Abstract
Background
The ubiquitin-editing cytosolic enzyme A20, the major negative regulator of toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated cellular inflammatory responses, has tight genetic linkage with systemic sclerosis (SSc). Because recent studies implicate endogenous ligand-driven TLR signaling in SSc pathogenesis, we sought to investigate the regulation, role and mechanism of action of A20 in skin fibroblasts.
Method
A20 expression and the effects of forced A20 expression or siRNA-mediated A20 knockdown on fibrotic responses induced by transforming growth factor-ß (TGF-ß) were evaluated was evaluated in explanted human skin fibroblasts. Additionally, A20 regulation by TGF-ß, and by adiponectin, a pleiotropic adipokine with anti-fibrotic activity, was evaluated.
Results
In normal fibroblasts, TGF-ß induced sustained downregulation of A20, and abrogated its TLR4-dependent induction. Forced expression of A20 aborted the stimulation of collagen gene expression and myofibroblast transformation induced by TGF-ß, and disrupted canonical Smad signaling and Smad-dependent transcriptional responses. Conversely, siRNA-mediated knockdown of A20 enhanced the amplitude of fibrotic responses elicited by TGF-ß. Adiponectin, previously shown to block TLR-dependent fibrotic responses, elicited rapid and sustained increase in A20 accumulation in fibroblasts.
Conclusion
These results identify the ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20 as a novel endogenous mechanism for negative regulation of fibrotic response intensity. Systemic sclerosis-associated genetic variants of A20 that cause impaired A20 expression or function, combined with direct suppression of A20 by TGF-ß within the fibrotic milieu, might play a significant functional role in persistence of fibrotic responses, while pharmacological augmentation of A20 inhibitory pathway activity might represent a novel therapeutic strategy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is characterized by autoimmunity, vascular injury and tissue fibrosis [1]. Fibroblast activation resulting in collagen overproduction and myofibroblast differentiation plays a central role in the development and progression of fibrosis in the skin and internal organs. The multifunctional cytokine transforming growth factor-ß (TGF-ß) is a potent stimulus for fibroblast activation, and is strongly linked to the pathogenesis of SSc [2]. Although multiple intracellular pathways have been implicated in TGF-β-mediated fibrotic responses, cross-regulation among these networks remain incompletely characterized. Moreover, the factors underlying persistence of pathological inflammation and fibrosis in SSc are largely unknown. Recent experimental studies and results from genetic and genomic surveys provide compelling evidence to link innate immune signaling and toll-like receptor (TLR) activation to TGF-β activity and persistent fibrotic response [3].
Toll-like receptors are evolutionary conserved cellular sensors recognizing both microbial (exogenous) pathogen-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) and endogenous “damage-associated molecular patterns” (DAMPs) [3, 4]. Deregulated or unchecked TLR activation leads to persistent and unresolving tissue damage. Recent studies provide evidence for an essential pathogenic role for TLR4 and endogenous TLR ligands in SSc [5]. In order to avoid injury resulting from aberrant or sustained innate immune responses, a number of cellular mechanisms have evolved that negatively regulate TLR signaling [3, 6]. Best studied of these to date is the ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20 (TNFAIP3), a direct downstream target of TLR signaling, which is rapidly and transiently induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and negatively regulates both TLR-dependent and TLR-independent inflammatory responses [7].
Genetic association studies have uncovered tight linkage of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the A20 locus with susceptibility to autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, including SSc, in multiple ethnic cohorts [8–10]. Whereas the key role of A20 in modulating TLR4 activity and target gene expression in immune cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells is now quite well-established, the regulation, mode of action and importance of A20 in stromal cells such as fibroblasts remain completely unknown. Furthermore, the expression and function of A20 in the context of physiologic and pathological matrix remodeling have not been explored to date. The genetic linkage of A20 variants with SSc susceptibility and the growing recognition of a pathogenic role for TLR signaling in fibrosis and SSc, coupled with the scleroderma-like skin phenotype described in A20 knockout mice [11] together suggest a likely important role for A20 in the pathogenesis of SSc.
In the present studies we demonstrate show that A20 is detectable in normal skin fibroblasts, and shows sustained downregulation in response to TGF-β. Forced transient A20 expression in fibroblasts resulted in suppression of fibrotic responses elicited by TGF-ß and TLR4 ligands. These inhibitory effects of A20 were accompanied by reduced amplitude of canonical TGF-ß signaling and Smad-dependent transcriptional responses. These results reveal an important novel physiologic role for A20 in negatively regulating the intensity of fibrotic responses in fibroblasts, which parallels its role in limiting inflammatory responses. Impaired tissue expression or function of A20 due to SSc-associated genetic variants, combined with environmental regulatory influences, might contribute directly to the development or progression of fibrosis in SSc.
