Abstract
We exploit the implementation of India’s National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme to identify exogenous shifts in mothers’ labor force participation and its impact on their children’s educational outcomes. Using child level panel data, we find that a mother’s participation in the labor force increases her children’s time spent in school and leads to better grade progression. These results account for age cohort trends and for differences in time trends by initial levels of economic development at the district and sub-district levels. We find evidence of greater household decision-making power of working mothers as an explanation of our results.
Jel codes: D1, I21, I38, J16
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
The World Development Report (World Bank 2012), focusing on gender equality, highlights the economic disadvantages faced by women in the poorer regions of the world. Although significant progress has been made in reducing gender disparities in health and educational outcomes, economic opportunities remain limited for women. In particular, existing research suggests that variation in women’s labor force participation is associated with changes in individual and household behavior on several fronts including marriage (viz., van der Klaauw 1996), fertility (viz., Goldin and Katz 2002), and intra-household resource allocation (viz., Luke and Munshi 2011). Thus, the policy priority of closing the gender differences in access to economic opportunities is critical not only for reducing poverty but also for improving individual and household welfare in developing countries.
In this paper, we exploit the exogenous, temporal sub-district level variation in the intensity of implementation of India’s National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (NREGS) to identify shifts in rural women’s participation in the labor market and its impact on their children’s educational outcomes. The scheme operationalized the National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (2005) by providing a legal guarantee for up to 100 days of annual employment at a predetermined wage rate to rural households willing to supply manual labor on local public works.Footnote 1 From a gender perspective, there are two interesting features of this program. First, the wage rate offered in the scheme is uniform across gender, and second, it gives priority to female employment on public works and mandates one third of the program beneficiaries to be women. Thus, NREGS not only brings employment opportunities to rural women’s doorstep but the equal wage rates provided in the program can also reduce any gender disparity prevalent in the rural labor markets.
A change in parental labor supply could affect children’s educational outcomes purely due to an income effect. However, labor force participation of mothers, per se, could impact her children’s education through additional channels. First, mothers are likely to have more alternative uses of their time than fathers—market work, household chores, and leisure. If children’s time in doing household chores substitutes for mother’s time, then an increase in labor force participation of mothers may lead to a decline in the educational attainment of her children. However, if the mother’s and children’s time are not close substitutes and child care services in the market are either unavailable or unaffordable, then it is possible that schools substitute for child care services and children attend school when mothers are at work. Note, however, that this mechanism is unlikely to hold if child care services are available within the household through the presence of older members (viz., grandparents).
Second, a working mother’s say in household resource allocation decisions may be greater due to her higher earned income. Existing research suggests that this is likely to have a positive effect on her children’s schooling. If an increase in mother’s earned income translates into greater weight being attached to her preferences in resource allocation decisions of the household and mothers prefer to invest more in their children’s health and education relative to fathers (Blumberg 1988; Thomas 1990; Hoddinott and Haddad 1995; Quisumbing and Maluccio 2003), then we should see an improvement in child outcomes.
In this paper, we focus on the latter two channels of impact of mother’s labor supply decisions on her children’s education. We, therefore, control for changes in household level income to account for any income effect. The net impact of mother’s participation in the labor force on her children’s time allocation and, thereby, schooling, would then depend on which of the two effects dominate—the negative substitution effect or the positive bargaining power effect.Footnote 2
There exists relatively little empirical research on the impact of parental labor supply on children’s time allocation, particularly in a developing country context. Skoufias (1993) shows that an increase in female wages (and thereby female labor supply) in rural India reduces the time in school significantly but only for girls. Similar results are found by Grootaert and Patrinos (1999) in a cross-country study. However, Ilahi (1999) does not find any impact of female wages on children’s time use in Peru.
In contrast to the sparse literature on time allocation effects, there is considerable empirical evidence suggesting that households’ resource allocation decisions are made in a “collective” or a bargaining framework where the final allocation usually depends on the bargaining power or weights attached to the preferences of the members of the household. The importance of labor income as a determinant of women’s bargaining power within the household has been highlighted by Anderson and Eswaran (2009). Using data from Bangladesh, the authors show that the effect of earned income on female autonomy is far greater than that of unearned income. Women who work on the household farm have no more autonomy than those who are housewives, while those who earn independent income have considerably greater autonomy. Luke and Munshi (2011) exploit data from tea plantations in South India where women are employed in permanent wage labor to find that a relative increase in female income has a positive effect on their children’s education. Qian (2008) shows that a change in agricultural pricing policy in post-Mao China, which increased female labor income, raised the educational attainment of all children within the household. However, when the policy increased male labor income, educational attainment of girls decreased but had no effect on boys’ attainment.
We utilize child and household level panel data for 2007 and 2009–2010 from the Young Lives Study in the state of Andhra Pradesh to assess the effect of mother’s participation in the labor force on three educational outcomes of her children—time spent in school, enrolment, and grade attainment. To identify exogenous shifts in mothers’ labor force participation, we take advantage of the temporal, sub-district level variation in the implementation of the NREGS. Our identification strategy utilizes the lagged amount of funds allocated for the implementation of the NREGS as well as lagged rainfall shocks within sub-districts as exogenous shifters of labor force participation of women in rural areas. The analysis accounts for unobservable child characteristics, age cohort trends, and differences in time trends by initial levels of economic development, both at the district both the sub-district level.
