Abstract
Background
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a rare disease characterized by proliferation and occlusion of small pulmonary arterioles, which has been associated with a high mortality rate. The pathogenesis of PH is complex and incompletely understood, which includes both genetic and environmental factors that alter vascular structure and function.
Methods
Thus we aimed to reveal the potential genetic etiology of PH by targeting 143 tag SNPs of 14 candidate genes. Totally 208 individuals from Chinese Han population were enrolled in the present study, including 109 non-idiopathic PH patients and 99 healthy controls.
Results
The data revealed that 2 SNPs were associated with PH overall susceptibility at p < 3×10− 4 after Bonferroni correction. The top hit was rs6557421 (p = 4.5×10− 9), located within Nox3 gene on chromosome 6. Another SNP rs3744439 located in Tbx4 gene, also showed evidence of association with PH susceptibility (p = 1.2×10− 6). The distribution of genotype frequencies of rs6557421 and rs3744439 have dramatic differences between PH patients and controls. Individuals with rs6557421 TT genotype had a 10.72-fold/14.20-fold increased risk to develop PH when compared with GG or GG/GT carriers in codominant or recessive model, respectively (TT versus GG: 95%CI = 4.79–24.00; TT versus GG/GT: 95%CI = 6.65–30.33). As for rs3744439, AG genotype only occurred in healthy controls but has not been observed in PH patients. We further validated the result by using 26 different populations from five regions around the globe, including African (AFR), American (AMR), East Asian (EAS), European (EUR), and South Asian (SAS). In consistent with the present case-control study’s results, significantly different genotype frequencies of the observed SNPs existed between PH patients and healthy individuals from all over the world.
Conclusions
The results suggested that rs6557421 variant in Nox3 and rs3744439 variant in Tbx4 might have potential effect on individual susceptibility to pulmonary hypertension, which could lead to therapeutic or diagnosis approaches in PH.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
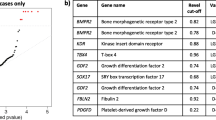
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a rare disease characterized by proliferation and occlusion of small pulmonary arterioles, leading to progressive elevation of pulmonary artery pressure, pulmonary vascular resistance, and right ventricular failure [1]. There are 3 subtypes of PH according to the National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD), including heritable pulmonary hypertension (HPH), idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPH) and associated pulmonary hypertension (APH) [2]. More than half of the PH patients are non-idiopathic PH, which are also known as secondary PH. During the present study, we focused on the genetic susceptibility of non-idiopathic PH. Revealing the genetic etiology of non-idiopathic PH would facilitate diagnosis and development of novel therapies in the future. During the present study, we reviewed and screened several candidate genes that are potentially or directly associated with PH occurrence (Table 1).
In summary, these genes were shown to be associated or potentially related with PH development though the molecular mechanism had not been well understood. To further clarify the association and reveal the candidate functional variants, we conducted the limited scale genome wide association study. One hundred forty-three tag SNPs were screened from the sequences between the upstream and downstream 2Kb of the 14 studied genes. The screening population data are from Chinese Han population in Beijing (CHB) of the Hapmap Project (NCBI build 36, dbSNPb126) and the candidate SNPs were screened by using Haploview software.
Methods
Samples
Totally 208 individuals were enrolled in the present study, including 109 non-idiopathic PH patients and 99 healthy controls. Patients were consecutively recruited from the Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University between May 2014 and July 2016. Clinical information was obtained from medical records, including gender, age, drink, smoke and coronary artery disease (CAD) history and so on. Baseline profiles of the studied population were summarized in Table 2. None of the patients have connective tissue diseases, HIV infection, portal hypertension, congenital heart diseases or thyroid dysfunction. The control subjects were collected from healthy volunteers who visited the Sir Run Run Hospital Nanjing Medical University for medical examination during the same period. The study was performed with the approval of the ethics committee of the Nanjing Medical University and the informed consent was obtained from each participant.