Methods
Cell culture and reagents
Primary cultures of dermal fibroblasts were established by explantation from neonatal foreskin or adult skin biopsies as described [12]. Cultures were maintained in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10 % fetal calf serum (FCS) (Gibco BRL, Grand Island, NY, USA), 1 % vitamin solutions and 2 mM L-glutamine. All other tissue culture reagents were from Lonza (Basel, Switzerland). For experiments, low-passage (3–5) fibroblasts were placed in serum-free media containing 0.1 % bovine serum albumin (BSA) for 24 h prior to addition of TGF-ß2 (PeproTech, Rocky Hill, NJ, USA), which has overlapping activity with TGF-ß1 and has been widely used to study the modulation of fibroblast activity (12,14). In other experiments, fibroblasts were incubated with recombinant human full-length adiponectin (BioVendor, Karasek, Czech Republic) or ultrapure LPS (InvivoGen, San Diego, CA, USA).
Isolation and analysis of RNA
Total RNA, isolated from fibroblasts cultures, was reverse-transcribed to complementary DNA (Cdna) using qScript cDNA SuperMix (Quanta Bio-Sciences, Gaithersburg, MD) and analyzed by real-time qPCR [12, 13]. Products (20 ng) were amplified using SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Applied Biosystems, Grand Island, NY, USA) using an Applied Biosystems 7500 Prism Sequence Detection System. Results were normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) RNA levels, and fold change was calculated in the samples [12].
Western analysis
At the end of each experiment, fibroblasts were harvested and whole-cell lysates subjected to western analysis as described [12]. The following antibodies were used: anti-phospho-Smad2 (Cell Signaling Technology, Boston, MA, USA), anti-type I collagen (Southern Biotech, Birmingham, AL, USA), A20 (Santa Cruz, Dallas, TX, USA), anti-α smooth muscle-actin (αSMA), beta actin and tubulin (all from Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA). Proteins were visualized using ECL reagents (Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA) and levels were quantitated by determining band intensities normalized to loading controls in each lane using ImageJ software.
Immunofluorescence confocal cytochemical analysis
Fibroblasts seeded on 8-well Lab-Tek II chamber glass slides (Nalgene Nunc International, Naperville, IL, USA) were incubated with TGF-ß (10 ng/ml) or transfected with A20 (Addgene, Cambridge, MA, USA) in serum-free DMEM with or without TGF-ß2 (Peprotech, Rocky Hill, NJ, USA) (10 ng/ml) for up to 24 h. Cells were then fixed, permeabilized, and incubated with anti-αSMA (1:100) (Sigma), anti-Smad2/3 (Cell Signaling Technology) and anti-A20 (1:100) (Santa Cruz) antibodies, followed by Alexa-fluor-labeled secondary antibodies (Invitrogen). Nuclei were identified using 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindone (DAPI) and immunofluorescence was evaluated under the Nikon A1 confocal microscope.
Transient transfection assays
Fibroblasts at early confluence were transfected with A20 or empty vector using Lipofectamine®2000 Reagent (ThermoFisher Scientific, Grand Island, NY, USA) in parallel [14]. Cultures were incubated in serum-free media containing 0.1 % BSA for 24 h, followed by TGF-ß2 for a further 24 h. At the end of the experiments, cultures were harvested and whole-cell lysates were prepared, or fibroblasts were fixed and subjected to immunofluorescence confocal microscopy. In selected experiments, fibroblasts were transiently transfected with [SBE]4-luc plasmid along with Renilla luciferase pRL-TK (Promega) as control for transfection efficiency. Following a 24-h incubation, whole-cell lysates were prepared and assayed for their luciferase activity.
Small interfering RNA-mediated knockdown
Fibroblasts were transfected with target-specific small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) (10 nM) coding for A20 or scrambled control siRNA (Dharmacon, Lafayette, CO, USA). At 24 h following transfection, fresh media containing TGF-ß2 (10 ng/ml) were added to the cultures, and incubations continued for a further 24 h, when total RNA was isolated for analysis.
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as means ± SD unless otherwise indicated. Differences between two groups were determined by Student’s t test. A p value <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Comparisons among three or more groups were performed using analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Sidak’s correction for multiple comparisons. Data were analyzed using Graph Pad prism (Graph Pad Software version 6, Graph Pad Software Inc., CA, USA).
Results
A20 is detected in skin fibroblasts and its basal and inducible expression is suppressed by TGF-ß
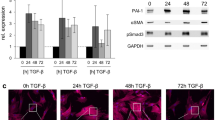
While constitutive A20 expression is low in most normal cell types, A20 was detectable in cultured human fibroblasts in the absence of stimulation [7]. In light of the central role of TGF-ß in modulating pathogenic fibroblast responses in SSc, we sought to examine the possibility that it might modulate the expression of A20. To this end, confluent foreskin fibroblasts were incubated with TGF-ß. The results demonstrated that TGF-ß treatment induced a dose-dependent and time-dependent decrease in A20 gene expression, with maximal inhibition after 24 h (Fig. 1a and b). Comparable results were seen when normal adult skin fibroblasts were used (Additional file 1: Figure S1 and data not shown). To investigate the cellular mechanisms underlying suppression of A20 by TGF-ß, we examined the effect of SB43542, a potent and selective inhibitor of ALK5 receptor-mediated Smad2/3 phosphorylation. The results showed that pretreatment with ALK5 inhibitor substantially reduced the suppressive effect of TGF-ß on A20 expression (Fig. 1c), indicating a key role for canonical Smad signaling in mediating this inhibitory effect of TGF-ß on A20.
