Abstract
Background
The inequity of healthcare utilization in rural China is serious, and the urban-rural segmentation of the medical insurance system intensifies this problem. To guarantee that the rural population enjoys the same medical insurance benefits, China began to establish Urban and Rural Resident Basic Medical Insurance (URRBMI) nationwide in 2016. Against this backdrop, this paper aims to compare the healthcare utilization inequity between URRBMI and New Cooperative Medical Schemes (NCMS) and to analyze whether the inequity is reduced under URRBMI in rural China.
Methods
Using the data from a national representative survey, the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS), which was conducted in 2015, a binary logistic regression model was applied to analyze the influence of income on healthcare utilization, and the decomposition of the concentration index was adopted to compare the Horizontal inequity index (HI index) of healthcare utilization among the individuals insured by URRBMI and NCMS.
Results
There is no statistically significant difference in healthcare utilization between URRBMI and NCMS, but in outpatient utilization, there are significant differences among different income groups in NCMS; high-income groups utilize more outpatient care. The Horizontal inequity indexes (HI indexes) in outpatient utilization for individuals insured by URRBMI and NCMS are 0.024 and 0.012, respectively, indicating a pro-rich inequity. Meanwhile, the HI indexes in inpatient utilization under the two groups are − 0.043 and − 0.028, respectively, meaning a pro-poor inequity. For both the outpatient and inpatient care, the inequity degree of URRBMI is larger than that of NCMS.
Conclusions
This paper shows that inequity still exists in rural areas after the integration of urban-rural medical insurance schemes, and there is still a certain gap between the actual and the expected goal of URRBMI. Specifically, compared to NCMS, the pro-rich inequity in outpatient care and the pro-poor inequity in inpatient care are more serious in URRBMI. More chronic diseases should be covered and moral hazard should be avoided in URRBMI. For the vulnerable groups, special policies such as reducing the deductible and covering these groups with catastrophic medical insurance could be considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Amartya Sen once noted that “health is the necessary basis for people to realize other capabilities”. Healthcare service, as the post intervention in diseases, is the last “safety net” to guarantee health, and the equalization of healthcare utilization is an important approach to guarantee health equity [29]. Since the reform and opening up of China, the medical industry and technology have developed rapidly, which also led to an increase in medical expenses. As a result, the inequity in healthcare utilization has also intensified among people of different income groups. Compared to high-income groups, low-income groups have a higher need for healthcare services due to their poor health status [20]. But constrained by income, the healthcare utilization for low-income groups is much less than that of high-income groups.
In China, the inequity in healthcare utilization is more serious in rural areas because there are a large number of low-income groups there [23]. Moreover, for low-income groups, a low level of healthcare utilization can consume most of their wealth, so some of them dare not see a doctor when they are ill. To reduce the inequity in healthcare utilization in rural areas, the Chinese government established the New Cooperative Medical Scheme (NCMS) for rural populations in 2003. By bearing a portion of the medical expenses of the insured, NCMS aims to reduce the economic barriers in healthcare utilization and to improve equity of healthcare services for rural populations regardless of individual socioeconomic factors such as marital status, education and income.
Although the coverage of NCMS has been above 90% since 2008, its services coverage and financial protections are less than those of the Urban Resident Basic Medical Insurance (URBMI) available to the urban populations. According to statistics, “urban residents per capita healthcare expenditure paid by medical insurance is around three times as much as that of the rural residents in 2012”.Footnote 1 The segmentation of the urban-rural medical insurance scheme has become a main factor that caused the urban-rural inequity in healthcare utilization and it is hardly to ensure the healthcare demands of low-income groups in rural areas [24]. This will be harmful to the implementation of rural revitalization strategies and poses a serious threat to social stability in that China is in a critical period of social and economic transformation.