Experimental design and Genotyping
Genomic DNA was extracted from 200 μl EDTA-anticoagulated peripheral blood using a commercial extraction kit (Tiangen Biotech Corporation, Beijing, China) according to the instruction manual. The 143 tag SNPs in 109 PH patients were firstly genotyped by using Illumina X-10 platform, and the sequencing was done by commercial company (Decode Genomics BioTech Co., Ltd, Nanjing, China). The genotyping results were then compared with healthy individuals from Southern Han Chinese (CHS) population of 1000G database. And 2 SNPs emerged at a significant level (P < 3×10-4) (Fig. 1). To confirm the finding, we further genotyped 2 SNPs in 99 healthy individuals from Nanjing, Jiangsu by performing fluorescent PCR and Ligase detection reaction (LDR). The primers were designed by using Primer 3 online software version 0.4.0 (http://frodo.wi.mit.edu/) and Oligo software version 6.3.1 (Molecular Biology Insights, USA). The SNPs were amplified in a final volume of 20 μl that contained 50 ng of DNA, 2 μl 1×buffer, 0.6 μl 3 mM Mg2+, 2 μl 2 mM dNTP, 0.2 μl Taq DNA polymerase (1 unit/μl) and appropriate concentrations of primers. The PCR reaction was subjected to an initial denaturation at 95 °C for 2 min, followed by 40 cycles of amplification consisting of denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s, annealing at 53 °C for 90 s, extension at 65 °C for 30 s, followed by final extension at 65 °C for 10 mim. The LDR was carried out on the PRISM 3730 DNA analyzer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA). The LDR were performed in a total volume of 10 μl that contained 4 μl PCR production, 1 μl 1×buffer, 1 μl probe mix, 0.05 μl Taq DNA polymerase (2 unit/μl). The LDR condition was 95 °C for 2 mim, followed by 40 cycles of 15 s at 94 °C and 25 s at 50 °C. The SNPs were further genotyped by using Genemapper.
Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed by using SPSS 19 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL). Genotype frequencies of SNPs were obtained by directed computing. Genotypic association analyses in a case-control pattern assuming codominant, dominant, recessive and overdominant genetic models were performed using SNPstats [3]. Odds ratio (OR) and respective 95% confidence interval were reported to evaluate the effects of any differences between allele and genotype frequencies.
Results
Candidate SNP selection
Totally 143 SNPs were successfully genotyped in 109 PH patients. After comparing the genotyping results with the data generated from 105 individuals from Southern Han Chinese population in 1000G database, the results demonstrated that 2 SNPs were associated with PH with overall susceptibility at p < 3×10− 4 after Bonferroni adjustment. The related analysis was shown in Fig. 1. The top hit was rs6557421 (p = 4.5×10− 9), which is located in Nox3 gene on chromosome 6. Another SNP rs3744439 located in Tbx4 gene, also showed evidence of association with PH susceptibility (p = 1.2×10− 6).
We further genotyped the 2 SNPs in 99 healthy control subjects. The distribution of genotype frequencies of rs6557421 and rs3744439 was illustrated in Fig. 2. Dramatic differences existed between PH patients and controls. As shown in Table 3, individuals with rs6557421 TT genotype had a 10.72-fold/14.20-fold increased risk to develop PH when compared with GG or GG/GT carriers in codominant or recessive model, respectively (TT versus GG: 95%CI = 4.79–24.00; TT versus GG/GT: 95%CI = 6.65–30.33). In dominant model, significantly increased PH susceptibility was associated with GT/TT genotypes compared with GG genotype (OR = 2.48, 95%CI = 1.39–4.41). Furthermore, dramatically decreased PH risk was associated with GT genotype when compared with GG/TT genotypes in an overdominant model.
As shown in Fig. 2b and Table 4, rs3744439 AG genotype only occurred in healthy controls which had not been observed in PH patients.
Stratification analysis was also performed, and PH patients were divided into three groups according to the Nox3 rs6557421 genotypes. The distribution of patients’ left atrial diameter (LA), left ventricular end diastolic diameter (LvIDd), interventricular septal thickness (IVST), left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and systolic pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) were compared between each groups (Fig. 3). No significant differences were observed among different genotyping groups.
Comparison between different populations around globe
We further validated the observation by using 26 different populations from five regions around the globe, including African (AFR), American (AMR), East Asian (EAS), European (EUR), and South Asian (SAS). As illustrated in Fig. 4a and b, the distribution of rs6557421 and rs3744439 genotypes’ frequencies of control group from Chinese Han population was quite similar to which from Asian populations. In consistent to the present case-control study’s results, significantly different genotype frequencies existed between PH Patients and healthy individuals from all over the world (Fig. 4a and b).
