Abstract
Background
Iodine is important for thyroid hormone synthesis, and iodine deficiency in pregnancy may impair fetal neurological development. As perchlorate and thiocyanate inhibit sodium-iodide symporter reducing the transport of iodine from circulation into the thyroid follicular cells, environmental exposure to these substances in pregnancy may impair maternal thyroid hormone synthesis. We aimed to explore the impact of perchlorate and thiocyanate exposure on thyroid status in a cohort of pregnant mothers from South West England.
Methods
Urine samples were obtained from 308 women participating in a study of breech presentation in late pregnancy. They had no known thyroid disease and a singleton pregnancy at 36–38 weeks gestation. Samples were analysed for urinary concentrations of iodine (UIC), perchlorate (UPC) and thiocyanate (UTC). Blood samples were taken for free T4 (FT4), thyrotropin (TSH) and thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPO-Ab). Baseline data included age, parity, smoking status, ethnicity and BMI at booking. Following delivery, data on offspring’s sex, gestational age at birth and birthweight were collected.
Results
Participants had a mean (SD) age 31 (5) years, median (IQR) BMI 24.4 (22.0, 28.3) kg/m2, 42% were primiparous, 10% were smokers, and 96% were Caucasian. Median UIC was 88 μg/l, and 174/308 (57%) women had UIC < 100 μg/l. Log transformed UPC negatively correlated with FT4, but not with TSH, in the whole cohort (r = − 0.12, p = 0.03) and in the subgroup of women with UIC < 100 μg/l (r = − 0.15, p = 0.04). Regression analysis with the potential confounders (TPO-Ab status, UIC and UTC) identified UPC to be negatively associated with FT4 (p = 0.01). There was no correlation between UTC and FT4 or TSH. Maternal UPC or UTC was not associated with offspring birthweight.
Conclusion
Environmental perchlorate exposure is negatively associated with circulating FT4 levels in third trimester pregnant women. This may have an adverse impact on neurocognitive development of the fetus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Optimal level of maternal thyroid hormone in pregnancy is important for fetal neurological development, and as iodine is an essential component of thyroid hormone, iodine deficiency in pregnancy may impair fetal neurological development [1]. In recent years, there has been increasing concern that exposure to environmental pollutants during pregnancy may result in reduced maternal thyroid hormone synthesis affecting fetal neurodevelopment [2, 3].
Perchlorate and thiocyanate are common environmental pollutants that can disrupt normal thyroid function by reducing the uptake of iodine from the circulation into the thyroid follicular cells through competitive inhibition at the sodium-iodide symporter [2]. Perchlorate can be found in water, milk and some food crops, including green leafy vegetables and fruits. It was found to be present in 77 out of 342 food items tested in the UK between 2014 and 15 [4]. It is also present in fertilisers, rocket fuels, explosives, fireworks, road flares and air bags. Cigarette smoke is the main source of thiocyanate, but it can also be found in some vegetables of the Cruciferae family, such as cabbage, broccoli and cauliflower. Perchlorate is about 15 times stronger than thiocyanate as an inhibitor of the sodium-iodide symporter [5], and in pharmacological doses is known to suppress thyroid hormone synthesis [2]. However, there is a concern that even a low-level exposure of perchlorate or thiocyanate could disrupt thyroid hormone synthesis, particularly in the presence of iodine deficiency. This could lead to health hazards that may be more pronounced in vulnerable populations, such as pregnant women. Several studies have examined the effect of perchlorate and thiocyanate exposure during pregnancy on maternal thyroid function, however these showed conflicting results, and the potential adverse impact of exposure remains controversial [6,7,8,9,10,11,12].
Therefore, we aimed to study the impact of perchlorate and thiocyanate exposure on thyroid function of pregnant mothers from South West England where iodine deficiency has been shown to be common [13].