Therefore, the integration of urban-rural medical insurance has gained governmental attention since 2008, and the government established the Urban and Rural Resident Basic Medical Insurance (URRBMI) based on NCMS and URBMI to make residents participate in the same medical insurance regardless of household registration. In 2016, the central government announced that the URRBMI was gradually implemented nationwide in China. Against this backdrop, comparing the inequity in healthcare utilization between URRBMI and NCMS can provide important information for the implementation and development of URRBMI.
Previous studies have revealed that inequity in healthcare utilization exists widely in the world [4, 6, 16]. Apart from inequity between countries, it also exists between regions within one country [1, 3, 21, 25]. The influencing factors of inequity in healthcare utilization are different because of differences in the economy, medical insurance systems and cultures between countries and regions. In previous studies, scholars investigated the relationship between income and the inequity in healthcare utilization, and they found that the inequity is pro-rich in both developed and developing countries, causing an interest transfer between the rich and the poor [4, 6, 17]. Some scholars have also taken other socioeconomic factors into consideration, and they found that factors like medical insurance can also influence the inequity in healthcare utilization [2, 24].
Theoretically, medical insurance can reduce inequity as it provides a financial support in healthcare utilization and covers a large proportion of medical expenses for low-income groups. In China, although medical insurance schemes are a major payment system for healthcare utilization, there are conflicting opinions about the relationship between medical insurance and healthcare utilization inequity. First, some of the studies claim that the implementation of medical insurance narrowed the gap of healthcare utilization [11,12,13]; second, others argue that medical insurance failed to reduce the degree of inequity in healthcare utilization [17, 18, 26,27,28, 31], and some scholars also found that medical insurance has intensified the inequity of healthcare utilization instead of narrowing it [2, 23].
The reason that medical insurance fails to reduce healthcare utilization inequity is that the top-level design of the Chinese medical insurance system pays more attention to economic efficiency during the period of primitive accumulation of capital. Studies have shown that the income gap, the fragmentation management of medical insurance and the difference in medical insurance benefits have become the main factors of healthcare utilization inequity [8, 9, 14, 15, 24]. In China, the urban-rural segmentation of the medical insurance system ensures that the rural population experiences lower medical insurance benefits than the urban population. Meanwhile, the proportion of low-income groups in rural areas is higher than that in urban areas. As a result, NCMS cannot meet the healthcare demands of low-income groups and improve the healthcare utilization inequity completely in rural China.
The aim of URRBMI is to provide the same services coverage and financial protections to both urban and rural residents. We assume that the healthcare utilization inequity in rural areas will be reduced as URRBMI improves the medical insurance benefits of rural populations. Referring to URRBMI, some studies found that the opportunity inequity of healthcare utilization was reduced in URRBMI [13], and it also promoted the healthcare utilization of the insured [7, 14, 19, 30]. Meanwhile, other studies implied that the effect of URRBMI on outpatient and inpatient care utilization is not significant [22] and that the rural regional difference in medical insurance benefits still exists under URRBMI [10, 22].
In summary, the previous studies have analyzed the influence of socioeconomic factors on the inequity of healthcare utilization comprehensively, and most of them employed the Concentration Index (CI) to quantify the degree of inequity. Moreover, they also revealed the profound reasons for the healthcare utilization inequity in rural areas by analyzing the urban-rural segmentation of medical insurance, which provided a reference for this article. However, few of them focus on the healthcare utilization inequity in rural areas under URRBMI. Although Ma Chao et al. measured the opportunity inequity of healthcare utilization between urban and rural areas after the integration of urban-rural medical insurance, their research was only limited to three counties in Jiangsu Province of China and did not analyze the inequity within rural areas [13].
Based on the existing studies, this paper analyzes the relationship between URRBMI and the inequity of healthcare utilization in rural areas by comparing the inequity in healthcare utilization under URRBMI and NCMS. Theoretically, the degree of inequity in URRBMI will be lower than in NCMS in that the services coverage and financial protections of URRBMI are better than those of NCMS, but the assumption needs to be verified by data analysis in the next section. This paper is organized as follows:
First, as the fact that healthcare utilization is mainly affected by health status and socioeconomic factors, we use the chi-square test to make a comparison of differences in healthcare utilization and other influence factors among the individuals who were insured by URRBMI and NCMS.