Transforming growth factor-ß (TGF-ß) down-regulated basal A20 expression and prevented its induction. Confluent foreskin fibroblasts were incubated with TGF-ß2 (10 ng/ml or indicated concentrations) or ultrapure lipolysaccharide (LPS) (500 ng/ml) for 24 h or indicated periods. RNA and whole cell lysates were examined by qPCR (a, b (left panels), c) and western analysis (a, b (right panels), d). Representative immunoblots (n = 3). Band intensities, normalized for beta actin or tubulin in each lane are shown below. qPCR results, normalized with glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), are means ± SD of triplicate determinations (n = 3); *p < 0.05
Expression of A20 is rapidly and transiently induced by the prototypic TLR4 ligand LPS, and one of the best characterized roles of A20 is negative regulation of TLR signaling in an inhibitory feedback loop [6]. We had shown previously that in normal fibroblasts LPS by itself, or together with TGF-ß, elicits TLR4-dependent fibrotic responses [14]. To explore whether LPS induction of A20 is modulated by TGF-ß, fibroblasts were incubated with LPS [15], in the presence or absence of TGF-ß. While LPS enhanced A20 expression as expected, stimulation was completely abolished by pretreatment of the cultures with TGF-ß, indicating a dominant inhibitory role for TGF-ß in the regulation of basal and inducible A20 expression (Fig. 1d).
A20 abrogates TGF-ß-induced fibrotic responses in skin fibroblasts
While A20 has been convincingly implicated in negative regulation of nuclear factor (NF)-kB-mediated inflammatory responses in a variety of cell types [6, 16], its potential impact on modulating fibrotic responses in fibroblasts has not been explored. We therefore investigated the effect of A20 in transiently transfected human fibroblasts. While TGF-ß caused marked suppression of A20, confirming our earlier observations, forced expression of A20 in these cells attenuated TGF-ß-induced stimulation of collagen and α-smooth muscle actin (αSMA) gene expression and myofibroblast differentiation in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 2a-c). To investigate the mechanisms underlying these anti-fibrotic effects, we focused on canonical Smad signaling, which is recognized as a fundamental pathway driving fibrotic TGF-ß responses [2]. TGF-ß-induced rapid stimulation of Smad2 phosphorylation and nuclear localization were substantially attenuated by ectopic A20 expression in these fibroblasts (Fig. 3a and b). Moreover, transient transfection assays indicated attenuated stimulation of [SBE]4-luc activity in fibroblasts with A20 overexpression (Fig. 3c). Together, these findings demonstrate a novel function for A20 as a potent endogenous inhibitor of Smad-dependent fibrotic responses in fibroblasts.
A20 attenuates fibrotic responses elicited by transforming growth factor-ß (TGF-ß). Foreskin fibroblasts transiently transfected with A20 or empty vector were incubated with TGF-ß2 (10 ng/ml) for 24 h and harvested. RNA, whole cell lysates and media were isolated, and examined by qPCR (a) and western analysis (b). qPCR results, normalized with glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), are means ± SD of triplicate determinations (n = 3). Cgn I Type I collagen, L cell lysates, S secreted. Representative immunoblots (n = 3). Band intensities, normalized for tubulin in each lane are shown below. c Immunofluorescence confocal microscopy using antibody to αSMA (red). Nuclei identified by 6-diamidino-2-phenylindone (DAPI) (blue). Bar = 25 μm
A20 blocks intracellular canonical transforming growth factor-ß (TGF-ß)-Smad signaling. Foreskin fibroblasts transiently transfected with A20 or empty vector were incubated with TGF-ß2 (10 ng/ml) for 24 h. a Whole cell lysates were examined by western analysis (n = 2). b Immunofluorescence confocal microscopy using antibody to Smad2/3 (green color). Nuclei identified by 6-diamidino-2-phenylindone (DAPI) (blue). Bar = 25 μm. c Fibroblasts were transiently co-transfected with [SBE]4-luc and A20 (50 ng) in absence or presence of TGF-ß2 along with Renilla luciferase pRL-TK. Following a 24-h incubation, whole-cell lysates were collected and assayed for their luciferase activity. Results are means ± SD of triplicate determinations (n = 2)
Ectopic A20 attenuates LPS-induced fibrotic responses in skin fibroblasts
In light of the previously established profibrotic effects of TLR4 [14], in complementary experiments we sought to examine the modulation of these responses by A20. For this purpose, confluent fibroblasts expressing ectopic A20 were incubated with LPS and/or TGF-ß. Forced expression of A20 completely abrogated LPS-induced stimulation of type I collagen synthesis, COL1A1 and COL1A2 mRNA expression, and myofibroblast differentiation. These results indicate that A20 blocked TLR4-dependent fibrotic responses in a manner similar to its inhibitory effects on TLR4-dependent inflammation (Fig. 4). Indeed, LPS-induced stimulation of interleukin-6 (IL-6) was completely abrogated by A20.