Methods
Participants
We studied 308 women participating in a study of breech presentation in late pregnancy [14]. They were recruited during routine antenatal care at the Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital (RD&E), a secondary care hospital in South-West England serving a population of about 450,000. They had a singleton pregnancy at 36–38 weeks gestation. They had no known thyroid disease, and were not on any drugs which may affect thyroid function. We collected baseline clinical data (including age, parity, smoking status, ethnicity and body mass index (BMI) at booking), and blood and spot urine samples from the participants. Following delivery, we collected data on sex, gestational age at birth and birth-weight of the babies; these data were unavailable for one baby as their mother moved away out of area before delivery.
Sample analysis
Blood samples were analysed at the RD&E Blood Sciences department for serum thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), free thyroxine (FT4) and thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPO-Ab) using the electrochemiluminescent immunoassay, run on the Modular E170 Analyser (Roche, Burgess Hill, UK). Intra-assay coefficients of variations were < 5.3% for both TSH and FT4. The manufacturer’s population reference ranges were: TSH 0.35–4.5 mIU/l and FT4 11–24 pmol/l. Serum TPO-Ab titre above 34 IU/l was considered positive.
Urine samples were analysed for iodine, perchlorate, and thiocyanate concentration using ion chromatography-mass spectrometry at the Iodine Research Laboratory (Boston University, Boston, Massachusetts) [15]. The inter-assay coefficient of variation ranges from 3.1–8.2% for the three analytes.
Statistical analysis
We assessed variables for normal distribution and log transformed (log) where appropriate. Where this did not result in a normal distribution, these data are presented as median (IQR). Correlations between two variables were assessed and results presented as Pearson correlation coefficients. Regression analysis was undertaken to identify independent predictors of thyroid status. As iodine deficiency may aggravate the effect of perchlorate and thiocyanate exposure, we also carried out subgroup analyses in women with urinary iodine concentration (UIC) less than 100 μg/l.
We analysed correlations between offspring birthweight (corrected for sex and gestational age at birth) and maternal urinary perchlorate concentration (UPC) and urinary thiocyanate concentration (UTC). We also carried out subgroup analyses considering birthweight (corrected for gestational age) of male and female infants separately.
With a sample size of 300, we can detect correlation coefficients r ≥ 0.12 as statistically significant at p < 0.05.
Statistical analysis was undertaken using SPSS (version 22).
Results
Baseline characteristics
Baseline clinical characteristics and thyroid function of the 308 participants are shown in Table 1. Ninety-six percent were Caucasian. The median UIC was 88 μg/l [13]. Fifty-seven percent (174 out of 308) women had UIC below 100 μg/l. The median UPC was 2.1 μg/l (IQR 1.4–3.8, range 0.3–143), and the median UTC was 436 μg/l (IQR 302–683, range 29–3290).
Correlation between urinary perchlorate and maternal thyroid status
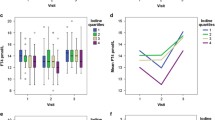
Log UPC was negatively correlated with FT4 (r = − 0.12, p = 0.03) but not with log TSH (r = − 0.01, p = 0.9) (Fig. 1, Panels a and b). In the subgroup of women with UIC less than 100 μg/l, log UPC remained negatively correlated with FT4 (r = − 0.15, p = 0.04) but not with log TSH.
Correlation between urinary thiocyanate and maternal thyroid status
There was no correlation between log UTC and FT4 (r = 0.08, p = 0.15) or log TSH (r = − 0.08, p = 0.17) (Fig. 1, Panels c and d). Likewise, in the subgroup of women with UIC less than 100 μg/l, there was no correlation between log UTC and FT4 (r = 0.08, p = 0.17) or log TSH (r = − 0.08, p = 0.17).
Multivariate analysis to assess the impact of potential confounders
We carried out multiple regression analysis to assess the impact of potential confounders (TPO-Ab, UIC, UPC and UTC). Maternal smoking was not included in the regression analysis because of its collinearity with thiocyanate levels (significant correlation between maternal smoking and log UTC, r = 0.4, p < 0.001). The regression analysis showed that only log UPC was significantly independently associated with FT4, with higher UPC associated with lower serum FT4 (β = − 0.29, 95% CI -0.52 to − 0.07, p = 0.01) (Table 2). The addition of smoking to the multivariable regression analysis did not change the association. The regression coefficient (β) of − 0.29 suggests that for every 10% increase in UPC, there will be a 0.03 pmol/l decrease in serum FT4.