Discussion
Among NADPH oxidases, Nox3 seems to have the most restricted expression pattern in the mammalian organism. Nox3 is specifically localized to the inner ear. Thus the previous studies mostly focused on the unique function of Nox3 involving in the biogenesis of otoconia/otolith [4]. However, few studies have revealed the potential critical role of Nox3 in the pathophysiological process of PH development. Nox3 is the predominant source of palmitate-induced ROS generation [5]. Nox3 activation during ischemia-reperfusion injury may contribute to the development of primary graft dysfunction after lung transplantation [6]. Upregulated Nox3 leads to increased oxidant generation and elastolytic activity, resulting in increased oxidant injury and death in mice and lung endothelial cells [7]. Treatment of Tlr−/− mice or endothelial cells with Nox3 siRNA or chemical NADPH inhibitors could reverse the phenotype [7]. Overall, the studies identified that Nox3 could be a potential therapeutic target in the lungs.
The present case-control study revealed that a Nox3 tagSNP rs6557421 had a significantly association with the PH susceptibility. When random individuals carry rs6557421 TT genotype, they have nearly 10-fold increased risk to develop PH when compared with GG or GG/GT carriers. Moreover, GT genotype carriers have a significantly decreased PH risk compared with GG/TT genotype carriers. To further investigate the racial disparities, we enrolled 26 populations from 1000G to make a comparison. All the populations from different continents possessed relatively low frequency of TT genotype (AFR = 0.006, AMR = 0.052, EAS = 0.113, EUR = 0.056, SAS = 0.08, Han in present = 0.101). On the contrary, the proportion of TT genotype carriers in PH patients reached 0.615. The data indicated that TT genotype might be associated with increased PH in different races.
Mutations in Tbx4 have been proved to be associated with PH onset [8]. Tbx4 shows high specific expression in lung fibroblasts and broadly regulates fibroblast-related pathway that partly contributes to super-enhancer-mediated transcriptional programs [9]. Decreased Tbx4 in the pulmonary mesenchyme during fetal lung development may lead to the decrease or arrest of airway branching, thus contributing to PH [10]. Tbx4 was also regarded as a mesenchymal transcription factor that drove myofibroblasts accumulation and the development of lung fibrosis [11].
Our research revealed that Tbx4 rs3744439 had a significant association with PH risk. The frequencies of AG genotype in present control Chinese Han population and other 26 populations around the globe are all over than 0.10 (Han in present = 0.24, AFR = 0.23, AMR = 0.19, EAS = 0.17, EUR = 0.10, SAS = 0.14). Interestingly, during the PH patients, AG and GG genotype frequencies were 0. The data suggested that AG genotype could be a protective factor for the PH development.
The present study has an obvious limitation. As noted in the Methods section that the ages of patients and controls are significantly different. The controls are younger, and they might develop PH in the future. Considering the relative low incidence of PH, we believe the results are reliable. To further validate the results, healthy independent individuals from 1000G database were also included. And the results were consistent.
Conclusions
In summary, it is biologically plausible that rs6557421 variant in Nox3 and rs3744439 variant in Tbx4 may have potential effects on individual susceptibility to pulmonary hypertension, which could lead to therapeutic or diagnosis approaches in PH.
Abbreviations
- ATP8B4:
-
ATPase phospholipid transporting 8B4
- CHX7:
-
Chromobox 7
- CYBB:
-
Cytochrome b-245 beta chain
- IL6:
-
Interleukin 6
- NORD:
-
National Organization for Rare Disorders
- Nox3:
-
NADPH oxidase 3
- Nox4:
-
NADPH oxidase 4
- Nox5:
-
NADPH oxidase 5
- OLR-1:
-
Oxidized low density lipoprotein receptor 1
- PH:
-
Pulmonary hypertension
- SLC4A4:
-
Solute carrier family 4 member 4
- Tbx4:
-
T-box4
- TFEC:
-
Transcription factor EC
- THBS1:
-
Thrombospondin 1
References
Barman SA, Chen F, Li X, Haigh S, Stepp DW, Kondrikov D, Mahboubi K, Bordan Z, Traber P, Su Y, Fulton DJR. Galectin-3 promotes vascular remodeling and contributes to pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018;197:1488–92.