Our results suggest that participation of mothers in the workforce results in more time spent in school by their children. Almost half of the rise in children’s time in school can be accounted by an increase in the probability of a child being enrolled in school when the mother works. Further, this increase in school participation is reflected in higher grade attainment of children. Labor force participation by the mother reduces the gap between the child’s actual and ideal grade by more than 40 percentage points. Our results are robust to the inclusion of a host of other variables that account for alternative explanations for the improved educational attainment of children: changes in fathers’ labor force participation, creation of household assets, migration, impact on private wages, and increased supply or demand for public schools arising from NREGS beneficiaries’ heightened awareness of their entitlements.
In order to understand the mechanisms through which these effects occur, we exploit household level data on education expenditures and on household members’ say in decision-making and control over income from various sources. The analysis of panel data on household level expenditures shows that mother’s participation in the workforce significantly increased the share of education in total household expenditure of less landed households. Moreover, cross-sectional two-stage least squares (2SLS) analysis suggests that the probability that mothers have a say or control over utilization of household earnings from different sources increases when they participate in the labor force.
These results suggest that greater weightage on working mothers’ preferences in household decision-making could be among the primary drivers of the improvements in educational attainment of their children. While we cannot completely rule out the possibility that schools serve as child care centers while mothers work, this mechanism cannot account for all of our results: the impact of mother’s labor force participation on children’s time spent in school is robust to the presence of older members or potential child care givers in the household and is equally significant for older children who are relatively less likely to require child care services than the young. Our findings can, hence, be explained within the framework of a bargaining model of household resource allocation.
This study not only informs us about the relevance of women’s labor supply to intra-household outcomes but it also addresses the broader policy issue of the role of the design of public programs in improving household outcomes in developing countries. Specifically, our paper extends the debate on the effect of workfare programs on household and individual welfare (Jalan and Ravallion 2003; Azam 2012; Dasgupta 2013; Zimmermann 2014; Klonner and Oldiges 2014; Imbert and Papp 2015) and finds evidence which suggests that mandating women’s participation in public programs has consequences beyond those immediately intended by policy makers.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 describes the data and the methodology used in this paper. Section 3 discusses the results and Section 4 concludes.
2 Data and methodology
Our study is focused on Andhra Pradesh (AP)—India’s fifth largest state in terms of population. We utilize data from the Young Lives Study (YLS)—a child and household level panel from six districts of AP. To date, there have been three rounds of YLS surveys. We conduct our empirical analysis at the level of the child using the two comparable waves of the YLS surveys—2007 and 2009–2010.Footnote 3
The sample is restricted to children who were 5 to 14 years old, the school-going age group, in 2007. In order to construct our data set, we use the following exclusion rules: first, we only include households living in rural areas in both periods. Thus, children in households which moved from rural to urban areas between the two rounds (less than 1 % of our sample) were dropped. Of the remaining sample, 2.8 % of the children in 2007 were not present in the subsequent round and were, therefore, dropped. Attrition is, therefore, negligible in the sample. Finally, we exclude children for whom there is some missing information on relevant covariates in either of the years. Our data set, after these exclusions, contains information on 3275 children for both years.
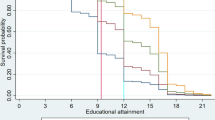
Table 1 describes the summary statistics for 2007 and 2009–2010. The time spent in school by children in the reference period (a typical day in the last week) went up from 5.78 h in 2007 to almost 7 h in 2009–2010. This increase is not driven by the changing age composition of children over the 2 years—a comparison of children by age cohorts shows that the time spent in school is significantly higher in 2009–2010 relative to 2007 (Fig. 1), reflective of more regular school attendance. Children in the survey, who reported attending school regularly, spent almost 2 h more in school than those who reported going to school irregularly, on a typical day. We can, therefore, interpret greater time spent in school by a child as an indicator of greater number of days of school attendance. The rise in time spent in school was accompanied by a rise in the highest grade completed as well as the average grade progression during this period. Footnote 4 Enrolment rates also rose by 8 percentage points, largely a result of several 5-year-olds joining school by 2009–2010.
During the same period, there was a substantial rise in the proportion of children whose mothers were part of the labor force, i.e., self-employed (farm or non-farm), wage employed (farm or non-farm), or in salaried employment. Mothers’ labor force participation rate increased from 69 % in 2007 to 88 % in 2009–2010 as shown in Table 1. This was accompanied by a 34 percentage point increase in the proportion of children whose mothers were participating in projects under the NREGS. A significant part of the rise in mothers’ NREGS participation is due to the phasing of the program. To elaborate, the NREGS was first rolled out in 2006 in the 200 “poorest” districts of India (February 2006). Thereafter, it was extended to 130 additional districts in May 2007 and to all districts in the country by 1 April 2008. Our study period coincides with the initial implementation of the NREGS (four YLS districts in phase 1), followed by nationwide coverage by 2008 (an additional YLS district each in phases 2 and 3).Footnote 5 Given that the increase in mothers’ overall work participation rate was accompanied by an increase in their participation in the NREGS, it suggests a potential impact of the scheme on mothers’ labor force participation. We discuss this in detail later in our identification strategy.
The rise in mothers’ labor force participation correlates positively with the change in time spent in school by their children, as shown in Fig. 2. When we classify mothers into those who worked in 2007 but dropped out of the labor force in 2009–2010, those who did not change their workforce participation status between 2007 and 2009–2010 and those who did not work in 2007 but entered the labor force in 2009–2010, we find that while the change in children’s time spent in school is positive for all three categories, it has been largest for the last group. In contrast to the rising labor force participation of mothers, fathers’ participation in paid labor (approximately 98 %) was largely unchanged during this period. Footnote 6 The real, average annual household income (in 2009 rupees) also increased during this period, primarily due to a rise in non-agricultural income.