Second, as the dependent variables in this paper are discrete, and the inequity in healthcare utilization is income-related, the binary logistic regression model is employed in this paper to analyze the differences in healthcare utilization among different income levels under the two medical insurance schemes.
Third, the concentration index (CI) and horizontal inequity index (HI index) are used to quantify the degree of inequity in healthcare utilization under the two groups, the decomposition of the concentration index is used to present the contribution of each independent variable to the concentration index.
Methods
Data source
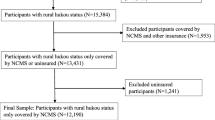
The data analyzed in this paper are from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS) in 2015.Footnote 2 This is a high-quality micro database about individuals who are aged 45 and above in China, and the database was established by the National Development Research Institute of Peking University. These data cover around 12,400 households and 23,000 respondents in different regions of China by using the method of population proportion sampling (PPS), and 450 communities of 150 counties in 28 provinces were interviewed in this investigation. Therefore, these data have a good sample representation. The data questionnaire contains information about individuals’ demographics, health status, healthcare utilization, medical insurance, family structure and income. According to the household registration status, there are 12,426 rural respondents in the 2015 CHARLS data, and the respondents studied in this paper are individuals who were insured only by URRBMI or NCMS. After removing the study subjects with missing variables data, those who changed the household registration (having a rural household registration but participating in URBMI) and whose per capita household income was less than 0, the final effective sample size was 9002. All respondents were weighted by sampling probability.
Measurement of healthcare utilization, health needs and socioeconomic factors
In general, healthcare utilization includes outpatient and inpatient care. Based on the characteristics of the selected data, this paper selects “outpatient visit in the last month” and “inpatient visit in the last year” as indicators to measure healthcare utilization. In addition, referring to previous studies, health need factors include gender, self-assessed health and chronic morbidity; socioeconomic factors include education level, per capita household income, living areas and community. The detailed definition of variables can be seen in Table 1.
Statistical analysis
First, this paper uses the chi-square test to examine whether there are significant differences in healthcare utilization and other influence factors among individuals insured by URRBMI and NCMS.
Binary logistic regression
Since the dependent variables are discrete and the inequity in healthcare utilization is income-related, we employed binary logistic regression to analyze the differences in healthcare utilization among different income levels under the two medical insurance schemes. The marginal effect estimated in this model will be used to decompose the concentration index in the next part. The model is as follows:
p/(1-p) indicates the healthcare utilization; xji indicates health needs variables; xki indicates the socioeconomic variables; \( {\beta}_j^m \) and \( {\gamma}_k^n \) indicate the marginal effects of each variable; and εi indicates the error term. The income variable in xki is the focus in this model.
Measurement of healthcare utilization inequity
The Concentration Index is employed to quantify the inequity degree of healthcare utilization relating to socioeconomic characteristics, reflecting the changes in the distribution of healthcare utilization among different socioeconomic groups [4]. The Concentration Index can be given by the following equation:
C is the Concentration Index; yi represents the status of healthcare utilization of individual i; ri indicates the scoring rank of income of individual i; and μ is the mean of healthcare utilization. The Concentration Index is defined as twice the area between the concentration curve and the line of equality.Footnote 3 In the graph of the concentration curve, the diagonal is the line of equality. The value of the Concentration Index ranges from − 1 to 1. In addition, if the concentration curve coincides with the diagonal, the value of the Concentration Index is 0, meaning that there is no healthcare utilization inequity; if the concentration curve is above the diagonal, meaning the value of the Concentration Index is negative, there is pro-poor inequity in healthcare utilization; if the concentration curve is below the diagonal, meaning the value of the Concentration Index is positive, then the healthcare utilization is concentrated among the rich.
