Abstract
Background
Taiwan has been considered free from canine parvovirus type 2c (CPV-2c) based on the last report of canine parvovirus type 2 (CPV-2) surveillance. However, since January 2015, the first report of CPV-2c in a puppy has occurred in Taiwan. There is currently limited information about the CPV-2c variant in Taiwan. In the present study, we characterized the previously unidentified CPV-2c variant and investigated the distribution of CPV-2 variants in Taiwan.
Methods
During January 2014 to April 2016, fecal or rectal swab samples from 99 dogs with suspected CPV-2 infection in Taiwan were collected. Eighty-eight were identified as being either CPV-2a, −2b or -2c variants positive by real-time PCR and sequence analysis.
Results
Sequence analysis of the 88 isolates confirmed CPV-2c as the dominant variant (54.6 %), followed by CPV-2b (26.1 %) and CPV-2a (19.3 %). Phylogenetic analysis demonstrated that the recent CPV-2c variants are similar to the Chinese CPV-2c strain but can be considered as novel Asian CPV-2c isolates.
Conclusion
The present study provides evidence for the existence of a novel CPV-2c variant in Taiwan.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Canine parvovirus type 2c (CPV-2c) was first detected in Italy in 2000 [1]. Antigenic differences among CPV-2a, −2b, and -2c are observed only in residue 426 (Asn in 2a, Asp in 2b, and Glu in 2c) [2], which is located in the major VP2 antigenic site of the parvovirus [3]. The functions of capsid protein VP2 include facilitating receptor binding, controlling host range [4], and eliciting neutralizing antibodies [3]. Although CPV-2c infection results in almost the same clinical signs as for CPV-2a and CPV-2b, including anorexia, vomiting, acute gastroenteritis, and hemorrhagic diarrhea, infection by CPV-2c has been reported to be indicative of a more severe disease [5, 6].
A retrospective analysis revealed that the oldest CPV-2c strain was identified in Germany in 1996 [7]. Another retrospective analysis revealed that the frequency of CPV-2 variants underwent rapid fluctuation in Italy between 1995 and 2005, with CPV-2c very rapidly replacing CPV-2b [8]. CPV-2c infection has not only been observed in Italy, but it is also widely distributed in other European countries [7, 9, 10], including Germany, Portugal [11], Spain [12], Belgium, France, Greece [13], Bulgaria [14], Sweden [15], Turkey [16], and the United Kingdom. In recent years, CPV-2c has also been found to be widespread in Tunisia [17], the USA [18], Uruguay [19], Brazil [20], Argentina [21], Ecuador [5], Mexico [22], and Morocco [23]. Surprisingly, since the first reported finding in Vietnam in 2004, the CPV-2c variant has not been prevalent in Asia [24]. Indeed, only a few CPV-2c strains have been isolated in India [25] and China [26–28], with either CPV-2a or -2b being prevalent in Asian countries thus far [25–27, 29–42].
In Taiwan, as in other Asian countries, both the CPV-2a and -2b genotypes constitute the prevalent CPV-2 field strains circulating in the last two decades [30, 31, 39, 41]. Before the present study, no report indicated the occurrence of a CPV-2c variant in Taiwan [30, 31, 39, 41]. However, in January 2015, the first report of CPV-2c in a puppy in Taiwan occurred, and there is to date limited information about the CPV-2c variant in Taiwan. In the present study, we examined this CPV-2c variant and investigated the distribution of CPV-2 variants in Taiwan.
Methods
Specimen collection
Clinical specimens (feces and/or rectal swab) were collected from 99 dogs with suspected CPV-2 infection from northern, central, southern, and eastern Taiwan from January 2014 to April 2016. These samples were mainly acquired from dogs with diarrhea and/or bloody diarrhea. The year of sampling and the age, clinical history, and CPV-2 types of the sampled dogs are summarized in Additional file 1.
CPV-2 screening and partial VP2 gene amplification
Viral DNA was extracted from the clinical samples (either feces or rectal swab) and screened for CPV-2 by real-time PCR, as described by Lin et al. [43]. Samples showing positive results for either type of specimen were included in this study. The partial VP2 gene of CPV-2 was amplified by PCR, as described by Buonavoglia et al. [1], and the DNA fragments were purified and sequenced as described by Lin et al. [41].