2.1 Methodology
We estimate the following specification:
TSS chmdt is the time spent in school by child c in household h in a sub-district or mandal m in district d at time t. Footnote 7 MOTHER_WORK chmdt is a dummy variable that takes the value 1 if the mother participates in the labor market and 0 otherwise. INC hmdt is the total annual household income from all sources. It includes parental income from participation in any paid work, including the NREGS. Footnote 8 Since time allocation decisions are a function of household demographics, we include the number and the average age of household members in Z hmdt . Schooling decisions depend on the age and gender of the child. For instance, older children are more likely to spend time working for wages or taking care of their siblings. We allow for this effect to be non-linear in age by including dummy variables for each age cohort (5 to 14 years) in 2007.Footnote 9 We also address any time trends in girls’ education by including a dummy for female child. Since both these variables—the age of the child in 2007 and gender—are time invariant, they are included in X chmd and interacted with the time trend t, which takes the value 0 for the year 2007 and 1 for the period 2009–2010. V hmd is a vector of households’ wealth—asset and land ownership in 2007—interacted with t to allow for trends in the households’ economic status affecting investments in child’s education.Footnote 10
We allow regions with different initial levels of economic development to have different trends: first, we include the total night lights in 2006 in a mandal, DEV md , and interact it with t.Footnote 11 Second, districts where the NREGS was implemented earlier (phase 1) were less developed than districts where the program was implemented later (phases 2 and 3). We include a dummy which equals 1 if the child belongs to a phase 1 district, otherwise 0, in DEV_DIST d .Footnote 12 In addition, to account for differences in the initial level of school participation, we also include the average primary school enrolment rate (for children aged 5–10 years) at the district level, in 2004–2005 in DEV_DIST d .Footnote 13 This vector is then interacted with t.
Given this specification, and using data on a balanced panel of children over the two time periods, we estimate a child fixed effects model. In doing so, we eliminate α chmd or any unobservable, time invariant child characteristics.Footnote 14 If we assume that the deviations of the observed variables from their mean values are not correlated with the deviation of the error term from its mean, this specification yields a consistent estimate of our main coefficient of interest, φ 1.
The main concern with our estimation strategy is that household income and mothers’ labor supply decisions are likely to be determined simultaneously with investments in children’s education. To address this simultaneity issue, we adopt a 2SLS estimation procedure using temporal variation in rainfall shocks in the previous agriculture year and allocation of funds to the NREGS program at the beginning of a financial year, both at the mandal level, as instruments. We describe our instruments and discuss their validity next.
2.2 Validity of instruments
Using the YLS data, we find that the crop which the largest proportion of rural households cultivate (almost 36 % across rounds 2 and 3) is rice. The cultivation of rice is highly water-intensive. Rice seedlings are grown in nurseries which are then manually transplanted into the flooded fields. It is therefore expected that rainfall will promote the development of rice seedlings enabling farmers to increase their cultivation of rice which in turn could raise agricultural incomes. Furthermore, studies suggest that rural women’s labor force participation in India may be higher when households face adverse shocks. Women, for instance, could be expected to contribute to household income when agricultural employment opportunities and earnings are lower for men during a drought (Himanshu 2011). Weather shocks could, therefore, carry implications for women’s labor force participation as well. Hence, we use mandal level rainfall shock as one of the instruments.
We define rainfall shock as the deviation of actual rainfall from the long-term average rainfall, divided by the long-term standard deviation, at the mandal level.Footnote 15 Corresponding to the reference period for agricultural income in each YLS survey round, we calculate rainfall shocks during June 2005 to May 2006 (for the 2007 YLS round) and during June 2008 to May 2009 (for the 2009–2010 YLS round). Note that the reference period for children’s time spent in school is the previous week—January to July 2007 for the 2007 round of the YLS and August 2009 to March 2010 for the 2009–2010 round. Thus, rainfall shock is lagged with respect to children’s educational outcomes (hence, we refer to it as “lagged rainfall shock” from now). This obviates any direct effect of contemporaneous rainfall shocks on children’s time in school.
However, if rainfall shocks affect children’s health outcomes contemporaneously and the latter persist into subsequent years, then previous rainfall shocks could directly impact current schooling outcomes. We use data on school attendance in the last 12 months for a subset of “indexed” children to investigate this link.Footnote 16 We find that, conditional on being enrolled, approximately 11 % of these children reported missing school due to illness or injury in each round. To check whether missing school due to current morbidity is correlated with past rainfall shocks, we run a pooled ordinary least squares (OLS) regression of a dummy variable for whether a child missed school due to an illness on lagged rainfall shock (results are available on request). The coefficient on lagged rainfall shock is insignificant. This provides suggestive evidence that, in our sample, past rainfall shock is unlikely to directly impact children’s current time in school but should affect it via the impact on past household income.
