Abstract
Background
Thyroid metastasis of soft tissue sarcoma is very rare, and the diagnosis is especially difficult when only a single lesion is present.
Case presentation
A 50-year-old man was diagnosed with myxoid liposarcoma of the right thigh and treated with wide resection. Two and a half years after the surgery, a growing low-density area was incidentally observed in the right lobe of his thyroid gland on follow-up chest computed tomography. Fine needle aspiration biopsy was performed twice, and the thyroid mass was suspected of being a sarcoma metastasis. He was treated by hemithyroidectomy, and the lesion was pathologically confirmed as a metastasis of myxoid liposarcoma.
Conclusion
We experienced single thyroid gland metastasis in patients with myxoid liposarcoma in whom a growing mass is observed in the thyroid gland after radical surgery of the primary site.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Metastasis to the thyroid gland has been reported in 0.4–1.5% of patients undergoing surgery for malignant thyroid tumors [1, 2], but thyroid gland metastasis is very rare in myxoid liposarcoma, and its clinical features are not well recognized.
Soft tissue sarcoma is a highly metastatic tumor, whose most common metastatic site is the lung, but myxoid liposarcoma is recognized to metastasize to unusual locations such as soft tissue, retroperitoneum, and spine [3]. The reason for metastasis to these peculiar lesions has not been elucidated. A previous report suggested that myxoid liposarcoma has a high incidence of osseous metastases and often associated with the most common type of type II TLS-CHOP transcript [4]. Myxoid liposarcoma is known as a translocation-related sarcoma, and there is a possibility that the specific fusion gene may affect the metastatic organotropism. We incidentally detected a single thyroid gland metastasis of myxoid liposarcoma on follow-up chest computed tomography (CT) after definitive surgery and report here a rare myxoid liposarcoma thyroid metastasis from a thigh in an adult.
Case presentation
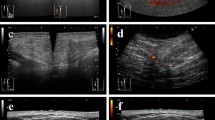
A 50-year-old man consulted an orthopedic clinic with a chief complaint of a painless mass in his right thigh. He consulted our university hospital 2 weeks later. He was suspected of having a localized myxoid liposarcoma of the right thigh by clinical imaging (Fig. 1a–c) and open biopsy. The maximum tumor diameter was 10 cm. Myxoid liposarcoma was suspected in histological examinations of the biopsy specimens. He was treated by wide resection which involved tumor, vastus intermedius, and vastus lateralis. Histological examination of the resected specimens revealed a mixture of uniform oval shaped non-lipogenic cells and small signet ring lipoblasts in a prominent myxoid stroma, and he was diagnosed with myxoid liposarcoma (Fig. 2). There was no round cell component, and the surgical margin was negative. Two and half years after the surgery, a growing low-density area was incidentally observed in the right lobe of his thyroid gland on follow-up chest CT (Fig. 3a, b). Ultrasound showed a solid hypoechoic nodule with taller than wide shape in the right robe of his thyroid gland (Fig. 4). Ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy was performed twice (first biopsy: undeterminable and second biopsy: false-positive), and the thyroid mass was suspected of being a sarcoma metastasis. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed that the mass in the right lobe of his thyroid gland was isointense on T1-weighted images, hyperintense on T2-weighted images, and well enhanced (Fig. 5a–c). He was treated by hemithyroidectomy (Fig. 6a, b), and the lesion was pathologically confirmed as a metastasis of myxoid liposarcoma. Round component was also not observed in the metastatic myxoid liposarcoma. Postoperative chemotherapy was not done because patient consent was not obtained. There has been no recurrence at one and a half years after the hemithyroidectomy.
Discussion and conclusions
Recent reports of non-small round cell soft tissue sarcoma metastasis from an extremity to the thyroid gland are listed in Table 1. Six cases of non-small round cell soft tissue sarcoma metastasis from an extremity to the thyroid gland were reported in this century [2, 5,6,7,8,9]. Of these six cases, four had liposarcoma and one of them was diagnosed with myxoid liposarcoma like our case. Especially, a thyroid mass after resection of liposarcoma should be considered a possible thyroid metastasis. Five of seven sarcoma metastases to the thyroid gland occurred in the right lobe in Table 1, but the reason is unknown because the thyroid gland has no left-right difference in weight and blood supply [10].