A20 attenuates toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-dependent fibrotic responses. Fibroblasts transiently transfected with A20 or empty vector were incubated with ultrapure lipolysaccharide (LPS) and/or transforming growth factor-ß2 (TGF-ß2) (10 ng/ml). Following a 24-h incubation, RNA isolated and was examined by qPCR; results, normalized with glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), are means ± SD of triplicate determinations (n = 2)
Suppression of fibroblast A20 is associated with enhanced fibrotic responses
These results suggested that A20 might have a novel cell-autonomous negative regulatory role in fibrotic responses. To directly evaluate this possibility, we used an RNAi approach. Transfection of foreskin fibroblasts with A20 siRNA caused a substantial reduction in cellular A20 levels that was accompanied by significantly enhanced stimulation of collagen and αSMA gene expression elicited by TGF-ß (Fig. 5a and c). Moreover, A20 knockdown enhanced both LPS and TGF-ß-induced stimulation of type I collagen synthesis, COL1A1 and COL1A2 mRNA expression, and myofibroblast differentiation (Fig. 5b). These results point to a hitherto-unrecognized cell-autonomous function of A20 in repressive modulation of fibrotic responses elicited by TGF-ß or TLR4 ligands.
Fibrotic responses are negatively regulated by cellular A20. Foreskin fibroblasts were transfected with A20-specific siRNA or scrambled (Scr) control, followed by incubation with transforming growth factor-ß2 (TGF-ß2) (10 ng/ml), lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (500 ng/ml) or both for 24 h. a, b mRNA levels were determined by real-time qPCR. Results, normalized with glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), are means ± SD of triplicate determinations (n = 2). c Western analysis of secreted Type I collagen (Cgn I). ns nonspecific band
Adiponectin stimulates the expression of A20
Adipokines secreted from white adipose tissue exert pleiotropic local and hormonal effects and play key roles in regulating metabolism, inflammation and tissue repair (13). Adiponectin is unique among adipokines in that it is decreased in obese humans and experimental animals [17, 18]. Adiponectin is secreted from, and targets, not only adipocytes, but also macrophages and resident stromal cells. Transcriptional profiling in macrophages previously revealed that one of the top genes upregulated by adiponectin was A20 [15]. We had shown earlier that treatment of fibroblasts with adiponectin was associated with potent anti-fibrotic effects [19]. To investigate whether adiponectin might have an effect on modulating the expression of A20 in skin fibroblasts, confluent monolayers were incubated with recombinant full-length human adiponectin for various periods. The results showed that adiponectin treatment in these cells resulted in rapid upregulation of A20 mRNA, with increased levels as early as 15 minutes (Fig. 6). Increased A20 protein levels were detected in these cells at 3 h and were persistently elevated for up to 24 h.
Adiponectin induces A20 gene expression in fibroblasts. Foreskin fibroblasts were incubated with ultrapure lipolysaccharide (LPS) (500 ng/ml, 30 minutes) (lane 5, left panel) and/or recombinant adiponectin (APN) (10 μg/ml in left panels or as indicated in the right panel) for 0–45 minutes or as indicated. Left panel, levels of RNA determined by qPCR. Results, normalized with glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), are means ± SD of triplicate determinations (n = 2). Right panels, western analysis of whole-cell lysates. Representative immunoblots (n = 2). Band intensities, normalized for tubulin in each lane are shown below
Discussion
Persistent fibrosis in multiple organs, the hallmark of SSc, is due to excessive extracellular matrix (ECM) secretion and matrix stiffening driven by metabolically activated myofibroblasts. While growth factors and morphogens such as TGF-ß, platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and Wnt ligands have been broadly implicated in triggering fibroblast activation, the mechanism responsible for maintaining persistent activation in pathological tissue repair remain poorly understood [5]. The ubiquitin-editing enzyme A20 inhibits NF-kB-dependent responses, and alterations in its expression or function are implicated in a variety of chronic inflammatory and malignant conditions [7]. In light of the multi-ethnic genetic association of several SNPs of A20/TNFAIP3 with SSc [10, 20], the present studies sought to investigate the potential regulatory function of A20 in modulating fibroblast responses.
Our results show, for the first time, that while A20 is detectable in unstimulated skin fibroblasts, treatment with TGF-ß caused marked suppression and prevented its induction by LPS. Moreover, A20 exerted a potent cell-autonomous inhibitory effect on fibrotic gene expression, and reducing cellular A20 levels was associated with accentuated fibrotic responses and Smad2/3 activation. The results indicate that A20 is capable of antagonizing intracellular TGF-ß/Smad signaling. In light of the frequent genetic alterations in the A20 locus in SSc patients leading to altered A20 expression and/or regulatory function, our findings suggest that unchecked TGF-ß signaling and persistent fibrosis in SSc might result from impaired A20 in SSc fibroblasts. Conversely, pharmacologic rescue of A20 in SSc might restore appropriate regulation of fibrotic processes, and could therefore represent a novel approach to treatment.