Our second instrument is lagged NREGS funds sanctioned at the beginning of each financial year (April) for a mandal in 2009 rupees.Footnote 17 Note that the NREGS is envisaged as a demand-driven program: households are expected to apply for work to the village council (or gram panchayat, GP) and once a critical mass of demand is generated in a GP (a collection of one to three villages) in a mandal, a project has to be selected from the approved list of works and sanctioned by the district administration.Footnote 18 Thus, to avoid any reverse causality, i.e., current NREGS funds being determined by current demand for work, we use lagged sanctioned NREGS funds as an instrument. This is preferred to using actual expenditure on NREGS which is more likely to be driven by the demand for the program. Since the NREGS was initiated only in 2006–2007, we use the 2006–2007 financial year sanctioned program funds as an instrument for the 2007 YLS round.Footnote 19 For the 2009–2010 survey, we take a 1-year lag with respect to the households’ reference period for work activities and use the sanctioned funds in the financial year 2007–2008 as the instrument.Footnote 20
Our identification strategy, thus, uses the change in sanctioned program funds within mandals irrespective of the NREGS phase the district belongs to. But what determines differential changes in NREGS fund allocation? A plausible explanation is that sanctioned program funds change to reflect demand that varies by the level of economic development of the mandal. However, we have already controlled for trends by baseline economic prosperity (i.e., DEV md *t and DEV_DIST d *t) in our specification. Another possible determinant of systematic changes in funds sanctioned at the mandal level could be electoral exigencies during the 2009 state elections in AP. However, Sheahan et al. (2014) do not find any evidence of vote buying through NREGS expenditures before the 2009 legislative council elections at the constituency level (which roughly correspond to mandals). Thus, controlling for the above trends, the residual variation in changes in NREGS fund allocation (which we use in our identification strategy) is likely to be quasi-random.Footnote 21
A concern that remains is temporal learning by the local administration. To elaborate, say, that the administration is learning how to implement NREGS, which improves between 2006 and 2009 along with the quantum of sanctioned funds, this learning spills over to the provision of the public good of interest to us—education. In this case, our IV will not meet the exclusion restriction as it would have a direct effect on educational outcomes. However, in Andhra Pradesh, school participation is near universal.Footnote 22 According to the Annual Survey of Education Report (ASER 2006), the percentage of out of school rural children in the 6–14 age group was from 0 to 5 % in all the YLS districts except West Godavari where it was between 5 to 10 % in 2006. Further, the Right to Education (RTE) Act of India, which guarantees schooling for 6–14-year-olds, came into effect in April 2010, after our study period. Thus, any administrative “learning” with respect to public schooling would be minimal, if at all. Second, while it is quite likely that administrative capacity and NREGS implementation improved over time, it is unlikely that this was accompanied by administrative improvements in public schooling. The administrative machinery that has been created for the NREGS implementation at the grassroots level and which helps expand capacity for the program is different and delinked from that required for public schooling. Third, elections to village councils for a 5-year term were held in 2006. Since there were no changes in local governments during the period of our study, there are unlikely to have been significant changes in local political will for implementation of public programs during 2007–2010.
Finally, our third instrument is the interaction of lagged rainfall shock with lagged NREGS funds. This allows for the effect of rainfall shock on household income and mothers’ labor force participation to vary with NREGS funds. For instance, the effect on household income of a drought may be lower if there are more NREGS funds allocated to provide local employment in a mandal.
3 Results
3.1 Impact of mother’s work status on child’s education
Table 2 shows the results for children’s time spent in school. The coefficient on “mother is working” is positive and significant in column (1). If the mother works, her child’s time spent in school goes up by 0.293 h in a day. To account for the possible endogeneity of labor force participation of mothers and household income, we conduct the 2SLS analysis. But before discussing the second stage, we show the first stage results in Table 3. For the endogenous variable “mother is working,” the coefficient on lagged rainfall shock is significantly negative in column (1). This result lines up with the existing literature which suggests that in India, women are more likely to work during periods of economic distress such as droughts. While the coefficient on lagged funds is insignificant, the interaction term is positive and significant in column (1), implying that the effect of NREGS on mother’s workforce participation depends on the level of lagged rainfall shock. To elaborate, at the mean lagged rainfall shock, the total effect of NREGS funds on mother’s labor force participation is significantly positive. The coefficient on lagged rainfall shock is positive and significant for annual household income in column (2). An increase in the lagged funds sanctioned for NREGS projects in a mandal increases the household income significantly. In times of good rainfall, however, the sanctioned funds have a lower marginal effect on the total income (as indicated by the negative coefficient of the interaction term). Our instruments are good predictors of the endogenous variables as indicated by the F statistics reported in the last row in Table 3.
Moving back to the second stage results in column (2) of Table 2, we find that the coefficient on the dummy for mother working continues to be positive, significant, and has a higher coefficient than in the ordinary least squares fixed effect (OLS-FE) specification. When a mother works, it leads to her children attending school 6.506 h a day more. This effect is over and above the income effect from working, the point estimate of which is positive but not significant.
The coefficient of the 2SLS estimator measures the local average treatment effect (LATE)—the impact on time spent in school among children whose mothers changed their labor force participation status—in contrast to the OLS estimator which measures the impact of mothers’ labor force participation for the full sample.Footnote 23 The increase in the magnitude of the 2SLS coefficient, as compared to the OLS, typically suggests that the impact of the treatment on those who changed their behavior (referred to as compliers) is much larger than on the rest of the population (Angrist and Pischke (2009), Chapter 4.4–4.5). Footnote 24 Further, the instruments pass the over-identification test and the weak identification critical value cut-offs.Footnote 25
The significant coefficient on the age dummies, interacted with time, declines at higher age groups. Thus, the older the child, the smaller is the point estimate on the increase in time spent in school. This reflects the higher opportunity cost of time in school for older children. The negative coefficient on the initial district level average enrolment rate in both the OLS-FE and 2SLS-FE specifications, together with the positive coefficient on age dummies interacted with time, suggests that in districts where school participation was high prior to 2007, there was a smaller increase in time spent in school between 2007 and 2009–2010.Footnote 26
The large increase in the number of hours spent in school suggests that mothers’ work may play an important role in the school enrolment decisions of children. We, therefore, estimate the same specification used for time spent in school but with the dependent variable “enrolment status.” The results are shown in Table 4. While the impact of a mother working on her child’s school enrolment status is insignificant in OLS, it is positive and significant in the 2SLS estimate—probability of a child being enrolled in school rises by 47.2 percentage points. There are two factors that may drive this result. First, those children who are 5 years old and not enrolled in school at the baseline may enrol in a primary school as they get older if their mothers work. Second, typically children in older cohort at the baseline tend to drop out of school over time. Mothers entering the workforce may result in lower drop outs. This 47.2 percentage point increase in the probability of enrolment can potentially account for almost half of the increase in the time spent in school.Footnote 27
The impact of current household income is positive and significant (0.003) when the dependent variable is enrolment status of the child. This suggests that any income effect of changes in labor force participation status of a mother (or parents and other household members) predominantly influences enrolment decisions. This contrasts with the insignificance of household income on the child’s time spent in school (Table 2), an outcome that measures both the extensive (enrolment) and the intensive margins (more regular attendance) of children’s school participation.