The concentration index indicates the overall inequity in healthcare utilization. However, healthcare utilization is influenced by a variety of factors, including health needs and socioeconomic factors. The World Health Organization defines the equalization of healthcare utilization as “People who have similar health needs should have the same healthcare utilization”, which indicates that differences in healthcare utilization caused by different health status is reasonable. Therefore, this paper employs the horizontal inequity index to quantify the healthcare utilization inequity caused by the differences in socioeconomic factors, rather than the differences in health needs. By decomposing the concentration index, the contribution of health needs and socioeconomic factors to the inequity of healthcare utilization can be measured separately. The horizontal inequity index can be obtained by subtracting the contribution of health needs from the total concentration index, and the absolute value of it measures the degree of inequity. The specific definitions of variables are shown in Table 1.
The decomposition formula of the concentration index is:
C is the total concentration index; \( \overline{y} \) is the mean of healthcare utilization (including outpatient care and inpatient care), \( \overline{x_j} \) and \( \overline{z_k} \) are the mean values of xj and zk, respectively; Cj and Ck are the concentration index of the health needs and of the socioeconomic variables, respectively; and GCu is the concentration index of the error term. The first part of the formula represents the contribution of health needs to inequity, and the second is the contribution of socioeconomic factors.
Results
Descriptive analysis
Table 2 shows the results of the Chi-square test. As shown in the table, 3593 individuals are insured by URRBMI and 5409 are insured by NCMS.Footnote 4 The differences in healthcare utilization between the two groups are not significant, and the individuals who are insured by NCMS show greater health needs, but the differences are also not significant. However, there are significant socioeconomic differences (education, per capita household income and region) between the URRBMI insured and NCMS insured. Specifically, the socioeconomic status of the population insured by URRBMI is better than that of the population insured by NCMS, especially in per capita household income.
Binary logistic regression analysis
Before measuring the inequity of healthcare utilization, we used binary logistic regression to explore the influence of income on healthcare utilization. Table 3 and Table 4 present the logistic regression results on outpatient and inpatient care, respectively. In terms of outpatient care, there are no statistical disparities among the different income levels in URRBMI. However, among the individuals who are insured by NCMS, the high-income groups tend to have significantly higher healthcare utilization. With regard to inpatient care, as Table 4 shows, there are no significant disparities among different income groups, regardless of the medical insurance schemes. Besides, compared to the highest income groups, the lowest groups show greater utilization of inpatient care, although it is not significant. For other control variables, the health status of individuals who are insured by both insurance schemes has a significant influence on healthcare utilization. The marginal effect estimated in this part was used for the decomposition of the concentration index, and all values were weighted by the sampling probability.
Measurement of inequity of healthcare utilization
Table 5 shows the concentration index of healthcare utilization among the individuals insured by the two medical insurance schemes. The concentration index of outpatient care in URRBMI is positive but small, indicating a tendency of pro-rich inequity in outpatient care, and the concentration index of inpatient care in URRBMI is negative, indicating a pro-poor inequity in inpatient care. In NCMS, both outpatient and inpatient care are negative, which means that they are concentrated in the poor. However, the values in Table 5 represent the concentration index of healthcare utilization that is influenced by health needs and socioeconomic factors, which not fully reflect the inequity. We then make a decomposition of the concentration index in the next part.
Table 3 and Table 4 have shown the marginal effect of the independent variables that is estimated from the binary logistic regression, which is used to decompose the concentration index of healthcare utilization in Eq. 3.
Table 6 and Table 7 show the contributions of independent variables on the concentration index of healthcare utilization in URRBMI and NCMS, and the percentage of each variable’s contribution to the concentration index is also included. From Table 6, we can see that per capita household income shows the greatest contribution to the concentration index of outpatient care in URRBMI and NCMS (401.004% and − 199.016%, respectively), and the second largest is self-assessed health (− 243.945 and 95.848%, respectively). With regard to inpatient care, the contribution percentage of per capita household income to the concentration index is also the greatest in URRBMI and NCMS (22.228 and 39.707%, respectively).