A20 is a dual function ubiquitin-editing enzyme with both deubiquitinase and E3 ubiquitin ligase activities [7]. A20 is most prominently implicated in regulating the duration and intensity of inflammation, but an expanding range of biological processes is recognized as modulated by A20. By inhibiting tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF6) ubiquitin ligase, a critical node in proinflammatory signal transduction, A20 prevents recruitment of TAK1 and activation of NF-kB [16]. Additionally, A20 also has been shown to inhibit inflammatory signaling downstream of the IL-1 receptor, TNF receptor, Nod-like receptor, CD40 and most importantly, TLRs [21]. The expression of A20 is itself positively regulated by these inflammatory signals via NF-kB; thus, induction of A20 constitutes a critical negative feedback loop for NF-kB signaling.
Recent studies indicate that the deubiquitinase activity of A20 is not absolutely required for controlling NF-kB signaling [22]. A20-deficient cells show sustained NF-kB activation and enhanced inflammatory cytokine production in response to TNF and TLR ligands. Mouse models provide compelling evidence for the critical role of A20 in modulating inflammatory responses. Global deletion of A20 is associated with premature mortality due to spontaneous multi-organ inflammation [11], while partial loss in haplo-insufficient mice is associated with impaired tissue regeneration and spontaneous neuroinflammation [23, 24]. Conditional ablation of A20 in myeloid cells results in spontaneous arthritis, while ablation of A20 in dendritic cells causes autoimmune disease with lupus-like and inflammatory bowel disease features [6]. Mice with A20 ablation in keratinocytes manifest psoriasis-like epidermal hyperproliferation and disheveled hair in the absence of inflammation [25]. Several lymphoma types are associated with somatic mutations and chromosomal deletions in the TNFAIP3 locus, and show reduced A20 expression or activity [26]. Genetic studies have linked germline SNP variants to susceptibility to a variety of autoimmune and auto-inflammatory diseases along with SSc [6]. Many of these genetic variants cause reduced expression or activity of A20.
Recent studies implicate A20 in the pathogenesis of SSc. Strong association of SSc with a SNP within intron 2 (rs5029939) of A20 was found, particularly in patients with diffuse cutaneous involvement and fibrosing alveolitis [27]. In a subsequent genome-wide association study (GWAS) SSc was also associated with the non-synonymous coding variant rs2230926 [28]. This SNP, the most common A20 coding SNP identified to date in autoimmune diseases, causes a phenylalanine-to-cysteine change at residue 127, resulting in a protein with impaired NF-kB inhibitory activity [29].
In addition to the genetic evidence, further interest in the A20-SSc link comes from recent studies indicating a pathogenic role of aberrant TLR signaling in SSc [3]. The expression of both TLR4 and of its DAMP endogenous ligands is markedly enhanced in SSc skin and lung tissue [12, 30]. Moreover, TLR4 activation on stromal cells elicits sustained fibrotic signaling, and contributes to failure to resolve experimental fibrosis in mice [14]. The TLR4-dependent fibrotic response is further amplified in the presence of TGF-ß [14], suggesting a pathogenic role for the TLR4 ligand-receptor signaling axis in SSc. Computational gene network analysis showed that A20 serves as a central hub for inflammatory-fibrotic networks in skin lesions in SSc [31]. In view of the consistent genetic associations of A20 SNPs with disease susceptibility, its fundamental role in constraining TLR4 signaling, and the central location of A20 in tissue-specific gene networks in SSc, it was of substantial interest to examine expression, regulation and function of A20 in the context of fibrogenesis.
Expressed in most cell types at low or undetectable levels, A20 is induced rapidly and transiently by inflammatory signals [7]. In autoimmune diseases associated with A20 SNPs there is reduced NF-kB binding to the A20 promoter, attenuating A20 expression [32]. Epigenetic modifications such as histone acetylation or promoter methylation, might further contribute to reduced A20 expression or induction, as has been shown in peripheral blood monocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) [33] and B cell lymphoma [34]. We found that treatment of normal fibroblasts with TGF-ß resulted in time-dependent and dose-dependent repression of A20. Moreover, in the presence of TGF-ß, LPS treatment of fibroblasts failed to elicit maximal induction of A20. While the precise mechanisms underlying negative regulation of A20 by TGF-ß are currently unknown, these observations provide evidence that excessive local TGF-ß activity within the fibrotic milieu, a hallmark of SSc [35], might directly suppress A20. Future studies will be needed to precisely delineate the reciprocally antagonistic relationship between TGF-ß activity and A20 expression in SSc.