Sequence and phylogenetic analyses
The VP2 DNA sequences of our samples were compared to those of reference FPV (M38246), CPV-2 (M38245), CPV-2a (M24003), CPV-2b (M74849), new CPV-2a (JX048605), new CPV-2b (JX048607), and CPV-2c (JF414818, JF414820, JF414822, FJ005247, GU380303, GU380305, KR611522, KT074339, KT162005, KF149962, FJ005196, GQ865518, FJ222821, FJ005213, FJ005238, FJ005214, KC196099, KM457119, AB120727, KP071956, KR559893, FJ005235). Multiple alignments of the nucleic acid and amino acid sequences were performed using the Clustal W method and the MegAlign program (DNASTAR, Madison, WI, USA). Phylogenetic analyses were performed with the maximum likelihood method using MEGA 6, version 6.06.
Results
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification and genotype analysis
A total of 88 samples from 99 dogs were positive for CPV-2. Of the 88 CPV-2 isolates, 17, 23, and 48 were identified as CPV-2a (19.3 %), CPV-2b (26.1 %), and CPV-2c (54.6 %), respectively. First, we observed the CPV-2c variant collected in January 2015 (Additional file 1, Fig. 1). This variant rapidly spread throughout the Taiwanese dog population, and detection rates were 53.1 % (26/49) and 68.8 % (22/32) in 2015 (January to December) and 2016 (January to April), respectively (Fig. 1). Taken together, our data revealed co-circulation of CPV-2a, −2b, and -2c on the island, and CPV-2c was identified as the current dominant variant.
Geographical distribution of the CPV-2 variants
Of the 17 CPV-2a variants, 2 (11.8 %), 7 (41.2 %), and 8 (47.0 %) isolates were collected from central, southern, and eastern Taiwan, respectively (Fig. 2). Of the 23 CPV-2b variants, 10 (43.5 %), 8 (34.8 %), 4 (17.4 %), and 1 (4.3 %) isolates were collected from northern, central, southern, and eastern Taiwan, respectively (Fig. 2). Of the 48 CPV-2c variants, 13 (27.1 %), 16 (33.3 %), 13 (27.1 %) and 6 (12.5 %) isolates were collected from northern, central, southern, and eastern Taiwan, respectively (Fig. 2). Taken together, our results showed distribution of the CPV-2c variant throughout Taiwan.
DNA sequence analysis
Partial VP2 nucleotide sequences were analyzed using DNASTAR software, revealing 96.6–100 %, 98.3–100 %, and 98.5–100 % homology within local CPV-2a isolates, CPV-2b isolates, and CPV-2c isolates, respectively (Table 1). The same nucleotide sequences for local CPV-2c isolates exhibited 96.9–99 % and 97.5–99.2 % homology with those of the CPV-2a and -2b isolates, respectively (Table 1). In contrast to the low nucleotide sequence similarity between prototype CPV-2c (FJ222821, from Italy) and CPV-2c from Taiwan (97.9–99.0 %), the homology levels between our analyzed CPV-2c isolates (97.7–100 %) and Chinese CPV-2c (GU380303, GU380305, KR611522, KT074339, KT162005) appeared to be much higher (Table 1).
Amino acid sequence analysis
Comparisons among the 88 isolates and 12 reference strains at amino acids 267–440 are presented in Table 2. For the partial VP2 analysis, 17 sequences with an Asn at position 426 were classified as CPV-2a. All of the CPV-2a strains show substitution at position 324 (Tyr to Ile) caused by mutation of TAT to ATT at nucleotide positions 970–972 of the VP2 gene (Table 2). Interestingly, five CPV-2a strains from eastern Taiwan are identical in nucleotide sequence but have distinctive residues (Phe267Tyr, Tyr324Ile, and Thr440Ala) (Table 2). Four CPV-2b strains are identical to the prototype of CPV-2b (Table 2). Fifteen of the 19 CPV-2b strains show substitution at position 267 (Phe to Tyr) and 324 (Tyr to Ile), and four CPV-2b strains only show substitution at position 324 (Tyr to Ile). Glu426, which is unique to strain CPV-2c, was first observed in 48 samples in this study. One unique amino acid substitution was found in the all CPV-2c isolates (Gln370Arg) (Table 2), which is caused by mutation of CCA to CGA at nucleotide positions 1,108-1,110 of the VP2 gene. All CPV-2c variants also show amino acid substitution at position 267 (Phe to Tyr) and 324 (Tyr to Ile). Interestingly, 10 of 48 CPV-2c variants show a unique substitution on Phe420Ser.