Only TPO Ab positive was an independent predictor of serum TSH (Table 2). UPC or UTC was not an independent predictor of serum TSH.
The multiple regression analysis in the subgroup of women with UIC less than 100 μg/l also showed that log UPC was borderline significantly independently associated with serum FT4, with higher UPC associated with lower serum FT4 (β = − 0.33, 95% CI -0.66 to 0.001, p = 0.05) (Table 3). UPC or UTC was not an independent predictor of serum TSH.
Effect of maternal perchlorate and thiocyanate exposure on offspring birthweight
There was no correlation between maternal UPC and offspring birthweight (r = − 0.07, p = 0.2 for the whole cohort; r = − 0.04, p = 0.6 for the subgroup of women with UIC less than 100 μg/l) or between maternal UTC and infant birthweight (r = 0, p = 1.0 for the whole cohort; r = 0.03, p = 0.7 for the subgroup of women with UIC less than 100 μg/l). Subgroup analyses using birthweight (corrected for gestational age) of male and female infants separately also failed to show association between offspring birthweight and maternal UPC (r = − 0.09, p = 0.3) or maternal UTC (r = 0.09, p = 0.3).
Discussion
Our study has shown that environmental exposure to perchlorate and thiocyanate is ubiquitous and the exposure to perchlorate is associated with lower circulating FT4 levels in third trimester pregnant women. We did not identify an association between exposure to thiocyanate in pregnancy and maternal thyroid hormone. Maternal exposure of perchlorate or thiocyanate was not associated with offspring’s birthweight.
Previous studies examining association between perchlorate exposure and maternal thyroid function in pregnancy have shown inconsistent results (Table 4). Although some studies [6,7,8, 12] found no association between UPC and maternal thyroid function, others have shown that UPC is associated with low maternal FT4 and/or high TSH [9,10,11]. Possible reasons for the discrepant results include diverse study populations, different iodine status, and variable gestational age at the time of perchlorate and thyroid function assessment. In our study, there was a 0.03 pmol/L decrease in maternal serum FT4 level with every 10% increase in UPC, providing additional evidence to support the association between perchlorate exposure and reduced maternal thyroid hormone levels. This is in keeping with observations outside pregnancy, where perchlorate exposure has been shown to be associated with decreased FT4 in the general population, including non-pregnant women and adolescent girls [16, 17].
The association between perchlorate exposure during pregnancy and reduced maternal serum FT4 could potentially have important clinical implications as maternal thyroid hormone insufficiency has been shown to be associated with impaired neurocognitive development of offspring and other adverse obstetric outcomes [18, 19]. In a recent study, pregnant women with subclinical hypothyroidism or hypothyroxinaemia and UPC in the upper 10% were found to have a 3-fold increased odds of having offspring with an intelligence quotient (IQ) in the lowest 10% at age of 3 years [20]. However, UPC was not associated with maternal thyroid hormone status in this cohort. Therefore, the mechanism for the association between maternal perchlorate exposure and reduced offspring IQ in this study remains uncertain although it may be due to the effect of perchlorate exposure on fetal thyroid function [20]. Another recent study has suggested that maternal perchlorate exposure in pregnancy could also affect obstetric outcomes, with maternal perchlorate exposure associated with increased birthweight in male infants, particularly in infants born prematurely [21]. However there was no assessment of maternal thyroid function in the cohort; therefore it is uncertain whether the association seen was mediated through changes in maternal thyroid hormone levels. Our study was unable to confirm the association between maternal perchlorate exposure and offspring birthweight in the whole cohort as well as in the subgroup of male infants. This is in keeping with a previous study which also found no association between perchlorate exposure in pregnancy and offspring’s birthweight, birth length or gestational age at birth [22]. However, taken together, these observations highlight the need for further investigations to examine whether environmental exposure to perchlorate during pregnancy has adverse health outcomes beyond minor changes on maternal thyroid hormone levels.