Myxoid liposarcoma without round cell component is considered to be a generally low-grade tumor, with 5-year disease-specific and disease-free survivals of 90 and 77% in our sarcoma group, respectively [11]. Histological diagnosis showed no round cell component in the primary myxoid liposarcoma of the thigh, but thyroid gland metastasis occurred at two and half years after definitive surgery. Interestingly, there was no round cell component in the resected metastatic myxoid liposarcoma of thyroid gland. Wood et al. reported 15 cases of thyroid metastasis, 9 of which had other metastases as well [2]. In our case, the presence of only a single thyroid metastasis made it difficult to diagnosis.
On ultrasound imaging for thyroid mass, the presence of a solid hypoechoic nodule or solid hypoechoic component of a partially cystic nodule with one or more of the following features such as irregular margins, microcalcifications, taller than wide shape, rim calcifications with small extrusive, soft tissue component, and evidence of extra thyroidal extension were recognized as indicating a high risk of malignancy [12]. In this case, ultrasound showed a solid hypoechoic nodule with taller than wide shape in the right robe of his thyroid gland, suggesting the possibility of malignant thyroid tumor. However, it was difficult to distinguish primary thyroid tumor from thyroid metastasis on images.
In our case, there were two other differential diagnoses in thyroid metastasis on MRI, namely primary thyroid tumors such as follicular adenoma and adenocarcinoma. Most of these tumors show similar MRI features to those of myxoid liposarcoma such as isointensity on T1-weighted images and hyperintensity on T2-weighted images [13], making it difficult to distinguish a sarcoma metastasis from these follicular tumors without biopsy. Fine needle aspiration biopsy is known to be the most accurate and cost-effective method for evaluating thyroid nodules [12]. Previous studies have reported lower rates of both non-diagnostic and false-negative cytology in ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy [14, 15]. In our case, ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy was performed twice (first biopsy: undeterminable and second biopsy: false-positive), which may depend partially on the low cellularity of myxoid liposarcoma.
We performed hemithyroidectomy for the single thyroid metastasis after resection of the primary myxoid liposarcoma. A previous report mentioned that thyroidectomy should be considered for thyroid metastasis when curability of the primary disease is expected and/or to improve quality of life by securing respiratory and swallowing function [1]. In our case, the primary tumor had already been resected and disease-free status was obtained by thyroidectomy which could improve survival in metastatic non-small round cell soft tissue sarcoma [16].
In our case, postoperative chemotherapy was not done because patient consent was not obtained. A meta-analysis showed that doxorubicin-based chemotherapy prolonged distant and overall recurrence in adults with localized, resectable soft tissue sarcoma, and the overall survival advantage was marginally determined [17]. However, in a randomized controlled trial, adjuvant chemotherapy with doxorubicin and ifosfamide showed no benefit in relapse-free survival or overall survival in patients with resectable soft tissue sarcoma [18]. Neoadjuvant and/or adjuvant chemotherapy may be one of the treatment options for patients with resectable primary soft tissue sarcoma, but the evidence is still controversial. Recent study showed that adjuvant treatment with anthracycline-based chemotherapy had survival benefits for high-risk patients with resectable primary tumor [19]. Doxorubicin-based chemotherapy has been also considered as a standard treatment for chemotherapy naïve advanced or metastatic soft tissue sarcoma patients [20, 21]. There is no strong evidence of the value of neoadjuvant and/or adjuvant chemotherapy for patients with resectable metastasis of soft tissue sarcoma, but doxorubicin-based chemotherapy was a treatment option for our patient. The overall response rates were reported as 43.2% using Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) and 86.5% using Choi criteria after treatment of first-line doxorubicin and ifosfamide in patient with myxoid liposarcoma [22].