Phylogenetic analysis
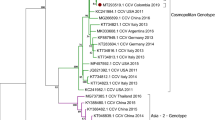
The phylogenetic tree of the partial VP2 gene for the 88 isolates and 28 reference strains was generated using the maximum likelihood method with MEGA 6, version 6.06. Two clusters based on the phylogenetic relationship of the partial VP2 gene of CPV-2c were detected (Fig. 3). The first cluster comprises prototype isolates, European isolates, American isolates, and Asian isolates of CPV-2c. The second cluster consists of all 48 Taiwanese isolates from this study and 4 Chinese isolates of CPV-2c (Fig. 3). To date, these novel CPV-2c isolates have only been detected in China and Taiwan. Our findings demonstrated that the recent CPV-2c isolates in Taiwan are more genetically similar within the VP2 gene to Chinese CPV-2c strains than to prototype strains of CPV-2c.
Phylogenetic analysis of nucleotide sequences of the partial VP2 genes of CPV-2 strains (522 bp). The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the maximum likelihood method with bootstrap analysis (n = 1,000) to determine the best fitting tree. CPV variants are indicated by □, ●, ○, and ▲ for CPV-2, 2a, 2b, and 2c, respectively. The gray diagram represents the Taiwanese CPV-2 variants in this study
Discussion
This is the first study to demonstrate the CPV-2c variant in Taiwan. Previous studies have shown that both the CPV-2a and -2b genotypes constitute the prevalent CPV-2 field strains circulating in Taiwan, and no CPV-2c cases were reported in the last two decades (Table 3). In our continuous surveillance and sequence analysis, Taiwan was considered to be free of CPV-2c. However, since January 2015, one case of CPV-2c occurred in a puppy in Taiwan. The CPV-2c variant appears thus far to have the highest detection rate in the dog population of Taiwan. Similar results have shown that CPV-2c replaced the previous circulation of CPV-2 strains in Italy [8], Uruguay [19], Argentina [21], Brazil [20], and the United States [44]. Interestingly, comparative VP2 genome analysis of the isolated CPV-2c reference revealed that the partial VP2 genome sequence of the Taiwanese strain is similar (97.7–100 %) to that of Chinese CPV-2c strains. Our results indicate that the recent CPV-2c isolate from Taiwan shares a common evolutionary origin with the Chinese CPV-2c strains and should be classified as novel Asian CPV-2c isolates. According to genotype surveillance between Taiwan [30, 31, 39, 41] and China [26–28, 37, 45–48], CPV-2c was first detected in China in 2009 [28]. In contrast, no CPV-2c variant was observed in studies conducted over the last two decades in Taiwan (Table 3). In addition, the Taiwanese CPV-2c variant is more closely related to the Chinese CPV-2c strains than the recent Taiwanese CPV-2a (JX048605) and -2b (JX048607) isolates (Fig. 3). Taken together, our results suggest that the Taiwanese CPV-2c may be present due to import from China at some time between the end of 2014 to early 2015 rather than to evolution of existing CPV-2a or -2b genotypes. An ongoing investigation and complete VP2 genome sequence analysis is needed to trace the genetic evolution of this novel CPV-2c variant.
The recent Taiwanese CPV-2a is composed of two divergent lineages that have different ancestors. Most Taiwanese CPV-2a strains belong to the recent Taiwanese lineage of CPV-2a, sharing a common amino acid substitution (Tyr324Ile). The second lineage of the Taiwanese CPV-2a variant is more closely related to recent Uruguayan and Chinese CPV-2a strains and has distinctive amino acid substitutions of Phe267Tyr, Tyr324Ile, and Thr440Ala. This new CPV-2a variant was discovered in China and Uruguay between 2006 and 2009 and in 2010 [49], respectively. This is the first detection of this lineage of CPV-2a in eastern Taiwan in 2015. However, this new CPV-2a variant recently emerged in Uruguay and underwent clonal expansion [49]. An ongoing investigation is aimed at determining whether this new CPV-2a variant will replaced the CPV-2c variant in the Taiwanese dog population.
