Abstract
Background
The transanastomotic feeding tube (TAFT) is widely used around the world in patients with esophageal atresia (EA). However, the safety of the use of TAFT is still unknown and remains to be clarified.
Methods
The following electronic databases were searched: PubMed, EMBASE and Cochrane. Studies comparing outcomes in patients with the use of TAFT (TAFT+) and patients without the use of TAFT (TAFT-) were scrutinized. The quality of included studies was evaluated with the Newcastle–Ottawa scale score. Statistical heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 value. A fixed or random-effect model was applied.
Results
Four retrospective controlled studies involving 455 patients were included. The pooled estimates showed that the use of TAFT significantly increased the risk of stricture, with a risk ratio (RR) of 1.83 (95% CI 1.30–2.58; P = 0.0005). The meta-analyses of other postoperative complications did not show significant differences between TAFT+ and TAFT- group, with a RR of 1.65 (95% CI 0.93–2.93; P = 0.09) for anastomotic leakage, 0.91 (95% CI 0.34–2.44; P = 0.85) for sepsis, 1.89 (95% CI 0.22–16.20; P = 0.56) for tracheomalacia, 0.50 (95% CI 0.13–1.93; P = 0.31) for gastroesophageal reflux, 1.29 (95% CI 0.28–5.92; P = 0.74) for wound infection, and 0.97 (95% CI 0.03–36.75; p = 0.99) for pneumonia.
Conclusions
This study demonstrates that the use of TAFT in patients with EA significantly increases the risk of stricture. However, TAFT is not associated with other complications, including anastomotic leakage, sepsis, tracheomalacia, gastroesophageal reflux, wound infection and pneumonia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Esophageal atresia (EA) is a rare congenital gastrointestinal anomaly that affects 1 per 4000 newborns [1,2,3]. Approximately 93% of EA are associated with tracheoesophageal fistula [1]. Although the survival rate of EA is higher than 90% with the advances in perioperative management and surgical techniques, the postoperative complications are still frequent [4,5,6]. The most common complication is stricture with an estimated prevalence of 40%, followed by anastomotic leakage occurring in about 20% of patients [6, 7].
In 1996, Moriarty et.al [8] first reported the use of transanastomotic feeding tube (TAFT) in patients with EA. Currently, TAFT is widely used around the world [9]. However, studies investigating the effects of TAFT on patients with EA have conflicting results [10,11,12,13,14]. Proponents recommend that TAFT is able to allow earlier initiation of enteral feeds and potentially supports anastomosis as stenting [8, 10]. However, other researchers believe that TAFT is implicated in increased risk of stricture and anastomotic leakage [11, 13, 14]. Unfortunately, most studies had small sample sizes. The benefits and risks of TAFT in patients with EA still remain to be clarified.
Thus, we conducted this meta-analysis with the aim to elucidate the safety of TAFT in patients with EA by evaluating the prevalence of postoperative complications.
Methods
Study selection
Only controlled studies comparing outcomes in patients with the use of TAFT (TAFT+) and without the use of TAFT (TAFT-) were eligible for inclusion. In addition, eligible studies were requested to report at least one of the following complications: stricture and anastomotic leakage. The eligible literatures were limited to being published in English.
Search strategy
Two investigators (C.W. and L.F.) systematically searched the PubMed, EMBASE and Cochrane Library databases to identify studies and determine eligibility. The core search terms were ‘esophageal’, ‘oesophageal’, ‘atresia’, ‘tracheoesophageal fistula’, ‘transanastomotic’, ‘transanastomosis’ and ‘tube’, and these words were combined with Boolean operators AND, OR, and NOT. Both of the two reviewer scrutinized titles and abstracts, and screened full-text manuscripts of selected studies eligible for inclusion criteria independently. Reference lists of eligible literatures were scrutinized to identify any other potential studies.
Data extraction and quality assessment
We defined anastomotic leakage and stricture as the primary outcomes. Other complications, including sepsis, tracheomalacia, gastroesophageal reflux, wound infection and pneumonia, were defined as the secondary outcomes. Data, including first author, publication year, numbers of cases and controls, study design, characteristics of the study population, the primary outcomes, and the secondary outcomes, were extracted using a standardized data-extraction sheet by two reviewers (C.W. and L.F.). Disagreements were resolved by checking the manuscripts and/or contacting the authors if necessary. The quality of included cohort studies was assessed in accord with the Newcastle-Ottawacriteria scale (NOS) scores [15]. The total scores were ranged from 0 to 9 for cohort studies. Studies with a score of at least 6 were categorized as “high quality.”