While we find that the time spent in school has risen due to mother’s participation in the workforce, a pertinent question to ask is whether there was a concomitant improvement in the educational attainment of a child. Therefore, we conduct our analysis for grade attainment by a child with the dependent variable “actual grade attainment of a child divided by the grade the child should have completed at her/his age” with the same specification. The sample for this outcome, therefore, consists of children aged 6–14 years. We find a significant effect of mother’s work participation on her child’s grade progression—as reported in Table 5—the gap between a child’s actual and ideal grade declines by 40.6 percentage points. Footnote 28 We do not find any heterogeneity in the average impact for any of our measures of educational attainment.Footnote 29 To elaborate, the impact of mother’s work is significant and of comparable magnitude across both genders and age groups (younger children or 5- to 10-year-olds and older children or 11- to 14-year-olds in 2007). The significant impact on the older age group of children, in particular, cannot be explained away by the argument that the mothers use schools as day care centers while they work.
3.2 Robustness checks
In this section, we report further robustness tests of our results for time spent in school by accounting for alternative confounding mechanisms in Table 6.Footnote 30
While the Right to Education Act, which aims to increase school participation rates of disadvantaged children, was implemented in Andhra Pradesh (and nationwide) after our study period in April 2010, it may have been preceded by construction of additional schools which may in turn be correlated with NREGS intensity at the mandal level.Footnote 31 Using school administrative data from the District Information System for Education (DISE) at the mandal level for the years 2006 and 2009, we include the number of schools as a control variable to address this concern. We do not find any significant change on the coefficient of “mother working” in column (2) of Table 6.Footnote 32
In our analysis, so far, we have focused on the working status of the mother. However, if mothers’ and fathers’ decisions to work are correlated and the NREGS program affects fathers’ work status as well, then our analysis may be identifying the impact of fathers’ work status. However, inclusion of this variable does not affect the coefficient of the mothers’ workforce participation in column (3).
Past rainfall shocks as well as income earned from participation in the NREGS in previous periods may affect current schooling through an effect on current household wealth. For example, households may have bought or sold assets in response to the shocks and NREGS work opportunities in the previous periods. However, inclusion of current wealth may be endogenous as decisions to accumulate assets may correlate with schooling as well as labor supply decisions. Hence, we have included baseline household wealth trends in our main specification. However, in order to see whether our estimated coefficient is affected by lagged effects of shocks and program fund allocation on household wealth, we include current household wealth as a regressor. Results in column (4) suggest that the inclusion of this variable does not have any significant impact on our estimated coefficient on mother’s work status. Similarly, past NREGS work may affect migration in the household and that may impact schooling outcomes directly. To see whether this is the case, we control directly for the number of household members who were present in the previous YLS round but are absent in the current round to approximate migration.Footnote 33 Again, the inclusion of this variable does not affect our results (column (5)).
It has been contended that NREGS may affect wages for private work in the local labor market. If any increase in past wages influences current wages (Kaur 2014), it may affect current school outcomes. The inclusion of current income in our main specification accounts for this possibility. However, to show that our results are robust to any remaining concerns on this count, we control for the highest current daily wage for males and females in the local community (columns (6) and (7)).Footnote 34 Again, the coefficient on mother’s work remains unchanged.
The NREGS mandates the conduct of regular audits of program projects by local stakeholders.Footnote 35 Since one of the objectives of the audits is to make beneficiary households aware of their rights and entitlements, it is possible that a higher frequency of these audits leads to a greater demand for access to better quality schools by parents as well as a rise in women’s participation in the NREGS and in the workforce. Hence, any observed relationship between mother’s labor market participation and children’s time in school could be driven by a rise in households’ awareness levels. To control for this, we allow the trend to depend on the number of social audits that have taken place in the mandal between the two survey rounds interacted with time in column (8). Our results are unaffected.
Finally, to test for the possibility that schools substitute for day care for working mothers, we control for the demographic composition of the household in column (9) in Table 6. The effect of mothers working on children’s time in school should be insignificant if there are older siblings or grandparents in the household to take care of the younger ones. But the interpretation of our results is unchanged when we control for the presence of older siblings and of household members in the 60+ age group.
4 Discussion of results
Our results establish that when a mother works, there is a significant, positive impact on her children’s educational attainment. Since we have accounted for any income effects in our specification, can an improvement in mothers’ say in household decision-making when she participates in the labor market explain our results? If so, we should see a positive effect of mother’s labor force participation on other schooling indicators that provide more direct evidence on investments in children. We, therefore, use household level data on the share of total expenditure that is spent on education to test our hypothesis further.Footnote 36
Our specification is now run at the household level (since these data are not available at the child level) with additional controls for the number of children in the 5–17 age group (boys and girls separately), the square of the number of these children and the average age and gender composition of this group in the household. Our main coefficient of interest is working status of the mother of the indexed child and his/her siblings in the household.