Amino acid substitution of Tyr324Ile has been observed in Korea [32, 34], China [26, 27, 37, 45–48], Thailand [36], Uruguay [49, 50], Japan [38], Taiwan [39, 41], and India [40, 42]. Interestingly, the frequency of the Ile324 variant has reached a high prevalence among Taiwanese CPV-2 isolates (94.5 %), and our results revealed that this variant is not only present among Taiwanese CPV-2a strains but also CPV-2b and -2c strains. In addition, this study reports for the first time the amino acid substitution of Phe267Tyr in Taiwan. Surprisingly, all of the Tyr267 variants among Taiwanese CPV-2a, −2b, and −2c strains contain the amino acid substitution of Tyr324Ile. Our review of sequence analysis in the literature indicated that this phenomenon is also found in Uruguay [51]. The functions of CPV-2 residues 267 and 324 are still unknown and remain to be elucidated.
The substitution of Gln370Arg is unique to the Taiwanese CPV-2c strains, and this mutation is also observed in Chinese panda parvovirus [52] and Chinese CPV-2c strains [26, 27]. Residue 359 and 375 constitute a flexible surface loop of the capsid protein that is adjacent to a double Ca2+-binding site; this region is essential for virus infectivity, and changes are correlated with the ability of the virus to cause erythrocyte hemagglutination [53]. Therefore, it remains to be investigated whether Gln370Arg substitution causes antigenic alterations.
Mutation of residue 420 had been reported in Brazilian reference CPV-2c strains (Phe420Leu) [54]. In the present study, we detected 10 CPV-2c strains with a unique change at the same position, yet Phe420Ser was unique in these 10 Taiwanese CPV-2c strains. Therefore, further studies focusing on potential variants of the CPV-2c strains should be conducted to elucidate the relationship between Phe420Ser substitution and viral pathogenicity.
Although several studies have demonstrated the efficacy of the current CPV-2 vaccine against CPV-2c infection [55, 56], some evidence suggests that dogs with the complete vaccination program still suffer from CPV-2c [6]. In the present study, four of 22 CPV-2c-diseased dogs died despite vaccination (C104-030, C104-031, C104-042, C104-216) (Additional file 1). Among those that died, three were under 6 months of age. Surprisingly, despite having undergone the complete vaccination program, one adult dog (strain no. C104-216) was infected by this novel CPV-2c variant. Therefore, co-infection with other diseases needs to examined, and the efficacy of the current vaccine against this novel CPV-2c variant remains to be evaluated, especially in regard to the amino acid substitutions observed in this novel CPV-2c variant compared to the CPV-2c prototype.
Conclusions
This is the first report to identify a novel CPV-2c variant in Taiwan. The novel CPV-2c variant was found to be distributed throughout Taiwan, revealing that this novel CPV-2c variant is currently circulating on the island. Phylogenetic analysis demonstrated that the recent CPV-2c isolate from Taiwan shares a common evolutionary origin with Chinese strains of CPV-2c, as classified into novel Asian CPV-2c isolates (Phe267Tyr, Tyr324Ile, Gln370Arg). Continuous and intensive surveillance of this novel CPV-2c is needed, especially in previously disease-free countries.
Abbreviations
- CPV-2:
-
Canine parvovirus type 2
- CPV-2c:
-
Canine parvovirus type 2c
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
References
Buonavoglia C, Martella V, Pratelli A, Tempesta M, Cavalli A, Buonavoglia D, Bozzo G, Elia G, Decaro N, Carmichael L. Evidence for evolution of canine parvovirus type 2 in Italy. J Gen Virol. 2001;82:3021–5.
Martella V, Decaro N, Buonavoglia C. Evolution of CPV-2 and implication for antigenic/genetic characterization. Virus Genes. 2006;33:11–3.
Lopez de Turiso JA, Cortes E, Ranz A, Garcia J, Sanz A, Vela C, Casal JI. Fine mapping of canine parvovirus B cell epitopes. J Gen Virol. 1991;72(Pt 10):2445–56.
Chang SF, Sgro JY, Parrish CR. Multiple amino acids in the capsid structure of canine parvovirus coordinately determine the canine host range and specific antigenic and hemagglutination properties. J Virol. 1992;66:6858–67.
Aldaz J, Garcia-Diaz J, Calleros L, Sosa K, Iraola G, Marandino A, Hernandez M, Panzera Y, Perez R. High local genetic diversity of canine parvovirus from Ecuador. Vet Microbiol. 2013;166:214–9.
Decaro N, Desario C, Elia G, Martella V, Mari V, Lavazza A, Nardi M, Buonavoglia C. Evidence for immunisation failure in vaccinated adult dogs infected with canine parvovirus type 2c. New Microbiol. 2008;31:125–30.