The horizontal inequity index can be obtained by subtracting the contributions of health needs variables from the concentration index in healthcare utilization. Table 8 shows that the horizontal inequity indexes of outpatient utilization for the URRBMI insured and NCMS insured are 0.024 and 0.012, indicating that there is a pro-rich inequity in outpatient utilization. In other words, with the same need for outpatient care, the rich people utilize more outpatient care than the poor people in both the URRBMI and NCMS groups, and the inequity degree of outpatient utilization in URRBMI is larger than that in NCMS. Differing from outpatient care, with the reported horizontal inequity indexes of − 0.043 and − 0.028, the inequity of inpatient utilization for the URRBMI insured and NCMS insured is pro-poor, indicating that the poor utilize more inpatient care in the two groups. This seems to reduce the inequity that described in the introduction because of the poor’s greater need for healthcare. However, on one hand, the inequity that measured by the horizontal inequity index has been standardized for differences in need and it is only related to socioeconomic factors. On the other hand, excessive utilize healthcare services not only damages health, but also wastes medical resources. Especially in the case of medical insurance sharing a large proportion of hospitalization expenses, the poor are more sensitive to the price of healthcare than the rich, and the pro-poor inequity here can be regarded as the moral hazard of medical insurance. Similarly, the absolute value of the horizontal inequity index of inpatient utilization for the URRBMI insured is also larger than that of the NCMS insured, indicating a larger inpatient utilization inequity for the URRBMI insured.
Discussion
The urban-rural segmentation of medical insurance schemes has become an important factor of healthcare utilization inequity in rural China. To provide better coverage services and financial protection for the rural population and to reduce the healthcare utilization inequity in rural areas, China began to establish Urban and Rural Resident Basic Medical Insurance (URRBMI) based on Urban Resident Basic Medical Insurance (URBMI) and the New Cooperative Medical Scheme (NCMS) nationwide in 2016. Against this backdrop, it is worth analyzing the changes in inequity in healthcare utilization after the implementation of URRBMI.
Using the national representative data from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS) that was conducted in 2015, this paper compares the inequity of healthcare utilization between the URRBMI insured and the NCMS insured in rural China. The results reveal that there is no significant difference in healthcare utilization under the two medical insurance schemes. When comparing the inequity under the two medical insurance schemes, we find that the richest utilize more outpatient care in URRBMI, but the difference is not significant. Besides, in the NCMS group, the high-income group tends to utilize significantly more outpatient care. The horizontal inequity index (HI index) also shows that there is a pro-rich inequity of outpatient care in both the URRBMI and NCMS groups and that the HI index of URRBMI is larger than that of NCMS; the result is similar to Chen’s study, which also found that the individuals insured by NCMS have a pro-rich inequity in outpatient utilization [3]. The reason may be related to the characteristics of medical insurance policy in China. As the main aim of NCMS is to reduce the financial barriers in hospitalization and the critical diseases of outpatients, and the URRBMI in rural China was established on the basis of NCMS, so its reimbursement policy also places a higher emphasis on inpatient care initially. The individuals who are insured by URRBMI and NCMS in rural China need to pay most of their outpatient fees. Besides, the high-level hospitals mean better quality of healthcare, so people are more inclined to seek healthcare in high-level hospitals if it is possible. As a result, the individuals who are insured by URRBMI tend to seek outpatient care in high-level hospitals because they think the URRBMI has a higher benefit, which leads to higher medical expenses and a serious pro-rich inequity [5]. For the individuals who are insured by NCMS, most of them seek outpatient care in village clinics. Although the expenses of outpatient care are lower overall, some low-income populations still cannot afford of them.