We found that A20 exerts potent negative effects on the expression of collagen, αSMA and related genes involved in fibrosis. The inhibitory response involved disruption of receptor-dependent Smad2/3 activation, the canonical signaling pathway primarily responsible for pathological fibroblast activation in fibrosis [5]. In fibroblasts overexpressing A20, stimulation with TGF-ß resulted in attenuated Smad2/3 phosphorylation, nuclear localization, and induction of Smad-dependent transcriptional responses. Therefore, there appears to be a reciprocal negative cross-regulatory relationship between TGF-ß and A20, with TGF-ß suppressing basal and inducible A20 expression, and A20 blocking Smad-dependent fibrotic responses.
We had shown previously that LPS exerts TLR4-dependent profibrotic effects mediated, at least in part, through suppressing miR29, which is an endogenous negative regulator of fibrotic responses (14). It is noteworthy that miR29 itself augments A20 expression, due to its competition with the RNA-degrading HuR and prevention of HuR-mediated transcript decay [36]. Whether A20 modulates the regulation of miR29, and if such regulation might be potentially implicated in the anti-fibrotic effects of A20, remain to be investigated. RNAi experiments indicated that A20 plays a cell-autonomous negative regulatory role in fibrotic gene expression, and in preventing excessive or prolonged stimulation of these genes in response to TGF-ß. It is of interest, in this regard, that mice with global A20 deletion were found to have a scleroderma-like phenotype with marked thickening of the dermis and disappearance of the intradermal white adipose tissue [11]. These findings, consistent with unchecked activation of dermal fibroblasts, are pathological hallmarks of lesional skin changes in SSc [1]. In view of these observations, we propose that enhancing A20 expression or activity in fibroblasts might be a potential approach to limiting excessive fibrotic signaling elicited by TGF-ß, and perhaps by other fibrotic stimuli such as Wnt/ß-catenin [37]. In this regard, it is of great interest that adiponectin, which has both anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic activity [18], elicited sustained A20 induction in fibroblasts. Augmentation of A20 is likely to account for the mitigation by adiponectin of TLR4-mediated inflammatory and oxidative responses. While it is currently unknown how adiponectin induces A20, and whether endogenous A20 contributes to the anti-fibrotic effects elicited by adiponectin, therapeutic targeting of the adiponectin-A20 axis using peptide agonists of the AdipoR1/R2 adiponectin receptors, might be feasible [38].
Taken together, the present findings identify a potentially important novel regulatory role for A20, a pervasive genetic risk for SSc susceptibility, in connective tissue homeostasis and fibrosis. Our results also establish a potential mechanism for controlling A20 expression by TGF-ß, which represses A20 in fibroblasts and prevents A20 induction via TLR4. Moreover, the results indicate that A20 mitigates fibrotic responses induced by TGF-ß, and through TLR4 activation, while A20 appears to be important as a cell-autonomous mechanism for restraining the amplitude or duration of fibrotic signaling. These findings implicate A20 as a critical endogenous rheostat for fibroblast activation and of cutaneous fibrogenesis.
Appropriate induction of A20 in the skin is likely to be important in maintaining tight spatial and temporal regulation of fibrotic gene responses during wound healing, and a protective role in limiting excessive scar formation. These findings are broadly in line with a growing recognition of A20 as a pleiotropic guardian of tissue homeostasis by virtue of its combined anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, anti-oxidant and anti-fibrotic/pro-regenerative activities [39]. Augmenting A20 expression or function of A20 within injured tissue microenvironments might limit ongoing fibrogenic signaling, attenuate fibrosis and promote regeneration. Accordingly, pharmacologic agents that induce A20 expression such as vitamin E (γ-tocotrienol) and MALT inhibitors, along with adiponectin, hold promise as anti-fibrotic therapies via restoring endogenous A20 expression, particularly when targeted in a tissue-restricted manner, such as topical application to the skin.
Conclusions
The present findings identify an important novel physiologic role for the cytosolic deubiquitinase A20 in fibrosis. Our results also establish a mechanism for controlling A20 expression by TGF-ß, which represses A20 in fibroblasts and prevents induction via TLR4. Furthermore, the results indicate that A20 alleviates fibrotic responses induced by TGF-ß, and through TLR4. These finding altogether implicate A20 as a critical cell-intrinsic modulator of fibroblast activation and of cutaneous fibrogenesis. Induction of A20 is likely to serve an important function in physiologic regulation of cutaneous fibrosis gene responses during wound healing. Impaired A20 expression or function due to genetic variants, epigenetic modulation and/or environmental influences might contribute directly to the development or progression of fibrosis in SSc, and represents a promising target for therapy.
References
Varga J, Abraham D. Systemic sclerosis: a prototypic multisystem fibrotic disorder. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(3):557–67.
Varga J, Pasche B. Transforming growth factor beta as a therapeutic target in systemic sclerosis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009;5(4):200–6.
Bhattacharyya S, Varga J. Emerging roles of innate immune signaling and toll-like receptors in fibrosis and systemic sclerosis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2015;17(1):474.