In contrast to our findings on perchlorate exposure, we were unable to show an association between thiocyanate exposure and maternal thyroid hormone levels. This may be because thiocyanate is a much weaker inhibitor of sodium-iodine symporter as compared to perchlorate [5]. However, a small number of previous studies have suggested potential effects of thiocyanate exposure on maternal thyroid status [6, 8, 9] (Table 5). Furthermore, it is also possible that co-exposure of thiocyanate with other environmental pollutants have more deleterious impact on maternal thyroid function than exposure to an individual pollutant [10].
We acknowledge several limitations of the study: urinary iodine, perchlorate and thiocyanate concentrations were measured on a single spot urine sample, and thyroid hormone assessments were carried out only once. Our cohort was predominantly Caucasian, from South West England, thereby limiting generalisability.
Conclusions
This study provides further evidence that environmental perchlorate exposure is associated lower circulating serum FT4 levels in pregnant women. This may have an adverse impact on neurocognitive development of the fetus and other pregnancy outcomes.
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- FT4:
-
Free thyroxine
- IQ:
-
Intelligence quotient
- IQR:
-
Inter-quartile range
- RD&E:
-
Royal Devon & Exeter hospital
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- TPO-Ab:
-
Thyroid peroxidase antibodies
- TSH:
-
Thyroid stimulating hormone
- UIC:
-
Urinary iodine concentration
- UPC:
-
Urinary perchlorate concentration
- UTC:
-
Urinary thiocyanate concentration
References
Pearce EN, Lazarus JH, Moreno-Reyes R, Zimmermann MB. Consequences of iodine deficiency and excess in pregnant women: an overview of current knowns and unknowns. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016;104(Suppl 3):918S–23S.
Pearce EN, Braverman LE. Environmental pollutants and the thyroid. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;23(6):801–13.
Boas M, Feldt-Rasmussen U, Main KM. Thyroid effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012;355(2):240–8.
The UK Food Standards Agency. An investigation of perchlorate levels in fruit and vegetables consumed in the UK (2016). [https://www.food.gov.uk/sites/default/files/fera-perchlorate-levels-report.pdf] (Accessed 23 Apr 2018).
Tonacchera M, Pinchera A, Dimida A, Ferrarini E, Agretti P, Vitti P, Santini F, Crump K, Gibbs J. Relative potencies and additivity of perchlorate, thiocyanate, nitrate, and iodide on the inhibition of radioactive iodide uptake by the human sodium iodide symporter. Thyroid. 2004;14(12):1012–9.
Pearce EN, Lazarus JH, Smyth PP, He X, Dall'amico D, Parkes AB, Burns R, Smith DF, Maina A, Bestwick JP, et al. Perchlorate and thiocyanate exposure and thyroid function in first-trimester pregnant women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;95(7):3207–15.
Pearce EN, Spencer CA, Mestman JH, Lee RH, Bergoglio LM, Mereshian P, He X, Leung AM, Braverman LE. Effect of environmental perchlorate on thyroid function in pregnant women from Cordoba, Argentina, and Los Angeles, California. Endocr Pract. 2011;17(3):412–7.
Pearce EN, Alexiou M, Koukkou E, Braverman LE, He X, Ilias I, Alevizaki M, Markou KB. Perchlorate and thiocyanate exposure and thyroid function in first-trimester pregnant women from Greece. Clin Endocrinol. 2012;77(3):471–4.
Charatcharoenwitthaya N, Ongphiphadhanakul B, Pearce EN, Somprasit C, Chanthasenanont A, He X, Chailurkit L, Braverman LE. The association between perchlorate and thiocyanate exposure and thyroid function in first-trimester pregnant Thai women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(7):2365–71.
Horton MK, Blount BC, Valentin-Blasini L, Wapner R, Whyatt R, Gennings C, Factor-Litvak P. CO-occurring exposure to perchlorate, nitrate and thiocyanate alters thyroid function in healthy pregnant women. Environ Res. 2015;143(Pt A):1–9.
