslide susceptibility zonation of the Chamoli region, Gharwal Himalaya, using logistic regression model. Landslides 7: 411–423.
Chen, T., R. Niu, and X. Jia. 2016. A comparison of information value and logistic regression models in landslide susceptibility mapping by using GIS. Environment and Earth Science 75: 867. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5317-y.
Corominas, J., C. Van Westen, P. Frattini, L. Cascini, J.P. Malet, S. Fotopoulou, and K. Pitilakis. 2014. Recommendations for the quantitative analysis of landslide risk. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment 73 (2): 209–263.
Cruden, D.M. 1991. A simple definition of a landslide. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment 43 (1): 27–29.
Dahal, R.K., S. Hasegawa, S. Nonomura, M. Yamanaka, S. Dhakal, and P. Paudyal. 2008. Predictive modelling of rainfall induced landslide hazard in the lesser Himalaya of Nepal based on weights of evidence. Geomorphology 102: 496–510.
Dai, F., and C.F. Lee. 2002. Landslide characteristics and slope instability modelling using GIS, Lantau Island, Hong Kong. Geomorphology 42: 213–238.
Fell, R., J. Corominas, C. Bonnard, L. Cascini, E. Leroi, and W.Z. Savage. 2008. Guidelines for landslide susceptibility, hazard and risk zoning for land-use planning. Engineering Geology 102 (3): 99–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.03.014.
Ghosh, G.K., and A.K. Mahajan. 2011. Interpretation of intensity attenuation relation in 1905 Kangra earthquake with epicentral distance and magnitude in the northwest Himalayan region. Journal of the Geological Society of India 77: 511–520.
Ghosh, S., E.J.M. Carranza, C.J. Van Westen, V. Jetten, and D.N. Bhattacharya. 2011. Selecting and weighting spatial predictors for empirical modeling of landslide susceptibility in the Darjeeling Himalaya (India). Geomorphology 131: 35–56.
Guha-Sapir, D., F. Vos, R. Below, and S. Ponserre. 2012. Annual disaster statistical review 2011: The numbers and trends. Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED).
Gupta, R.P., D.P. Kanungo, M.K. Arora, and S. Sarkar. 2008. Approaches for comparative evaluation of raster GIS-based landslide susceptibility zonation maps. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation 10: 330–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2008.01.003.
Gupta, R.P., A.K. Saha, M.K. Arora, and A. Kumar. 1999. Landslide hazard zonation in a part of the Bhagirathi Valley. Garhwal Himalayas, using integrated remote sensing–GIS. Himalayan Geology 20: 71–85.
Guzzetti, F., A. Carrara, M. Cardinali, and P. Reichenbach. 1999. Landslide hazard evaluation: A review of current techniques and their application in a multi-scale study, Central Italy. Geomorphology 31 (1): 181–216.
Jaswal, A.K., N. Kumar, and P. Khare. 2014. Climate variability in Dharamsala-a hill station in western Himalayas. Journal of Indian Geophysical Union 18 (3): 336–355.
Kaur, H., S. Gupta, and S. Parkash. 2017. Comparative evaluation of various approaches for landslide hazard zoning: A critical review in Indian perspectives. Spatial Information Research 25 (3): 389–398.
Kayastha, P., M. Dhital, and F. De Smedt. 2012. Landslide susceptibility using the weight of evidence method in the Tinau watershed, Nepal. Natural Hazards 63: 479–498.
Kayastha P, Dhital MR, De Smedt F (2013) Application of the analytical hierarchy process (AHP) for landslide susceptibility mapping: a case study from Tinau watershed, west Nepal. Comput Geosci 52: 398–408. doihttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2012.11.003.
Komac, M. 2006. A landslide susceptibility model using the analytical hierarchy process method and multivariate statistics in perialpine Slovenia. Geomorphology 74: 17–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2005.07.005.
Kumar, K.V., R.R. Nair, and R.C. Lakhera. 1993. Digital image enhancement for delineating active landslide areas. Asia-Pac Remote Sensing Journal 6 (1): 63–66.