Statistical analysis and exploration of heterogeneity
All statistical analyses were conducted by using Reviewer Manager 5.3 (Cochrane Collaboration). Pooled results were expressed as the risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for all end points. The Mantel–Haenszel method was used to combine the summary statistics. The funnel plots were used to assess the potential for publication bias. The I2 method was used to assess heterogeneity among studies, with higher I2 value indicating higher heterogeneity. If the I2 value was less than 50%, a fixed-effects model of analysis was used. Otherwise, a random-effects model was used.
Results
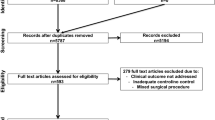
In total, we identified 51 articles through online search and reference lists of relevant publications (Fig. 1). After scrutinizing the titles and abstracts, a total of five full-text manuscripts were assessed for eligibility. Finally, four of five studies met the inclusion criteria. All of these studies were retrospective observational clinical studies [10,11,12,13]. The characteristics of the four studies were shown in Table 1. A total of 455 patients with EA were assigned to the TAFT+ group (n = 335) or the TAFT- group (n = 120). Data regarding outcomes of each study are summarized in Table 2. No obvious publication bias was detected in all analyses.
Primary outcome
Anastomotic leakage
All four studies investigated the postoperative occurrence of anastomotic leakage in patients with or without the use of TAFT [10,11,12,13]. The rate of anastomotic leakage was 18.5% (62, n = 335) in TAFT+ group and 10.8% (13, n = 120) in TAFT- group. There was no significant heterogeneity among studies (I2 = 0%). The overall pooled RR was 1.65 (95% CI 0.93–2.93; P = 0.09). The result showed no significant discrepancy for anastomotic leakage between two groups (Fig. 2).
Stricture
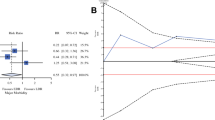
Stricture was reported in all four studies [10,11,12,13]. Two studies reported that the use of TAFT was associated with a high rate of stricture [11, 13]. In total, there were 162 of 335 patients in TAFT+ group and 30 of 120 patients in TAFT- group diagnosed as stricture (Fig. 2). The I2 method identified low heterogeneity among four studies (I2 = 31%). The pooled estimate showed the use of TAFT significantly increased the risk of stricture, with a RR of 1.83 (95% CI 1.30–2.58; P = 0.0005).
Secondary outcome
Sepsis
Two studies investigated the presence of sepsis. A total of 53 patients were involved [10, 12]. No discernible heterogeneity was detected with I2 = 0% (Fig. 3). There was no significant discrepancy for sepsis between TAFT+ and TAFT- group, with a RR of 0.91(95% CI 0.34–2.44; P = 0.85).
Tracheomalacia
Two studies recorded the occurrence of tracheomalacia [10, 12]. A moderate heterogeneity was examined with I2 = 50%. A random-effects model of analysis was used to calculate the pooled RR. No discernible difference for tracheomalcia was detected between TAFT+ and TAFT- groups, with a RR of 1.89 (95% CI 0.22–16.20; P = 0.56) (Fig. 3).
Gastroesophageal reflux
Gastroesophageal reflux was recorded in two studies [10, 12]. The pooled estimate indicated no significant difference between TAFT+ and TAFT- groups, with a RR of 0.50(95% CI 0.13–1.93; P = 0.31; I2 = 4%) (Fig. 3).
Wound infection
Wound infection as an outcome was reported in two studies, with a total of 53 patients involved [10, 12]. No heterogeneity was detected between two studies (I2 = 0%). The occurrence of wound infection was not significantly different between two groups, with a RR of 1.29 (95% CI 0.28–5.92; P = 0.74) (Fig. 3).
Pneumonia
Pneumonia after operation was reported in two studies [10, 12]. There were 23 patients and 30 patients in TAFT+ group and TAFT- group, respectively. A random-effects model of analysis was used owing to high heterogeneity (I2 = 82%). The occurrence of pneumonia was not significantly different between two groups, with a RR of 0.97 (95% CI 0.03–36.75; P = 0.99) (Fig. 3).