We find no significant result for the overall sample. Stratifying the households by baseline land ownership, we find significant results only for households with less than median landownership. We report only these significant results in Table 7 (other results are available on request). The analysis suggests that mothers’ participation in the labor force increases the share of total expenditure that is spent on schooling expenses for the less landed households. When mothers work, the share of expenditure towards education rises by 3.8 percentage points. The rise in the share of expenditure is largely accounted by fees, tuition, and school uniform (column (2)). This indicates that mothers’ labor force participation is indeed leading to more investment in education in less landed households.Footnote 37
To explore the bargaining power mechanism further, we use data available in the second round of the YLS to analyze whether participation in the labor market led to improvements in mothers’ decision-making abilities within households.Footnote 38 Our dependent variable is the binary response to two questions, each, for three sources of household income:
-
1.
“Is the caregiver responsible for making the key decisions about any of the plots (land)/work for wages activities (wage activities)/business and self-employment activities (business and self-employment)?”
-
2.
“Does the caregiver control the use of the earnings from the sale of goods or rent from any of these plots (earnings from land)/from any work for wages activities (earnings from wage activities)/from any business and self-employment activities (earnings from business and self-employment)?”
The sample is restricted to caregivers who are mothers in age group 16–60 years. Our main variable of interest is whether the mother works. Results for the 2SLS specification are reported in Table 8. The positive and significant coefficient on “mother is working” across all outcomes suggests that greater participation of mothers in the labor market does increase the say and control these women have on important decisions being made within the household. In rural areas, earnings from land, wages, and business and self-employment activities are likely to be the most important sources of income for households. This result, therefore, bolsters our claim that an increase in work opportunities for women is likely to have a positive effect on their decision-making abilities within the household.Footnote 39
5 Conclusion
We utilize the sub-district level temporal variation in the intensity of the National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (NREGS) and in rainfall shocks in Andhra Pradesh (AP) to determine the effect of exogenous changes in the demand for labor on women’s labor force participation and thereby their children’s educational outcomes.
Using panel data from the Young Lives Study for 2007 and 2009–2010, we find that participation of mothers in the workforce has a positive effect on the probability of her children being enrolled in school and her children’s time in school. This carries implications for the latter’s educational attainment as well. Specifically, children whose mothers work move closer to their ideal grade for age.
We find evidence that suggests that the positive impact of mothers’ participation in work could be due to her improved position in household decision-making. Our assertion is supported by recent qualitative evidence on the empowering effects of NREGS on rural women (Pankaj and Tankha 2010; Khera and Nayak 2009).
Although our results are contextual and specific to AP—a state which has traditionally exhibited high rates of women’s participation in work relative to the national average and has also been among the best implementers of the NREGS since its inception—they provide strong evidence of the beneficial effects of increasing women’s participation in the labor force. Furthermore, the findings suggest that the design of public programs matter and have consequences beyond those intended by policy makers.
Notes
We are abstracting from any long-term effects of changes in fertility due to increased labor force participation of women since we are looking at these changes over a short period of 2 to 3 years.
Data for 2002 (round 1 of YLS) are not comparable to the 2007 and 2009–2010 data (rounds 2 and 3 of YLS, respectively) because of differing methods of measuring labor supply. Moreover, there are no data on income earned by the household in 2002.
We measure grade progression as the ratio of actual grade completed to the ideal grade for age. Details in Section 3.
Anantapur, Cuddapah, Karimnagar, and Mahbubnagar implemented the NREGS in 2006. Srikakulam and West Godavari were the two districts that came under NREGS in 2007 and 2008, respectively.
There was a rise in fathers’ participation rate in NREGS during this period as well. Since overall labor force participation rate of fathers did not change, this suggests that fathers may have taken up NREGS work as an additional activity.
The time spent in school is recorded as hours spent in school on a typical day in the previous week. The total time spent on education on a typical day consists of time spent in school and time spent on studying outside school (private tuition and at home). The average time spent on education outside the school in the sample is less than 20 % of the total time spent on education on a typical day. While we focus on time spent in school (TSS) as the dependent variable here, the same specification is adopted for other child education outcomes.
Whether the income effect is significant or not is a function of the cost of schooling as well. If physical access to schooling is relatively easy and costs of schooling are subsidized (as is the case for public primary schools), any effect of an increase in household income may be muted for the age group under study here.
Note that we do not include the child’s age as a control variable because the change in age over our study period is the same for all children. Further, we do not include the secular time trend as it is a linear combination of the age cohort trends which are included in the specification.
Asset index was constructed using principal component analysis of binary variables indicating ownership of durable consumer goods by the household, viz., television, radio, car, motorbike, bicycle, telephone, mobile phone, refrigerator, fan, electric oven, table and chair, sofa, and bedstead.
Data on night lights is from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) website: http://www.noaa.gov.
Note that we do not use the phasing of the NREGS to identify the effect of mother’s labor force participation on her children’s schooling. The inclusion of the program phase trend as a control in our empirical specification invalidates district level phasing as the source of variation for identification.
We source this information from the question on the “status of current attendance (enrolment) in educational institutions” in the 2004–2005 employment and unemployment round of the National Sample Survey. One of the factors that could affect temporal changes in participation in schooling is a change in the quality of schools, specifically a shift from public to private schools. The YLS contains information on the type of school the child is enrolled in for only a subset of our sample. Community level data on the type of schools are not comparable between the two survey rounds. Our results are, however, robust to the inclusion of a dummy variable for whether a private school at any level existed in the locality in 2007 or 2009–2010.
The child fixed effects specification also accounts for any unobservables at the geographic (district, mandal, and village) level that may be correlated with regressors on the right-hand side and that may also affect children’s time spent in school.