There were some reports about the periods to recurrence in myxoid/round cell liposarcoma. Moreau et al. reported that the 5- and 10-year metastasis-free survival were 84 and 77% for myxoid liposarcoma and 69 and 46% for round cell liposarcoma, respectively [3]. In our sarcoma group, disease-free survival was 77% at both 5 and 10 years in pure myxoid liposarcoma [11]. Although postoperative recurrence after 5 years was rare, it would be reasonable to observe the follow-up for 10 years after surgery in patients with myxoid liposarcoma.
Finally, thyroid metastasis of soft tissue sarcoma is a very rare condition, but it should be considered especially in liposarcoma. Thyroidectomy may be optimal for the treatment of a single metastasis in the thyroid grand.
Summing up, even though thyroid metastasis of soft tissue sarcoma is very rare, we should consider the possibility of thyroid gland metastasis in patients with soft tissue sarcoma in whom a growing mass in the thyroid gland is observed.
Abbreviations
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- RECIST:
-
Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors
References
Ishikawa M, Hirano S, Tsuji T, Ito J. Management of metastasis to the thyroid gland. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2011;38:426–30.
Wood K, Vini L, Harmer C. Metastases to the thyroid gland: the Royal Marsden experience. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2004;30:583–8.
Moreau LC, Turcotte R, Ferguson P, Wunder J, Clarkson P, Masri B, Isler M, Dion N, Werier J, Ghert M, Deheshi B, S. Canadian Orthopaedic Oncology. Myxoid\round cell liposarcoma (MRCLS) revisited: an analysis of 418 primarily managed cases. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:1081–8.
Schwab JH, Boland P, Guo T, Brennan MF, Singer S, Healey JH, Antonescu CR. Skeletal metastases in myxoid liposarcoma: an unusual pattern of distant spread. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:1507–14.
Bashir H, Nawaz MK, Shah MA, Ahmad E. Pleomorphic liposarcoma metastatic to the thyroid gland. Clin Nucl Med. 2002;27:9–10.
Azar AR, Weynand B, Daumerie C, Coche E. Metastatic liposarcoma of the thyroid gland. Br J Radiol. 2003;76:750–2.
Brandwein-Gensler M, Urken M, Wang B. Collision tumor of the thyroid: a case report of metastatic liposarcoma plus papillary thyroid carcinoma. Head & neck. 2004;26:637–41.
Tysome JR, Sandison A, Clarke PM. Myxoid liposarcoma metastatic to the thyroid gland: a case report and literature review. J Laryngol Otol. 2006;120:511–3.
Vankalakunti M, Kaur J, Srinivasan R. Cytology of sarcoma metastasizing to the thyroid: a case report. Acta Cytol. 2008;52:729–32.
Tegler L, Gillquist J, Anderberg B, Lundstrom B, Johansson H. Thyroid blood flow rate in man. Electromagnetic flowmetry during operation in euthyroid normal gland, nontoxic goiter, and hyperthyroidism. J Endocrinol Invest. 1981;4:335–41.
Nishida Y, Tsukushi S, Nakashima H, Ishiguro N. Clinicopathologic prognostic factors of pure myxoid liposarcoma of the extremities and trunk wall. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468:3041–6.
Haugen BR, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty GM, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, Pacini F, Randolph GW, Sawka AM, Schlumberger M, Schuff KG, Sherman SI, Sosa JA, Steward DL, Tuttle RM, Wartofsky L. 2015 American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: the American Thyroid Association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid : offi jl Am Thyroid Assoc. 2016;26:1–133.
Higgins CB, Auffermann W. MR imaging of thyroid and parathyroid glands: a review of current status. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988;151:1095–106.
Danese D, Sciacchitano S, Farsetti A, Andreoli M, Pontecorvi A. Diagnostic accuracy of conventional versus sonography-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy of thyroid nodules. Thyroid : offi j Am Thyroid Assoc. 1998;8:15–21.