Discussion
EA is a rare malformation. The operation for EA is inevitable. However, the perioperative management for EA is variable [1]. Clinically, TAFT is widely used to initiate feeds. Dave Lal et al. [16] performed an international survey involving 170 pediatric surgeons from 31 countries. The results revealed that 83% of surgeons placed TAFT. Another study indicated that 90% of 168 surgeons used TAFT [13]. Although TAFT is widely used, the advantages and disadvantages are still debated. The important benefits of TAFT include early enteral feeding and reduction of total parenteral nutrition duration. However, there was no significant difference in the median number of postoperative days starting enteral feeds and total parenteral nutrition duration between TAFT+ and TAFT- group in retrospective studies [10, 13]. Some studies suggested the TAFT was related to harm. Little evidence exists regarding the safety of TAFT in patients with EA. The concern needs to be delineated.
Postoperative complications occur in 62% patients with EA [7, 13]. Anastomotic leakage and stricture occur frequently in approximately 20 and 40% of the population, respectively. Our study indicates that the use of TAFT is not associated with a higher risk of anastomotic leakage. Lal DR et al. suggested that TAFT might be associated with stricture [13]. Unfortunately, robust evidence is lacking to confirm the risk. Our meta-analysis confirmed that the use of TAFT was associated with an increased risk of stricture. This result is consistent with another study showing that the use of TAFT is associated with an increase of stricture and less ananstomotic collagen formation in animal models [17]. Two potential mechanisms were raised to explain the impact of TAFT on the occurrence of stricture, including mechanical shearing at the anastomosis and dilation of the lower esophageal sphincter resulting in increased exposure of the anastomosis to reflux [13]. It is high time to reconsider whether the worldwide use of TAFT is a right perioperative management in patients with EA.
There is a hypothesis that TAFT might dilate the esophageal sphincter, and therefore result in exposure of the anastomosis to reflux. It is concerned whether the use of TAFT can increase the risk of gastroesophageal reflux. Gastroesophageal reflux may lead to early postoperative complications including stricture formation, aspiration pneumonia and failure to thrive, or result in late complications, such as Barrett’s esophagus and cancer [18,19,20]. In the present study, however, we found that the utilization of TAFT in patients with EA was not related to the development of gastroesophageal reflux. Thus, the hypothesis that TAFT leads to exposure of the anastomosis to reflux in patients with EA might be untenable. Additionally, our meta-analysis revealed that TAFT did not increase the risk of pneumonia, suggesting that there might have no relationship between TAFT and gastroesophageal reflux. The risks of other complications using TAFT, including sepsis, tracheomalacia and wound infection, were also assessed. Similarly, we demonstrated that the use of TAFT did not significantly increase the risk of these complications.
Some limitations of this study should be recognized. Although all four studies were of high quality in accordance with the Newcastle-Ottawa criteria (all NOS ≥ 6), these studies were retrospective control studies. In addition, two of four studies had small sample sizes.
Conclusions
This meta-analysis provides valuable evidence regarding the risks of postoperative complications of the use of TAFT in patients with EA. Our study reveals that the use of TAFT significantly increases the risk of stricture. In addition, our data demonstrate that the use of TAFT is not associated with other complications, including anastomotic leakage, sepsis, tracheomalacia, gastroesophageal reflux, wound infection and pneumonia. Future prospective, randomized, and controlled studies are needed to extend these conclusions toward to further confirm the benefits and risks of the use of TFAT in patients with EA.
Abbreviations
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- EA:
-
Esophageal atresia
- NOS:
-
Newcastle-Ottawacriteria scale
- RR:
-
Risk ratio
- TAFT:
-
Transanastomotic feeding tube
References
Tam PKH, Chung PHY, St Peter SD, Gayer CP, Ford HR, Tam GCH, et al. Advances in paediatric gastroenterology. Lancet. 2017;390(10099):1072–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(17)32284-5.
Pedersen RN, Calzolari E, Husby S, Garne E. Oesophageal atresia: prevalence, prenatal diagnosis and associated anomalies in 23 European regions. Arch Dis Child. 2012;97(3):227–32. https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2011-300597.
Nassar N, Leoncini E, Amar E, Arteaga-Vazquez J, Bakker MK, Bower C, et al. Prevalence of esophageal atresia among 18 international birth defects surveillance programs. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 2012;94(11):893–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdra.23067.