Decaro N, Desario C, Addie DD, Martella V, Vieira MJ, Elia G, Zicola A, Davis C, Thompson G, Thiry E, et al. The study molecular epidemiology of canine parvovirus, Europe. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:1222–4.
Decaro N, Elia G, Martella V, Campolo M, Desario C, Camero M, Cirone F, Lorusso E, Lucente MS, Narcisi D, et al. Characterisation of the canine parvovirus type 2 variants using minor groove binder probe technology. J Virol Methods. 2006;133:92–9.
Decaro N, Buonavoglia C. Canine parvovirus: a review of epidemiological and diagnostic aspects, with emphasis on type 2c. Vet Microbiol. 2012;155:1–12.
Decaro N, Desario C, Billi M, Mari V, Elia G, Cavalli A, Martella V, Buonavoglia C. Western European epidemiological survey for parvovirus and coronavirus infections in dogs. Vet J. 2011;187:195–9.
Miranda C, Parrish CR, Thompson G. Epidemiological evolution of canine parvovirus in the Portuguese domestic dog population. Vet Microbiol. 2016;183:37–42.
Decaro N, Martella V, Desario C, Bellacicco AL, Camero M, Manna L, d’Aloja D, Buonavoglia C. First detection of canine parvovirus type 2c in pups with haemorrhagic enteritis in Spain. J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2006;53:468–72.
Ntafis V, Xylouri E, Kalli I, Desario C, Mari V, Decaro N, Buonavoglia C. Characterization of Canine parvovirus 2 variants circulating in Greece. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2010;22:737–40.
Filipov C, Desario C, Patouchas O, Eftimov P, Gruichev G, Manov V, Filipov G, Buonavoglia C, Decaro N: A Ten-Year Molecular Survey on Parvoviruses Infecting Carnivores in Bulgaria. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2014. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/tbed.12285/abstract. Accessed 6 Aug 2014.
Sutton D, Vinberg C, Gustafsson A, Pearce J, Greenwood N. Canine parvovirus type 2c identified from an outbreak of severe gastroenteritis in a litter in Sweden. Acta Vet Scand. 2013;55:64.
Muz D, Oguzoglu TC, Timurkan MO, Akin H. Characterization of the partial VP2 gene region of canine parvoviruses in domestic cats from Turkey. Virus Genes. 2012;44:301–8.
Touihri L, Bouzid I, Daoud R, Desario C, El Goulli AF, Decaro N, Ghorbel A, Buonavoglia C, Bahloul C. Molecular characterization of canine parvovirus-2 variants circulating in Tunisia. Virus Genes. 2009;38:249–58.
Hong C, Decaro N, Desario C, Tanner P, Pardo MC, Sanchez S, Buonavoglia C, Saliki JT. Occurrence of canine parvovirus type 2c in the United States. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2007;19:535–9.
Perez R, Francia L, Romero V, Maya L, Lopez I, Hernandez M. First detection of canine parvovirus type 2c in South America. Vet Microbiol. 2007;124:147–52.
Pinto LD, Streck AF, Goncalves KR, Souza CK, Corbellini AO, Corbellini LG, Canal CW. Typing of canine parvovirus strains circulating in Brazil between 2008 and 2010. Virus Res. 2012;165:29–33.
Calderon MG, Romanutti C, DA A, Keller L, Mattion N, La Torre J. Evolution of canine parvovirus in Argentina between years 2003 and 2010: CPV2c has become the predominant variant affecting the domestic dog population. Virus Res. 2011;157:106–10.
Pedroza-Roldan C, Paez-Magallan V, Charles-Nino C, Elizondo-Quiroga D, De Cervantes-Mireles RL, Lopez-Amezcua MA. Genotyping of Canine parvovirus in western Mexico. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2015;27:107–11.
Amrani N, Desario C, Kadiri A, Cavalli A, Berrada J, Zro K, Sebbar G, Colaianni ML, Parisi A, Elia G, et al. Molecular epidemiology of canine parvovirus in Morocco. Infect Genet Evol. 2016;41:201–6.
Nakamura M, Tohya Y, Miyazawa T, Mochizuki M, Phung HT, Nguyen NH, Huynh LM, Nguyen LT, Nguyen PN, Nguyen PV, et al. A novel antigenic variant of Canine parvovirus from a Vietnamese dog. Arch Virol. 2004;149:2261–9.