Mills KH. TLR-dependent T, cell activation in autoimmunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11(12):807–22.
Bhattacharyya S, Wei J, Varga J. Understanding fibrosis in systemic sclerosis: shifting paradigms, emerging opportunities. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(1):42–54.
Hamerman JA, Pottle J, Ni M, He Y, Zhang ZY, Buckner JH. Negative regulation of TLR signaling in myeloid cells-implications for autoimmune diseases. Immunol Rev. 2016;269(1):212–27.
Ma A, Malynn BA. A20: linking a complex regulator of ubiquitylation to immunity and human disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12(11):774–85.
Koumakis E, Giraud M, Dieude P, Cohignac V, Cuomo G, Airo P, Hachulla E, Matucci-Cerinic M, Diot E, Caramaschi P, et al. Brief report: candidate gene study in systemic sclerosis identifies a rare and functional variant of the TNFAIP3 locus as a risk factor for polyautoimmunity. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(8):2746–52.
Mayes MD, Bossini-Castillo L, Gorlova O, Martin JE, Zhou X, Chen WV, Assassi S, Ying J, Tan FK, Arnett FC, et al. Immunochip analysis identifies multiple susceptibility loci for systemic sclerosis. Am J Hum Genet. 2014;94(1):47–61.
Korman BD, Criswell LA. Recent advances in the genetics of systemic sclerosis: toward biological and clinical significance. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2015;17(3):21.
Lee EG, Boone DL, Chai S, Libby SL, Chien M, Lodolce JP, Ma A. Failure to regulate TNF-induced NF-kappaB and cell death responses in A20-deficient mice. Science. 2000;289(5488):2350–4.
Bhattacharyya S, Tamaki Z, Wang W, Hinchcliff M, Hoover P, Getsios S, White ES, Varga J. Fibronectin EDA promotes chronic cutaneous fibrosis through Toll-like receptor signaling. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6(232):232ra250.
Bhattacharyya S, Fang F, Tourtellotte W, Varga J. Egr-1: new conductor for the tissue repair orchestra directs harmony (regeneration) or cacophony (fibrosis). J Pathol. 2013;229(2):286–97.
Bhattacharyya S, Kelley K, Melichian DS, Tamaki Z, Fang F, Su Y, Feng G, Pope RM, Budinger GR, Mutlu GM, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 signaling augments transforming growth factor-beta responses: a novel mechanism for maintaining and amplifying fibrosis in scleroderma. Am J Pathol. 2013;182(1):192–205.
Folco EJ, Rocha VZ, Lopez-Ilasaca M, Libby P. Adiponectin inhibits pro-inflammatory signaling in human macrophages independent of interleukin-10. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(38):25569–75.
Catrysse L, Vereecke L, Beyaert R, van Loo G. A20 in inflammation and autoimmunity. Trends Immunol. 2014;35(1):22–31.
Ouchi N, Parker JL, Lugus JJ, Walsh K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11(2):85–97.
Wang ZV, Scherer PE. Adiponectin, the past two decades. Mol Cell Biol. 2016;8(2):93-100. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjw011. Epub 2016 Mar 18.
Fang F, Liu L, Yang Y, Tamaki Z, Wei J, Marangoni RG, Bhattacharyya S, Summer RS, Ye B, Varga J. The adipokine adiponectin has potent anti-fibrotic effects mediated via adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase: novel target for fibrosis therapy. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(5):R229.
Bossini-Castillo L, Lopez-Isac E, Mayes MD, Martin J. Genetics of systemic sclerosis. Semin Immunopathol. 2015;37(5):443–51.
Boone DL, Turer EE, Lee EG, Ahmad RC, Wheeler MT, Tsui C, Hurley P, Chien M, Chai S, Hitotsumatsu O, et al. The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat Immunol. 2004;5(10):1052–60.
De A, Dainichi T, Rathinam CV, Ghosh S. The deubiquitinase activity of A20 is dispensable for NF-kappaB signaling. EMBO Rep. 2014;15(7):775–83.
Studer P, da Silva CG, Revuelta Cervantes JM, Mele A, Csizmadia E, Siracuse JJ, Damrauer SM, Peterson CR, Candinas D, Stroka DM, et al. Significant lethality following liver resection in A20 heterozygous knockout mice uncovers a key role for A20 in liver regeneration. Cell Death Differ. 2015;22(12):2068–77.
Guedes RP, Csizmadia E, Moll HP, Ma A, Ferran C, da Silva CG. A20 deficiency causes spontaneous neuroinflammation in mice. J Neuroinflammation. 2014;11:122.
Lippens S, Lefebvre S, Gilbert B, Sze M, Devos M, Verhelst K, Vereecke L, Mc Guire C, Guerin C, Vandenabeele P, et al. Keratinocyte-specific ablation of the NF-kappaB regulatory protein A20 (TNFAIP3) reveals a role in the control of epidermal homeostasis. Cell Death Differ. 2011;18(12):1845–53.