In terms of inpatient utilization, binary logistic regression shows no significant difference among different income levels in both URRBMI and NCMS. However, the horizontal inequity index (HI index) reveals the inequity behind it, that pro-poor inequity exists in inpatient utilization under the two medial insurance schemes, indicating that the poor utilize more inpatient care than the rich. The absolute value of the HI index in URRBMI is larger than the absolute value in NCMS, meaning that the degree of inequity of URRBMI is higher than that of NCMS. Additionally, the degree of inequity in inpatient is higher than that in outpatient care. The result on inequity of inpatient care among those insured by NCMS is different than those reported for other studies, such as Chen (2018) and Pan (2017), who both found a pro-rich inequity in inpatient care in NCMS [3, 18]. The reason for the pro-poor inequity in our results may be that the NCMS has a high reimbursement rate on inpatient utilization. A large proportion of inpatient expenses can be reimbursed, indicating that the insured face a lower price of inpatient services. In this case, the low-income groups will utilize more inpatient care because they are more sensitive to changes in prices than the high-income groups. In addition, as the aim of URRBMI is to increase the rural residents’ medical insurance benefits and to reduce the disparities between urban and rural areas, the central and local governments have arranged lots of resources to finance the URRBMI. Thus, URRBMI has a higher benefit level than NCMS, such as a higher reimbursement rate in inpatient care [7], that caused a greater pro-poor inequity.
It is also important to bear in mind that there is limitation in this paper. Since the implementation of URRBMI is not a ‘natural experiment’, it is hardly to avoid the problem of self-selection in this process. Therefore, the results of this paper are statistical analysis rather than ‘causal’ analysis. Although the PSM method can solve the self-selection problem to some extent by matching the treatment and control groups, it cannot control the unobservable characteristics (such as the willingness of local leaders). Besides, the PSM has several candidate matching methods, such as one-to-one, one-to-four, radius and kernel matching et al. If the PSM method was applied, we must use the matched data to calculate the concentration index of healthcare utilization among the treatment and control groups, respectively. Against this backdrop, only the one-to-one method can be applied. However, the results we get will not be accurate because large numbers of samples are deleted, and it is also difficult to test the robustness of the PSM matching effect only by the one-to-one matching. As a result, the ‘causal’ relationship cannot be attained in this paper. Meanwhile, there are few studies to analyze the inequity of healthcare utilization in URRBMI and to compare it with that in NCMS. It is reasonable to make a statistical analysis firstly, and the future study could further identify the ‘causal’ effect between the inequity of healthcare utilization and URRBMI.
Conclusion
This paper shows that inequity still exists in rural areas after the integration of urban-rural medical insurance schemes, and there is a certain gap between the actual and the expected goal of URRBMI. Specifically, compared to NCMS, the pro-rich inequity in outpatient care and the pro-poor inequity in inpatient care are more serious in URRBMI. Thus, comprehensive measures to reduce the inequity should be taken: first, covering more outpatient diseases in URRBMI, especially chronic diseases; second, setting a reasonable reimbursement ratio in inpatient care to avoid the moral hazard in URRBMI; and third, for the vulnerable groups, special policies such as reducing the deductible and covering them in catastrophic medical insurance could be considered.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used during the current study are not publicly available due to the confidential policy but are available by applying on the CHARLS official website.
Notes
The data comes from China Statistical Yearbook.
Although the Chinese government began to promote the integration of urban-rural medical insurance nationwide in 2016, some provinces have piloted it previously. By 2014, seven provinces such as Tianjin, Qinghai, Ningxia, Guangdong, etc., had completed the integration of urban-rural medical insurance.
The concentration curve was first put forward by Wagstaff, and it is used to measure the disparities in health distribution that are caused by different socioeconomic characteristics.
In CHARLS 2015, there are only hundreds of rural samples with URRBMI in that some rural respondents do not know that they have covered by URRBMI. Many respondents who have been covered by URRBMI think that they are still covered by NCMS. Besides, URRBMI is implemented at the county level, and the CHARLS provides the respondent’s provincial, city and community information. Therefore, when a community has respondents who are insured by URRBMI, we treat all respondents of the community as being covered by URRBMI.
Abbreviations
- CHARLS:
-
China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
- CI:
-
Concentration Index
- HI:
-
Horizontal inequity
- NCMS:
-
New Cooperative Medical Insurance
- PPS:
-
Population proportion sampling
- URBMI:
-
Urban Residents Basic Medical Insurance
- URRBMI:
-
Urban and Rural Residents Basic Medical Insurance
References
Bobo FT, Elias AY, et al. Inequities in utilization of reproductive and maternal health services in Ethiopia. Int J Equity Health. 2017;16:105.