Soubrier F, Chung WK, Machado R, Grunig E, Aldred M, Geraci M, Loyd JE, Elliott CG, Trembath RC, Newman JH, Humbert M. Genetics and genomics of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:D13–21.
Sole X, Guino E, Valls J, Iniesta R, Moreno V. SNPStats: a web tool for the analysis of association studies. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:1928–9.
Zhang X, Shan P, Jiang G, Cohn L, Lee PJ. Toll-like receptor 4 deficiency causes pulmonary emphysema. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:3050–9.
Garcia-Redondo AB, Aguado A, Briones AM, Salaices M. NADPH oxidases and vascular remodeling in cardiovascular diseases. Pharmacol Res. 2016;114:110–20.
Cantu E, Shah RJ, Lin W, Daye ZJ, Diamond JM, Suzuki Y, Ellis JH, Borders CF, Andah GA, Beduhn B, et al. Oxidant stress regulatory genetic variation in recipients and donors contributes to risk of primary graft dysfunction after lung transplantation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015;149:596–602.
Zhang Y, Shan P, Srivastava A, Jiang G, Zhang X, Lee PJ. An endothelial Hsp70-TLR4 axis limits Nox3 expression and protects against oxidant injury in lungs. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016;24(17):991–1012.
Zhu N, Gonzaga-Jauregui C, Welch CL, Ma L, Qi H, King AK, Krishnan U, Rosenzweig EB, Ivy DD, Austin ED, et al. Exome sequencing in children with pulmonary arterial hypertension demonstrates differences compared with adults. Circ Genom Precis Med. 2018;11:e001887.
Horie M, Miyashita N, Mikami Y, Noguchi S, Yamauchi Y, Suzukawa M, Fukami T, Ohta K, Asano Y, Sato S, et al. TBX4 is involved in the super-enhancer-driven transcriptional programs underlying features specific to lung fibroblasts. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018;314:L177–l191.
Takahashi T, Friedmacher F, Zimmer J, Puri P. Expression of T-box transcription factors 2, 4 and 5 is decreased in the branching airway mesenchyme of nitrofen-induced hypoplastic lungs. Pediatr Surg Int. 2017;33:139–43.
Xie T, Liang J, Liu N, Huan C, Zhang Y, Liu W, Kumar M, Xiao R, D’Armiento J, Metzger D, et al. Transcription factor TBX4 regulates myofibroblast accumulation and lung fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2016;126:3063–79.
Yang HC, Liang YJ, Chen JW, Chiang KM, Chung CM, Ho HY, Ting CT, Lin TH, Sheu SH, Tsai WC, Chen JH, Leu HB, Yin WH, Chiu TY, Chern CL, Lin SJ, Tomlinson B, Guo Y, Sham PC, Cherny SS, Lam TH, Thomas GN, Pan WH. Identification of IGF1, SLC4A4, WWOX, and SFMBT1 as hypertension susceptibility genes in Han Chinese with a genome-wide gene-based association study. Plos One. 2012;7(3):e32907.
Wang H, Albadawi H, Siddiquee Z, Stone JM, Panchenko MP, Watkins MT, Stone JR. Altered vascular activation due to deficiency of the NADPH oxidase component p22phox. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2014;23(1):35-42.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81570378, No.81772020 and No.81801879), the Science and Technology of Jiangsu Province China (BK20170048 and BK20161034), and Jiangsu Specially-Appointed Professor program. The National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Science and Technology of Jiangsu Province China and Jiangsu Specially-Appointed Professor program played no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FC and PC designed the study and were major contributors in writing the manuscript. KL, ZQW and JCY collected samples of patients and controls. YFY, HJH and YJY performed the experiments. CYY, YP, ZL and DL analyzed and interpreted the data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was performed with the approval of the ethics committee of the Nanjing Medical University and the written informed consent was obtained from each participant.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, C., Li, K., Yu, Y. et al. Genome-wide association study identifies loci and candidate genes for non-idiopathic pulmonary hypertension in Eastern Chinese Han population. BMC Pulm Med 18, 158 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-018-0719-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12890-018-0719-0