The variable capturing rainfall shocks is constructed from the precipitation data available from the Center for Climatic Research at the University of Delaware. The data include monthly precipitation values at 0.5° intervals in latitude and longitude. To match this data at the mandal level, the nearest latitude-longitude to each mandal headquarter is taken. To construct the rainfall shock at the mandal level, we calculate the long-term (1990–1991 to 2008–2009) average mandal level rainfall in the months of an agriculture year. Standard deviation of rainfall for the same period is also calculated at the mandal level. Then rainfall shock is defined as the deviation of actual rainfall in the reference period from the long-term average, divided by the standard deviation.
The YLS has been collecting more detailed information on these children since the first round of the study in 2002. Data from the 2002 survey round is, however, not comparable to the later rounds used in our study as discussed in footnote 3 above.
Data on the sanctioned funds at the mandal level were obtained from the Department of Rural Development, Government of Andhra Pradesh.
Although the NREGS envisages a demand-driven program, the reality is quite different according to several recent studies. Research on Andhra Pradesh (Afridi et al. 2013) indicates that the program is supply- rather than demand-driven.
Our second stage results are similar when we use sanctioned NREGS funds in 2005–2006 as an instrument for the 2007 round of the YLS. However, since the NREGS did not exist in 2005–2006, the instrument takes the value 0 for all mandals, which makes our first stage weak. We, therefore, use sanctioned program funds in 2006–2007 instead. Since NREGS has just been initiated in 2006, the assumption that the sanctioned funds were not demand-driven is reasonable.
Note that an overwhelming proportion of NREGS funds have been utilized for irrigation and water conservation projects since the program’s inception in AP: soil and water conservation, drought proofing and afforestation, micro- and minor irrigation works, rehabilitation of tanks and traditional water bodies, land leveling, and bush and jungle clearance. It is unlikely, therefore, that the program could directly affect access to schools or children’s allocation of time to household chores, viz., fetching drinking water: http://nrega.ap.gov.in/Nregs/FrontServlet?requestType=Common_Ajax_engRH&actionVal=Display&page=WorkCatog_eng.
To test this claim, we first regress the change in the mandal level sanctioned NREGS funds (between 2006–2007 and 2007–2008) on the district’s NREGS phase and the mandal’s total night lights in 2006. We then regress the residual of this regression on various observable characteristics of the mandal that may determine NREGS fund allocation (viz., total number of households, the number of people belonging to disadvantaged communities such as scheduled castes and tribes). We do not find a significant effect of any of these variables on NREGS fund allocation. Moreover, the point estimates do not suggest any systematic determinant of NREGS fund allocation. See Table 9 in Appendix for details.
Enrolment of children in the 6–10 years age group was almost 93 % in both 2007 and 2009–2010, while enrolment in the 11–14 age group was almost 81 % in 2007 and 86 % in 2009–2010 in our sample.
In particular, of the 1019 mothers who did not work in 2007, almost 72 % entered the labor force in 2009–2010. Of these mothers, more than 66 % worked on NREGS projects in 2009–2010.
We recognize that any additional time spent in school could be substituted by less time spent studying outside school leading to an insignificant effect of mother’s work on total time spent on education on a typical day. In an alternate specification, therefore, we consider the total time spent on education (including time spent studying outside the school) as the dependent variable. Our results are unchanged.
Critical values for the Stock and Yogo (2003) weak instrument test (5 % significance) reported in the table, based on 2SLS size with 2 endogenous variables and 3 instruments, are 13.43, 8.18, 6.40 and 5.45 for the 10, 15, 20, and 25 % sizes, respectively.
Lagged rainfall shock may force children to drop out of school in the year previous to our reference period. To check that our results are robust to this possibility, we include a dummy for whether a child is enrolled in school as an endogenous regressor in our main specification (2SLS-FE). Our results do not change.
In our sample, the average hours spent in school by children who are enrolled in school is approximately 7.15 h. The 47.2 percentage point increase in enrolment rates, hence, accounts for an average increase of 3.37 h in school—almost half (or 47.13 %) of the increase in time spent in school.
This result also indicates that the effect of mothers working on schooling is not driven purely by the enrolment of those who were 5 years old in 2007.
There are certain caveats to interpreting the effect of mothers’ working status on children’s grade progression. First, the highest grade completed is right censored for the sub-sample of children who are still enrolled in school. This is not the case, however, for children who have completed schooling (17-year-olds in 2009–2010) or have dropped out by the time of the survey interview. Second, the effect of parental labor market activities may not be reflected completely in grade attainment for those households which are interviewed before April (March is the last month of an academic year) since the highest grade attained by children in these households would be right censored. Finally, the highest grade completed is a stock variable that may be determined not just by current labor force participation of mothers but also their participation between 2007 and 2009–2010.
We report similar robustness checks for the enrolment outcome in Table 10 in the Appendix.
The reference period for the 2009–2010 round of the YLS was August 2009–March 2010.
Our results also hold up if we include the total number of private and public schools separately.
For this calculation, we also use the data from the 2002 round of YLS. We exclude household members who died and women who left the household due to marriage between 2007 and 2009–2010.
We obtained this information from the community level questionnaire in the YLS.
A novel feature of the NREGS is the introduction of compulsory “social” audits of projects carried out under the program by beneficiary households (and therefore referred to as “social”) at regular intervals. The AP government has institutionalized the conduct of these audits in the state since the inception of the NREGS in 2006.