Carmeci C, Jeffrey RB, McDougall IR, Nowels KW, Weigel RJ. Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy of thyroid masses. Thyroid : offi j Am Thyroid Assoc. 1998;8:283–9.
Urakawa H, Kozawa E, Ikuta K, Hamada S, Ishiguro N, Nishida Y. Impact of disease free status on prognosis in metastatic non-small round cell soft tissue sarcomas. Clinical & experimental metastasis. 2016;33:799–807.
Pervaiz N, Colterjohn N, Farrokhyar F, Tozer R, Figueredo A, Ghert M. A systematic meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of adjuvant chemotherapy for localized resectable soft-tissue sarcoma. Cancer. 2008;113:573–81.
Woll PJ, Reichardt P, Le Cesne A, Bonvalot S, Azzarelli A, Hoekstra HJ, Leahy M, Van Coevorden F, Verweij J, Hogendoorn PC, Ouali M, Marreaud S, Bramwell VH, Hohenberger P, Tissue ES, Bone Sarcoma G, N.C.T.G.S.D.S.C. the. Adjuvant chemotherapy with doxorubicin, ifosfamide, and lenograstim for resected soft-tissue sarcoma (EORTC 62931): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:1045–54.
Gronchi A, Ferrari S, Quagliuolo V, Broto JM, Pousa AL, Grignani G, Basso U, Blay JY, Tendero O, Beveridge RD, Ferraresi V, Lugowska I, Merlo DF, Fontana V, Marchesi E, Donati DM, Palassini E, Palmerini E, De Sanctis R, Morosi C, Stacchiotti S, Bague S, Coindre JM, Dei Tos AP, Picci P, Bruzzi P, Casali PG. Histotype-tailored neoadjuvant chemotherapy versus standard chemotherapy in patients with high-risk soft-tissue sarcomas (ISG-STS 1001): an international, open-label, randomised, controlled, phase 3, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:812–22.
Judson I, Verweij J, Gelderblom H, Hartmann JT, Schoffski P, Blay JY, Kerst JM, Sufliarsky J, Whelan J, Hohenberger P, Krarup-Hansen A, Alcindor T, Marreaud S, Litiere S, Hermans C, Fisher C, Hogendoorn PC, dei Tos AP, van der Graaf WT, O. European, T. Treatment of Cancer Soft, G. Bone Sarcoma. Doxorubicin alone versus intensified doxorubicin plus ifosfamide for first-line treatment of advanced or metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma: a randomised controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:415–23.
Seddon B, Strauss SJ, Whelan J, Leahy M, Woll PJ, Cowie F, Rothermundt C, Wood Z, Benson C, Ali N, Marples M, Veal GJ, Jamieson D, Kuver K, Tirabosco R, Forsyth S, Nash S, Dehbi HM, Beare S. Gemcitabine and docetaxel versus doxorubicin as first-line treatment in previously untreated advanced unresectable or metastatic soft-tissue sarcomas (GeDDiS): a randomised controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:1397–410.
Katz D, Boonsirikamchai P, Choi H, Lazar AJ, Wang WL, Xiao L, Park MS, Ravi V, Benjamin RS, Araujo DM. Efficacy of first-line doxorubicin and ifosfamide in myxoid liposarcoma. Clin Sarcoma Res. 2012;2:2.
Acknowledgements
We thank Miss Eri Ishihara for the secretarial assistance.
Funding
One or more of the authors (HU) has received research funding from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan [Grant-in-Aid 17K10963 for Scientific Research (C)].
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HU was responsible for the design and drafting of the manuscript; HU for the concept; NI and YN were responsible for the revision of the manuscript and supervision; EA, KI, SH, and TO were responsible for the treatment of the soft tissue sarcoma; and KN was responsible for the surgical treatment of the thyroid gland metastasis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for the publication of this case report and any accompanying images.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Urakawa, H., Nakanishi, K., Arai, E. et al. Single metastasis of myxoid liposarcoma from the thigh to thyroid gland: a case report. World J Surg Onc 16, 71 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-018-1370-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-018-1370-1