Kato M, Sanada M, Kato I, Sato Y, Takita J, Takeuchi K, Niwa A, Chen Y, Nakazaki K, Nomoto J, et al. Frequent inactivation of A20 in B-cell lymphomas. Nature. 2009;459(7247):712–6.
Dieude P, Guedj M, Wipff J, Ruiz B, Riemekasten G, Matucci-Cerinic M, Melchers I, Hachulla E, Airo P, Diot E, et al. Association of the TNFAIP3 rs5029939 variant with systemic sclerosis in the European Caucasian population. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(11):1958–64.
Martin JE, Assassi S, Diaz-Gallo LM, Broen JC, Simeon CP, Castellvi I, Vicente-Rabaneda E, Fonollosa V, Ortego-Centeno N, Gonzalez-Gay MA, et al. A systemic sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus pan-meta-GWAS reveals new shared susceptibility loci. Hum Mol Genet. 2013;22(19):4021–9.
Bossini-Castillo L, Lopez-Isac E, Martin J. Immunogenetics of systemic sclerosis: Defining heritability, functional variants and shared-autoimmunity pathways. J Autoimmun. 2015;64:53–65.
Bhattacharyya S, Wang W, Morales-Nebreda L, Feng G, Wu M, Zhou X, Lafyatis R, Lee J, Hinchcliff M, Feghali-Bostwick C, et al. Tenascin-C drives persistence of organ fibrosis. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11703.
Mahoney JM, Taroni J, Martyanov V, Wood TA, Greene CS, Pioli PA, Hinchcliff ME, Whitfield ML. Systems level analysis of systemic sclerosis shows a network of immune and profibrotic pathways connected with genetic polymorphisms. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015;11(1), e1004005.
Wang S, Wen F, Tessneer KL, Gaffney PM. TALEN-mediated enhancer knockout influences TNFAIP3 gene expression and mimics a molecular phenotype associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Genes Immun. 2016;17(3):165–70.
Li D, Wang L, Fan Y, Song L, Guo C, Zhu F, Zhang L, Shi Y. Down-regulation of A20 mRNA expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Immunol. 2012;32(6):1287–91.
Hymowitz SG, Wertz IE. A20: from ubiquitin editing to tumour suppression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10(5):332–41.
Sargent JL, Milano A, Bhattacharyya S, Varga J, Connolly MK, Chang HY, Whitfield ML. A TGFbeta-responsive gene signature is associated with a subset of diffuse scleroderma with increased disease severity. J Invest Dermatol. 2010;130(3):694–705.
Balkhi MY, Iwenofu OH, Bakkar N, Ladner KJ, Chandler DS, Houghton PJ, London CA, Kraybill W, Perrotti D, Croce CM, et al. miR-29 acts as a decoy in sarcomas to protect the tumor suppressor A20 mRNA from degradation by HuR. Sci Signal. 2013;6(286):ra63.
Shao L, Oshima S, Duong B, Advincula R, Barrera J, Malynn BA, Ma A. A20 restricts wnt signaling in intestinal epithelial cells and suppresses colon carcinogenesis. PLoS One. 2013;8(5), e62223.
Fang F, Marangoni MR, Zhou X, Hong W, Ye B, Yoshihide A, Sato S, Masui Y, Zhang C, Lakota K, Wei J, Hinchcliff ME, Scherer P, Otvos L, Varga J. Adiponectin is an endogenous anti-fibrotic and target in systemic sclerosis: novel link between fibrosis and metabolism. ACR. 2014.
da Silva CG, Minussi DC, Ferran C, Bredel M. A20 expressing tumors and anticancer drug resistance. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;809:65–81.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Northwestern University Imaging Core for excellent technical support, and Drs Christian Stehlik and Warren Tourtellotte for helpful discussions.
Funding
Supported by grants from the NIH (AR42309 and AR064925 to JV, AR060710 to LG) and the Scleroderma Foundation (to SB).
Availability of data and materials
Supplemental data will be available.
Authors’ contributions
SB and JV conceived the project, designed experiments, interpreted and drafted the manuscript. WW, SB, and LG performed the major experiments, data acquisition and statistical analysis. WW and LG helped to revise the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Yes.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional file
Additional file 1: Figure S1.
TGF-ß suppresses A20 expression in adult skin fibroblasts. Confluent adult skin fibroblasts were incubated with TGF-ß2 (10 ng/ml) for indicated time-points. A RNA was examined by qPCR. Results, normalized with GAPDH, are means ± SD of triplicate determinations (n = 2). B Western analysis of whole-cell lysates. Representative immunoblots (n = 2). Band intensities, normalized for beta actin in each lane are shown below (PDF 50 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhattacharyya, S., Wang, W., Graham, L.V.D. et al. A20 suppresses canonical Smad-dependent fibroblast activation: novel function for an endogenous inflammatory modulator. Arthritis Res Ther 18, 216 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-016-1118-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-016-1118-7