Nandi S, Chidri S, Kumar M, Chauhan RS. Occurrence of canine parvovirus type 2c in the dogs with haemorrhagic enteritis in India. Res Vet Sci. 2010;88:169–71.
Geng Y, Guo D, Li C, Wang E, Wei S, Wang Z, Yao S, Zhao X, Su M, Wang X, et al. Co-Circulation of the Rare CPV-2c with Unique Gln370Arg Substitution, New CPV-2b with Unique Thr440Ala Substitution, and New CPV-2a with High Prevalence and Variation in Heilongjiang Province, Northeast China. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0137288.
Zhao H, Wang J, Jiang Y, Cheng Y, Lin P, Zhu H, Han G, Yi L, Zhang S, Guo L, Cheng S. Typing of Canine Parvovirus Strains Circulating in North-East China. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2015. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/tbed.12390. Accessed 28 Apr 2015.
Zhang RZ, Yang ST, Feng H, Cui CS, Xia XZ. The first detection of canine parvovirus type 2c in China. J Pathog Biol. 2010;5:246–9.
Ohshima T, Hisaka M, Kawakami K, Kishi M, Tohya Y, Mochizuki M. Chronological analysis of canine parvovirus type 2 isolates in Japan. J Vet Med Sci. 2008;70:769–75.
Chang WL, Chang AC, Pan MJ. Antigenic types of canine parvoviruses prevailing in Taiwan. Vet Rec. 1996;138:447.
Wang HC, Chen WD, Lin SL, Chan JP, Wong ML. Phylogenetic analysis of canine parvovirus VP2 gene in Taiwan. Virus Genes. 2005;31:171–4.
Jeoung SY, Ahn SJ, Kim D. Genetic analysis of VP2 gene of canine parvovirus isolates in Korea. J Vet Med Sci. 2008;70:719–22.
Kang BK, Song DS, Lee CS, Jung KI, Park SJ, Kim EM, Park BK. Prevalence and genetic characterization of canine parvoviruses in Korea. Virus Genes. 2008;36:127–33.
Yoon SH, Jeong W, Kim HJ, An DJ. Molecular insights into the phylogeny of canine parvovirus 2 (CPV-2) with emphasis on Korean isolates: a Bayesian approach. Arch Virol. 2009;154:1353–60.
Mohan Raj J, Mukhopadhyay HK, Thanislass J, Antony PX, Pillai RM. Isolation, molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of canine parvovirus. Infect Genet Evol. 2010;10:1237–41.
Phromnoi S, Sirinarumitr K, Sirinarumitr T. Sequence analysis of VP2 gene of canine parvovirus isolates in Thailand. Virus Genes. 2010;41:23–9.
Zhang R, Yang S, Zhang W, Zhang T, Xie Z, Feng H, Wang S, Xia X. Phylogenetic analysis of the VP2 gene of canine parvoviruses circulating in China. Virus Genes. 2010;40:397–402.
Soma T, Taharaguchi S, Ohinata T, Ishii H, Hara M. Analysis of the VP2 protein gene of canine parvovirus strains from affected dogs in Japan. Res Vet Sci. 2013;94:368–71.
Chou SJ, Lin HT, Wu JT, Yang WC, Chan KW. Genotyping of canine parvovirus type 2 VP2 gene in southern Taiwan in 2011. Taiwan Vet J. 2013;39:81–92.
Mukhopadhyay HK, Matta SL, Amsaveni S, Antony PX, Thanislass J, Pillai RM. Phylogenetic analysis of canine parvovirus partial VP2 gene in India. Virus Genes. 2013;48:89–95.
Lin CN, Chien CH, Chiou MT, Chueh LL, Hung MY, Hsu HS. Genetic characterization of type 2a canine parvoviruses from Taiwan reveals the emergence of an Ile324 mutation in VP2. Virol J. 2014;11:39.
Mittal M, Chakravarti S, Mohapatra JK, Chug PK, Dubey R, Narwal PS, Kumar A, Churamani CP, Kanwar NS. Molecular typing of canine parvovirus strains circulating from 2008–2012 in an organized kennel in India reveals the possibility of vaccination failure. Infect Genet Evol. 2014;23:1–6.
Lin CN, Chien CH, Chiou MT, Wang JW, Lin YL, Xu YM. Development of SYBR Green-Based Real-Time PCR for the Detection of Canine, Feline and Porcine Parvoviruses. Taiwan Vet J. 2014;40:1–9.