Steinmaus C, Pearl M, Kharrazi M, Blount BC, Miller MD, Pearce EN, Valentin-Blasini L, DeLorenze G, Hoofnagle AN, Liaw J. Thyroid hormones and moderate exposure to perchlorate during pregnancy in women in Southern California. Environ Health Perspect. 2016;124(6):861–7.
Mortensen ME, Birch R, Wong LY, Valentin-Blasini L, Boyle EB, Caldwell KL, Merrill LS, Moye J Jr, Blount BC. Thyroid antagonists and thyroid indicators in U.S. pregnant women in the vanguard study of the National Children’ study. Environ Res. 2016;149:179–88.
Knight BA, Shields BM, He X, Pearce EN, Braverman LE, Sturley R, Vaidya B. Iodine deficiency amongst pregnant women in south-West England. Clin Endocrinol. 2017;86(3):451–5.
Knight BA, Shields BM, Sturley R, Vaidya B. Maternal thyroid function in pregnant women with a breech presentation in late gestation. Clin Endocrinol. 2016;85(2):320–2.
Valentin-Blasini L, Mauldin JP, Maple D, Blount BC. Analysis of perchlorate in human urine using ion chromatography and electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2005;77(8):2475–81.
McMullen J, Ghassabian A, Kohn B, Trasande L. Identifying subpopulations vulnerable to the thyroid-blocking effects of perchlorate and thiocyanate. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102(7):2637–45.
Suh M, Abraham L, Hixon JG, Proctor DM. The effects of perchlorate, nitrate, and thiocyanate on free thyroxine for potentially sensitive subpopulations of the 2001-2002 and 2007-2008 National Health and nutrition examination surveys. J Exposure Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2014;24(6):579–87.
Thompson W, Russell G, Baragwanath G, Matthews J, Vaidya B, Thompson-Coon J. Maternal thyroid hormone insufficiency during pregnancy and risk of neurodevelopmental disorders in offspring: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Endocrinol. 2018;88(4):575–84.
Korevaar TIM, Medici M, Visser TJ, Peeters RP. Thyroid disease in pregnancy: new insights in diagnosis and clinical management. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13(10):610–22.
Taylor PN, Okosieme OE, Murphy R, Hales C, Chiusano E, Maina A, Joomun M, Bestwick JP, Smyth P, Paradice R, et al. Maternal perchlorate levels in women with borderline thyroid function during pregnancy and the cognitive development of their offspring: data from the controlled antenatal thyroid study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(11):4291–8.
Rubin R, Pearl M, Kharrazi M, Blount BC, Miller MD, Pearce EN, Valentin-Blasini L, DeLorenze G, Liaw J, Hoofnagle AN, et al. Maternal perchlorate exposure in pregnancy and altered birth outcomes. Environ Res. 2017;158:72–81.
Evans KA, Rich DQ, Weinberger B, Vetrano AM, Valentin-Blasini L, Strickland PO, Blount BC. Association of prenatal perchlorate, thiocyanate, and nitrate exposure with neonatal size and gestational age. Reprod Toxicol. 2015;57:183–9.
Acknowledgements
Authors wish to thank the participants, and the midwives of Royal Devon & Exeter Hospital for their help in the recruitment of these study participants.
Funding
This study was funded by the Small Grants Scheme of the Research & Development Department, Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital NHS Foundation Trust. BAK and BMS are funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) as core members of the NIHR Exeter Clinical Research Facility. This article presents independent research supported by the NIHR Exeter Clinical Research Facility. The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BAK, BMS, RS and BV designed the study; XH, ENP and LEB were involved in the analysis of urinary iodine, perchlorate and thiocyanate; BAK and BMS carried out statistical analyses; BAK and BV wrote first draft; all authors reviewed, commented and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the National Research Ethics Service (NRES) Committee South West – Exeter, and all participants gave informed written consent.
Consent for publication
All authors provide consent for this publication.
Competing interests
LEB and ENP have received research funding from Sociedad Química y Minera de Chile.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Knight, B.A., Shields, B.M., He, X. et al. Effect of perchlorate and thiocyanate exposure on thyroid function of pregnant women from South-West England: a cohort study. Thyroid Res 11, 9 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13044-018-0053-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13044-018-0053-x