Cai J, Coyte PC, Zhao H. Decomposing the causes of socioeconomic-related health inequality among urban and rural populations in China: a new decomposition approach. Int J Equity Health. 2017;16:128.
Chen R, Li N, Liu X. Study on the equity of medical services utilization for elderly enrolled in different basic social medical insurance systems in an underdeveloped city of Southwest China. Int J Equity Health. 2018;17:54.
Doorslaer EV, Wagstaff A, Han B, et al. Income-related inequalities in health: some international comparisons. J Health Econ. 1997;16(1):93–112.
Gu H, Sun J, et al. Research on the performance of the integration of urban-rural medical insurance. Dongyue Tribune. 2016;37(10):37–43.
Kim C, Saeed KM, Salehi AS, et al. An equity analysis of utilization of health services in Afghanistan using a national household survey. BMC Public Health. 2016;16:1226.
Liu P, Guo W, Liu H, et al. The integration of urban and rural medical insurance to reduce the rural medical burden in China: a case study of a county in Baoji City. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18:796.
Liu X, Wong H, Liu K. Outcome-based health equity across different social health insurance schemes for the elderly in China. BMC Health Serv Res. 2016;16:9.
Liu XT, Huang H. The reform of medical insurance system and health equality of the old, based on the research of Zhejiang Province. Sociol Res. 2015;(4):94–117.
Liu XL. The integrated urban and rural medical insurance and the utilization of medical care: evidence from China. J World Econ. 2017;(3):169–92.
Li J, Shi L, Liang H, et al. Urban-rural disparities in health care utilization among Chinese adults from 1993 to 2011. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18:102.
Ma C, Gu H, et al. Inequality of opportunity of urban-rural health care utilization under compensation principle. China Econ Q. 2017;16(4):1262–88.
Ma C, Sun XH, et al. The effects of urban-rural integrated medical insurance system on substantial equity of health care and health, based on equality of opportunity. J Public Manag. 2017;14(2):97–109.
Ma C, Zhao GC, et al. The effect of urban-rural integrated medical insurance system on rural residents’ health care behavior. Statistical Res. 2016;33(4):78–85.
Meng Q, Fang H, Liu X, et al. Consolidating the social health insurance schemes in China: towards an equitable and efficient health system. Lancet. 2015;386(2):1484–92.
Malqvist M, Pun A, Raaijmakers H, et al. Persistent inequity in maternal health care utilization in Nepal despite impressive overall gains. Glob Health Action. 2017;10(1):1–7.
Nunez A, Chi C. Equity in health care utilization in Chile. Int J Equity Health. 2013;12:58.
Pan B, Towne SD, Chen YX. The inequity of inpatient services in rural areas and the new-type rural cooperative medical system (NRCMS) in China: repeated cross-sectional analysis. Health Policy Plan. 2017;32(5):634–46.
Qiu YL, Wang ZQ. The evaluation and analysis of integrating urban and rural residents basic medical insurance system. China Health Insurance. 2018;(2):16–20.
Tan Z, Shi F, Zhang H, et al. Household income, income inequality, and health-related quality of life measured by the EQ-5D in Shaanxi, China: a cross-sectional study. Int J Equity Health. 2018;17:32.
Wang Y, Wang J, Elizabeth M, et al. Growing old before growing rich: inequality in health service utilization among the mid-aged and elderly in Gansu and Zhejiang provinces, China. BMC Health Serv Res. 2012;12:302.
Wu Y, Zhang L, Liu X, et al. Geographic variation in health insurance benefits in Qianjiang District, China: a cross-sectional study. Int J Equity Health. 2018;17:20.
Xie E. Income-related inequality of health and health care utilization. Econ Res J. 2009;(2):92–105.