Kapil S, Cooper E, Lamm C, Murray B, Rezabek G, Johnston 3rd L, Campbell G, Johnson B. Canine parvovirus types 2c and 2b circulating in North American dogs in 2006 and 2007. J Clin Microbiol. 2007;45:4044–7.
Yi L, Tong M, Cheng Y, Song W, Cheng S. Phylogenetic Analysis of Canine Parvovirus VP2 Gene in China. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2014 http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/tbed.12268. Accessed 11 Sept 2014.
Zhong Z, Liang L, Zhao J, Xu X, Cao X, Liu X, Zhou Z, Ren Z, Shen L, Geng Y, et al. First isolation of new canine parvovirus 2a from Tibetan mastiff and global analysis of the full-length VP2 gene of canine parvoviruses 2 in China. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15:12166–87.
Han SC, Guo HC, Sun SQ, Shu L, Wei YQ, Sun DH, Cao SZ, Peng GN, Liu XT. Full-length genomic characterizations of two canine parvoviruses prevalent in Northwest China. Arch Microbiol. 2015;197:621–6.
Xu J, Guo HC, Wei YQ, Shu L, Wang J, Li JS, Cao SZ, Sun SQ. Phylogenetic analysis of canine parvovirus isolates from Sichuan and Gansu provinces of China in 2011. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2015;62:91–5.
Perez R, Bianchi P, Calleros L, Francia L, Hernandez M, Maya L, Panzera Y, Sosa K, Zoller S. Recent spreading of a divergent canine parvovirus type 2a (CPV-2a) strain in a CPV-2c homogenous population. Vet Microbiol. 2012;155:214–9.
Perez R, Calleros L, Marandino A, Sarute N, Iraola G, Grecco S, Blanc H, Vignuzzi M, Isakov O, Shomron N, et al. Phylogenetic and genome-wide deep-sequencing analyses of canine parvovirus reveal co-infection with field variants and emergence of a recent recombinant strain. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e111779.
Maya L, Calleros L, Francia L, Hernandez M, Iraola G, Panzera Y, Sosa K, Perez R. Phylodynamics analysis of canine parvovirus in Uruguay: evidence of two successive invasions by different variants. Arch Virol. 2013;158:1133–41.
Guo L, Yang SL, Chen SJ, Zhang Z, Wang C, Hou R, Ren Y, Wen X, Cao S, Guo W, et al. Identification of canine parvovirus with the Q370R point mutation in the VP2 gene from a giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca). Virol J. 2013;10:163.
Simpson AA, Chandrasekar V, Hebert B, Sullivan GM, Rossmann MG, Parrish CR. Host range and variability of calcium binding by surface loops in the capsids of canine and feline parvoviruses. J Mol Biol. 2000;300:597–610.
Decaro N, Desario C, Parisi A, Martella V, Lorusso A, Miccolupo A, Mari V, Colaianni ML, Cavalli A, Di Trani L, Buonavoglia C. Genetic analysis of canine parvovirus type 2c. Virology. 2009;385:5–10.
Larson LJ, Schultz RD. Do two current canine parvovirus type 2 and 2b vaccines provide protection against the new type 2c variant? Vet Ther. 2008;9:94–101.
Spibey N, Greenwood NM, Sutton D, Chalmers WS, Tarpey I. Canine parvovirus type 2 vaccine protects against virulent challenge with type 2c virus. Vet Microbiol. 2008;128:48–55.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Prof. Ling-Ling Chueh and Prof. Hsin-Fu Liu for comments that greatly improved the manuscript.
Funding
No funding was obtained for this study.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Authors’ contributions
SYC analyzed the experimental data and wrote the manuscript. HYW and MTC managed the study, provided materials and reagents, contributed to the interpretation of the data, and co-wrote the manuscript. MCC contributed to the DNA extraction and PCR. CNL designed and analyzed the experimental data and wrote the manuscript. All of the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study did not involve any animal experiment. The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of National Pingtung University of Science and Technology did not deem it necessary for this research group to obtain formal approval to conduct this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional file
Additional file 1:
The genotypes of 88 canine parvovirus type 2 isolates collected from Taiwanese dogs. (DOCX 74 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Chiang, SY., Wu, HY., Chiou, MT. et al. Identification of a novel canine parvovirus type 2c in Taiwan. Virol J 13, 160 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12985-016-0620-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12985-016-0620-5