Wang B, Tashiro J, Allan BJ, Sola JE, Parikh PP, Hogan AR, et al. A nationwide analysis of clinical outcomes among newborns with esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistulas in the United States. J Surg Res. 2014;190(2):604–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2014.04.033.
Allin B, Knight M, Johnson P, Burge D. Outcomes at one-year post anastomosis from a national cohort of infants with oesophageal atresia. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e106149. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0106149.
Sulkowski JP, Cooper JN, Lopez JJ, Jadcherla Y, Cuenot A, Mattei P, et al. Morbidity and mortality in patients with esophageal atresia. Surgery. 2014;156(2):483–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2014.03.016.
Lal DR, Gadepalli SK, Downard CD, Ostlie DJ, Minneci PC, Swedler RM, et al. Perioperative management and outcomes of esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula. J Pediatr Surg. 2017;52(8):1245–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2016.11.046.
Moriarty KP, Jacir NN, Harris BH, Latchaw LA, Robertson FM, Crombleholme TM. Transanastomotic feeding tubes in repair of esophageal atresia. J Pediatr Surg. 1996;31(1):53–4 discussion 4-5.
Zani A, Eaton S, Hoellwarth ME, Puri P, Tovar J, Fasching G, et al. International survey on the management of esophageal atresia. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2014;24(1):3–8. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1350058.
Alabbad SI, Ryckman J, Puligandla PS, Shaw K, Nguyen LT, Laberge JM. Use of transanastomotic feeding tubes during esophageal atresia repair. J Pediatr Surg. 2009;44(5):902–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2009.01.027.
Fusco JC, Calisto JL, Gaines BA, Malek MM. A large single-institution review of tracheoesophageal fistulae with evaluation of the use of transanastomotic feeding tubes. J Pediatr Surg. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2017.10.026.
Narayanan SK, Vazhiyodan AP, Somnath P, Mohanan A. Is routine use of transanastomotic tube justified in the repair of esophageal atresia? World J Pediatr. 2017;13(6):584–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-017-0047-0.
Lal DR, Gadepalli SK, Downard CD, Ostlie DJ, Minneci PC, Swedler RM, et al. Challenging surgical dogma in the management of proximal esophageal atresia with distal tracheoesophageal fistula: outcomes from the Midwest pediatric surgery consortium. J Pediatr Surg. 2018;53(7):1267–72.
Pinheiro PF. Simoes e Silva AC, Pereira RM. current knowledge on esophageal atresia. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(28):3662–72. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i28.3662.
Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010 Sep;25(9):603–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z.
Lal D, Miyano G, Juang D, Sharp NE, St Peter SD. Current patterns of practice and technique in the repair of esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistua: an IPEG survey. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2013;23(7):635–8. https://doi.org/10.1089/lap.2013.0210 2018;53(7):1267–72.doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2017.05.024.
Yurtcu M, Toy H, Arbag H, Caglayan O. Surgical management with or without a nasogastric tube in esophageal repairs. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2012;76(1):104–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2011.10.012.
Gorodner V, Viscido G, Signorini F, Obeide L, Moser F. Gastroesophageal reflux disease and morbid obesity: evaluation and treatment. Updat Surg. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-018-0579-4.
Krug E, Bergmeijer JH, Dees J, de Krijger R, Mooi WJ, Hazebroek FW. Gastroesophageal reflux and Barrett's esophagus in adults born with esophageal atresia. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94(10):2825–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.1423_c.x.
Shawyer AC, Pemberton J, Flageole H. Post-operative management of esophageal atresia-tracheoesophageal fistula and gastroesophageal reflux: a Canadian Association of Pediatric Surgeons annual meeting survey. J Pediatr Surg. 2014;49(5):716–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2014.02.052.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81401606 and 81400862) and the Science Foundation for Excellent Youth Scholars of Sichuan University (2015SU04A15). These foundations provided financial support in publication charges.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YJ contributed to the design of the study. CW and LF performed the literature search, reviewed the data and analyzed the data. YJ, CW, LF and YL interpreted the statistical analysis and drafted the manuscript. All of the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Feng, L., Li, Y. et al. What is the impact of the use of transanastomotic feeding tube on patients with esophageal atresia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pediatr 18, 385 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-018-1359-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-018-1359-5