An alternative mechanism that could explain our results is the mandatory provision of child care facilities at NREGS work sites. Mothers who participated in NREGS work may have had better access to child care facilities. This would free up the time of school-going age siblings, particularly girls, who could then attend school more regularly. The 2007 YLS survey respondents were asked whether the NREGS participant had “benefited from child care facilities at the worksite.” In the 2009–2010 survey, the respondents were asked: “Were there child care facilities in the last (NREGS) worksite?” Only 1 % of households report using on-site child care facilities in 2007 while more than 80 % of households report absence of child care facilities at the last worksite in 2009–2010. We, therefore, do not consider this as a valid explanation of our findings.
Our results are unchanged if we use total expenditure on schooling as the dependent variable.
These data were not collected by the YLS in 2009–2010. Our analysis, therefore, is cross-sectional.
Alternative definitions of mother’s workforce participation—share of mother’s NREGS income in total household income and total number of days mother worked in the reference period—lead us to similar conclusions. See Table 11 in Appendix for details.
References
Afridi F, Iversen V, Sharan MR (2013) Women political leaders, corruption and learning: evidence from a large public program in India. Working paper, IZA and International Growth Centre (IGC).
Anderson S, Eswaran M (2009) What determines female autonomy? Evidence from Bangladesh. J Dev Econ 90(2):179–191
Angrist J, Pischke J-S (2009) Mostly harmless econometrics: an empiricist’s companion. Princeton University Press, Princeton
ASER (2006) Annual status of education report. Pratham Resource Centre, New Delhi
Azam M (2012) The impact of Indian job guarantee scheme on labor market outcomes: evidence from a natural experiment. IZA Discussion Paper 6548.
Blumberg RL (1988) Income under female versus male control: hypotheses from a theory of gender stratification and data from the third world. J Family Issues 9(1):51–84
Dasgupta A (2013) Can major public works policy buffer negative shocks in early childhood? Evidence from Andhra Pradesh, India. Young Lives Working Paper 112.
Goldin C, Katz LF (2002) The power of the pill: oral contraceptives and women’s career and marriage decisions. J Political Economy 110(4):730–770
Grootaert C, Patrinos H (1999) The policy analysis of child labor: a comparative study. St. Martin’s Press, New York
Himanshu (2011) Employment trends in India: a re-examination. Econ Political Weekly 46(37):43–59
Hoddinott J, Haddad L (1995) Does female income share influence household expenditure? Evidence from Cote D’Ivoire. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 57(1):77–96
Ilahi N (1999) Children’s work and schooling under shocks: does gender matter? Evidence from the Peru LSMS panel data. Background paper for Engendering Development. technical report. World Bank, Washington DC
Imbert C, Papp J (2015) Labor market effects of social programs: evidence from India's employment guarantee. Am Econ J: Appl Econ 7(2):233–63
Jalan J, Ravallion M (2003) Estimating the benefit incidence of an antipoverty program by propensity-score matching. J Bus Econ Stat 21(1):19–30
Kaur S (2014) Nominal wage rigidity in village labor markets. NBER Working Paper No. 20770.
Khera R, Nayak N (2009) Women workers and perceptions of the National Rural Employment Guarantee Act. Econ Political Weekly 44(43):49–57
Klonner S, Oldiges C (2014) Safety net for India's poor or waste of public funds? Poverty and welfare in the wake of the world’s largest job guarantee program. AWI Discussion Paper Series No. 564.
Luke N, Munshi K (2011) Women as agents of change: female income and mobility in India. J Dev Econ 94(1):1–17
Pankaj A, Tankha R (2010) Empowerment effects of the NREGS on women workers: a study in four states. Econ Political Weekly 45(30):45–55
Qian N (2008) Missing women and the price of tea in China: the effect of sex-specific earnings on sex imbalance. Q J Econ 123(3):1251–1285
Quisumbing A, Maluccio J (2003) Resources at marriage and intra-household allocation: evidence from Bangladesh, Ethiopia, Indonesia, and South Africa. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 65(3):283–327
Sheahan M, Liu Y, Barrett C, Narayanan S (2014) The political economy of MGNREGS spending in Andhra Pradesh. IFPRI Discussion Paper 01371, September.
Skoufias E (1993) Labor market opportunities and intrafamily time allocation in rural households in South Asia. J Dev Econ 40(2):277–310
Thomas D (1990) Intra-household resource allocation—an inferential approach. J Hum Resour 25(4):635–664
van der Klaauw W (1996) Female labour supply and marital status decisions: a life-cycle model. Rev Econ Stud 63(2):199–235
World Bank (2012) World Development Report. World Bank, Washington DC
Zimmermann L (2014) Why guarantee employment? Evidence from a large Indian public-works program. Working paper, University of Georgia.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Deborah DeGraff, Taryn Dinkelman, Andreas Georgiadis, Priscila Hermida, Clement Imbert, seminar and conference participants at the ISI (Delhi), the Indian School of Business (Hyderabad), NEUDC (Dartmouth), IZA World Bank Conference (Delhi), the Asian Meeting of the Econometric Society (Delhi), the German Economic Association AEL Conference (Munich), University of Heidelberg, YLS conference (Oxford), Jadavpur University, IIM Bangalore, the ASSA Meetings (Boston), and the anonymous reviewers for their comments. The authors are grateful to Young Lives for financial support and for providing the data set. The usual disclaimers apply.
Responsible editor: David Lam
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
The IZA Journal of Labor & Development is committed to the IZA Guiding Principles of Research Integrity. The authors declare that they have observed these principles.
Appendix: online supplementary material
Appendix: online supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Afridi, F., Mukhopadhyay, A. & Sahoo, S. Female labor force participation and child education in India: evidence from the National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme. IZA J Labor Develop 5, 7 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40175-016-0053-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40175-016-0053-y