Kumar, R., and R. Anabalgan. 2016. Landslide susceptibility mapping using analytical hierarchy process (AHP) in Tehri reservoir rim region, Uttarakhand. Journal of the Geological Society of India 87: 271–286.
Kumar, S., and A.K. Mahajan. 1991. Dharamsala seismotectonic zone–Neotectonic and state of stress in the area. Journal of Himalayan Geology 21: 53–57.
Lee, S., and T. Sambath. 2006. Landslide susceptibility mapping in the Damrei Romel area, Cambodia using frequency ratio and logistic regression models. Environmental Geology 50 (6): 847–855.
Lee, S., and J.A. Talib. 2005. Probabilistic landslide susceptibility and factor effect analysis. Environmental Geology 47: 982–990. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-005-1228-z.
Mahajan, A.K., and S. Kumar. 1994. Linear features registered on the landset imagery and seismic activity in Dharamsala Palampur region (NW Himalayas). Geofizika 11 (1): 15–25.
Mahajan, A.K., and N.S. Virdi. 2000. Preparation of landslides hazard zonation map of Dharamshala town & adjoining areas. District Kangra (H.P.): technical report, 45. Dehradun: Wadia institute of Himalayan Geology. ref No. Endst/281/MA dt 27/2/99..
Mathew, J., V.K. Jha, and G.S. Rawat. 2007. Weights of evidence modelling for landslide hazard zonation mapping in part of Bhagirathi valley, Uttarakhand. Current Science 92 (5): 628–638.
Onagh, M., V.K. Kumra, and P.K. Rai. 2012. Landslide susceptibility mapping in a part of Uttarkashi district (India) by multiple linear regression method. International Journal of Geology, Earth and Environmental Sciences 4 (2): 102–120.
Pachauri, A.K., and M. Pant. 1992. Landslide hazard mapping based on the geological attributes. Engineering Geology 32: 81–100.
Pradhan, B. 2010. Application of an advanced fuzzy logic model for landslide susceptibility analysis. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems 3 (3): 370–381.
Pham, B.T., Pradhan, B., Bui, D.T., Prakash, I. and Dholakia, M.B., 2016. A comparative study of different machine learning methods for landslide susceptibility assessment: a case study of Uttarakhand area (India). Environmental Modelling & Software 84:240-250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2016.07.005.
Pradhan, B., and S. Lee. 2010. Regional landslide susceptibility analysis using back-propagation neural network model at Cameron highland, Malaysia. Landslides 7 (1): 13–30.
Rai, P.K., K. Mohan, and V.K. Kumra. 2014. Landslide hazard and its mapping using remote sensing and GIS. Journal of Scientific Research 58: 1–13.
Rawat, M.S., D.P. Uniyal, R. Dobhal, V. Joshi, B.S. Rawat, A. Bartwal, and A. Aswal. 2015. Study of landslide hazard zonation in Mandakini Valley, Rudraprayag district, Uttarakhand using remote sensing and GIS. Current Science 109 (1): 158–170.
Rozos, D., G.D. Bathrellos, and H.D. Skilodimou. 2011. Comparison of the implementation of rock engineering system and analytical hierarchy process methods, based on landslide susceptibility maps, compiled in GIS environment. A case study from eastern Achaia County of Peloponnesus, Greece. Environment and Earth Science 63 (1): 49–63.
Saaty, T.L. 1980. The analytical hierarchy process. Priority Setting. MacGraw-Hill: Resource Allocation, New York International Book Company 287.
Saaty, T.L. 2005. Theory and application of the analytic network process. Pittsburg: RWS.
Saaty, T.L, L.G. Vargas. 2001. Models, methods, concepts and application of analytical hierarchy process, 333. Kluwer, Boston.
Saha, A.K., R.P. Gupta, and M.K. Arora. 2002. GIS-based landslide hazard zonation in the Bhagirathi (ganga) valley, Himalayas. International Journal of remote sensing 23 (2): 357–369.
Saha, A.K., R.P. Gupta, I. Sarkar, M.K. Arora, and E. Csaplovics. 2005. An approach for GIS based statistical landslide zonation with a case study in the Himalaya. Landslides 2: 61–69.