Xiong YG, Huang J. Inequality in health service between urban and rural areas in China:evidence from CHARLS 2013 data. Popul J. 2016;38(6):62–76.
Yan K, Jiang Y, Qiu JF. The equity of China’s emergency medical services from 2010–2014. Int J Equity Health. 2017;16:10.
Yao Q, Liu CJ, Liu ZY, et al. Urban-rural inequality regarding drug prescriptions in primary care facilities – a prepost comparison of the National Essential Medicines Scheme of China. Int J Equity Health. 2015;14:58.
Yiengprugsawan V, Carmichael GA, Lim L, et al. Explanation of inequality in utilization of ambulatory care before and after universal health insurance in Thailand. Health Policy Plan. 2011;26(2):105–14.
Yuan S, Rehnberg C, Sun X, et al. Income related inequalities in new cooperative medical scheme: a five-year empirical study of Junan County in China. Int J Equity Health. 2014;13:38.
Zhang X, Dupre ME, Li Q, et al. Urban-rural differences in the association between access to healthcare and health outcomes among older adults in China. BMC Geriatr. 2017;17:151.
Zhu K, Zhang LY, Yuan SS. Health financing and integration of urban and rural residents’ basic medical insurance systems in China. Int J Equity Health. 2017;16:194.
Zhou Z, Zhu L, Zhou Z, et al. The effects of China’s urban basic medical insurance schemes on the equity of health service utilization: evidence from Shaanxi province. Int J Equity Health. 2014;13:23.
Funding
This study is funded by “Social Security Rights and Income Distribution Equity”, the Philosophy and Social Science Major Research Project of Ministry of Education in China (Grant number: 16JJD840008). The funding bodies were not involved in the design of the study, or data collection, analysis, and interpretation or writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WZW designed the study CYC contributed to the study design, analyzed the data and took the lead in the manuscript writing. PTY helped in the writing of the final draft of the manuscript. LXD supervised the study design. HHW made critical revisions of the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
Zengwen Wang has an MSc and a Ph.D. degree in pure mathematics and public administration from Wuhan University, China, respectively. He is a Professor in the school of Government at Nanjing University and a Senior Researcher in the Center for Social Security Studies of Wuhan University. His research areas are social welfare and economic development, government management decision making, poverty analysis and employment. He has authored two books and published more than 60 articles to professional journals including journals such as Journal of Public Management, Symmetry, Journal of Political Science, The Population of China Science, Journal of Chinese Administrative Management, Journal of Chinese Soft Science and others.
Yucheng Chen is a Ph.D. student in the Center for Social Security Studies of Wuhan University, China.
Tianyi Pan is a postgraduate in the Center for Social Security Studies of Wuhan University, China.
Xiaodi Liu has an MSc and a Ph.D. degree in pure mathematics from Wuhan University, Management Science from College of Economics and Management at Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, China, respectively. He is an Associate Professor in the school of Mathematics and Physics at Anhui University of Technology. His research areas are multiple attribute decision making, clustering analysis and aggregation operators. He has published more than 20 papers in journals, including journals such as Technological and Economic Development of Economy, Complexity, Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, Journal of Business Economics and Management, Applied Soft Computing, Information Fusion, Symmetry, Journal of Grey System, Mathematical Problems in Engineering, Journal of Intelligent Systems and others.
Hongwei Hu has a Ph.D. degree in Social Security from Wuhan University, and he also has postdoctoral research experience in Guanghua School of Management, Peking University. Now he is an associate professor in School of Public Administration and Policy, Renmin University of China. His research areas are social security, social policy and social work. He has published more than 70 papers in journals, such as Children and Youth Services Review, BMC Geriatrics, International Journal for Equity in Health, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, Chinese Journal of Population Science, Population Research, Population and Society and so on.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent for publication
Author gives full consent for publication of this paper in International Journal for Equity in Health.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Chen, Y., Pan, T. et al. The comparison of healthcare utilization inequity between URRBMI and NCMS in rural China. Int J Equity Health 18, 90 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12939-019-0987-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12939-019-0987-1