Sarkar, S., and D.P. Kanungo. 2004. An integrated approach for landslide susceptibility mapping using remote sensing and GIS. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing 70 (5): 617–625.
Sarkar, S., D.P. Kanungo, and G.S. Mehrotra. 1995. Landslide hazard zonation: A case study of Gharwal Himalaya, India. Mountain Research and Development 15 (4): 301–309.
Sarkar, S., A. Roy, and T.R. Martha. 2013. Landslide susceptibility assessment using information value method in parts of the Darjeeling Himalayas. Journal of the Geological Society of India 82 (4): 351–362.
Sharma, M., and R. Kumar. 2008. GIS based landslide hazard zonation: A case study from the Parwanoo area, lesser and outer Himalaya, H.P., India. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment 67: 129–137.
Sharma, S., and A.K. Mahajan. 2018. A comparative assessment of information value, frequency ratio and analytical hierarchy process models for landslide susceptibility mapping of a Himalayan watershed, India. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment. 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1259-9.
Sharma, R., U.K. Sharma, and A.K. Mahajan. 2015. Rainfall and anthropologically accelerated mass movement in the outer Himalaya, north of Dharamshala town, Kangra district, Himachal Pradesh: A cause of concern. Journal of the Geological Society of India 86 (5): 563–569.
Sharma, R.K., and B.S. Mehta. 2012. Macro-zonation of landslide susceptibility in Garamaura – Swarghat - Gambhar section of national highway-21, Bilaspur district, Himachal Pradesh (India). Natural Hazards 60: 671–688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-011-0041-0.
Singh, T.N., A. Gulati, I.K. Dontha, and V. Bhardwaj. 2008. Evaluating cut slope failure by numerical analysis- a case study. Natural Hazards 47: 263–279.
Tofani, V., F. Raspini, F. Catani, and N. Casagli. 2013. Persistent Scatterer interferometry (PSI) technique for landslide characterization and monitoring. Remote Sensing 5 (3): 1045–1065.
Van Westen, C.J., E. Castellanos, and S.L. Kuriakose. 2008. Spatial data for landslide susceptibility, hazard and vulnerability assessment: An overview. Engineering Geology 102: 3–4.
Wu, Y.L., W.P. Li, P. Liu, H.Y. Bai, Q.Q. Wang, J.H. He, Y. Liu, and S.S. Sun. 2016. Application of analytic hierarchy process model for landslide susceptibility mapping in the Gangu County, Gansu Province, China. Environment and Earth Science 75: 1–11.
Yalcin, A., S. Reis, A.C. Aydinoglu, and T. Yomralioglu. 2011. A GIS based comparative study of frequency ratio, analytical hierarchy process, bivariate statistics and logistic regression methods for landslide susceptibility mapping in Trabzon, NE Turkey. Catena 85 (3): 274–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2011.01.014.
Yin, K.L., and T.Z. Yan. 1988. Statistical prediction model for slope instability of metamorphosed rocks. In proceedings of the 5th international symposium on landslides, Lausanne, Switzerland. Vol. 2, 1269–1272. The Netherlands: AA Balkema Rotterdam.
Acknowledgements
Authors Prof. A.K. Mahajan and Mrs. Swati Sharma are thankful to Department of Science and Technology (DST) for all the research facilities provided under the project no. NRDMS/11/3023/013(G) for carrying out the studies. Department of Earth and Environmental sciences, Central university of Himachal Pradesh is also acknowledged for providing all the resources.
Funding
Project no. NRDMS/11/3023/013(G) funded by department of Science and Technology (DST), India.
Availability of data and materials
Entire data prepared from this work is presented in the main manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SS has carried out the field investigations and preparation of the thematic maps with AKM for developing the landslide inventory. AKM has helped to conceptualize the methodology and SS has drafted the entire manuscript. Both the authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, S., Mahajan, A.K. Comparative evaluation of GIS-based landslide susceptibility mapping using statistical and heuristic approach for Dharamshala region of Kangra Valley, India. Geoenviron Disasters 5, 4 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40677-018-0097-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40677-018-0097-1