Abstract
Background
Congenital ocular melanocytosis has been shown to be extremely uncommon in studies of numerous infants and children with retinoblastoma and disorders such as retinopathy of prematurity.
Case presentation
A 33-month-old Caucasian boy presented with a solid white predominantly endophytic retinoblastoma filling most of the nasal aspect of the fundus and extensive vitreous seeding. Fundus exam of the contralateral eye showed a broad-based flat melanotic area of the choroid extending from the subfoveal region to the ora serrata temporally. The child was treated by enucleation of the retinoblastoma-containing eye (homozygous non-germline RB1 mutation) and is being monitored annually. The patient has been followed for 4 years.
Conclusions
This rare presentation of advanced unilateral retinoblastoma and contralateral isolated choroidal melanocytosis in a young child emphasizes the importance of detailed fundus mapping of the non-affected eye and has potential implications due to the increased incidence of uveal melanoma later in life.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Retinoblastoma is the most common pediatric neoplasm of the eye and it accounts for 2.5% to 4% of all pediatric cancers [1]. The incidence of retinoblastoma is approximately 11.8 per million children aged 0–4 years US [2]. This cancer has 2 distinct clinical forms: bilateral or multifocal, heritable form (25% of all cases), and unilateral or unifocal form (75% of all cases), 90% of which are nonhereditary. However, about 10% of germline cases can be unilateral and unifocal. Although patients with germline disease have an increased risk to develop skin melanoma, there is no established relationship between retinoblastoma and uveal melanoma [1].
Due to the rarity of ocular melanocytosis and the documented increased incidence of uveal melanoma in eyes with complete ocular melanocytosis [3], we thought this unprecedented association deserves to be reported.
Case presentation
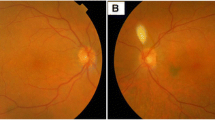
A 33-month-old Caucasian boy presented with leukocoria right eye (OD). Fundus examination OD revealed a solid white predominantly endophytic retinal tumor filling most of the nasal aspect of the fundus (Fig. 1a & b) and extensive vitreous seeding (Fig. 1c). The tumor extended to the posterior surface of the lens and exhibited preretinal neovascularization on its surface. B-scan ocular ultrasonography OD revealed dense intralesional particles consistent with calcific foci. Genetic testing demonstrated a homozygous non-germline RB1 nonsense mutation. Fundus examination of left eye (OS) revealed a broad-based flat melanotic area of the choroid extending from the subfoveal region to the ora serrata temporally (Fig. 1d). B-scan ocular ultrasonography OS showed no appreciable choroidal thickening corresponding to the melanotic patch. Anterior segment evaluation OS showed no iris or scleral melanocytosis. Our diagnoses were unilateral nonfamilial retinoblastoma OD and isolated choroidal melanocytosis1 OS. The child was treated by primary enucleation of the retinoblastoma-containing OD. Histopathologic evaluation confirmed the clinical diagnosis of retinoblastoma. The child has been followed for more than 4 years post-enucleation. Follow-up examinations of the fundus OS have shown no change in the patch of choroidal melanocytosis.
External (a) and fundus images (b,c) OD demonstrating solid white, predominantly endophytic retinal tumor with preretinal neovascularization on its surface (b) and extensive vitreous seeds (b, c). Fundus image OS (d) demonstrating broad-based flat melanotic area of choroid extending from the subfoveal region temporally
Discussion and conclusions
Isolated choroidal melanocytosis (also known as sectoral choroidal melanocytosis) is a limited form of congenital ocular melanocytosis [3]. Examinations of numerous infants and children with retinoblastoma and disorders such as retinopathy of prematurity have shown such lesions to be extremely uncommon. Incidence of the broader category of ocular melanocytosis has been reported to be 0.038% in Caucasians in the US, however, no incidence reports are available for the isolated choroidal form [4]. Currently, no research indicates a correlation between retinoblastoma and isolated choroidal melanocytosis.
Complete ocular melanocytosis is recognized to be an important risk factor for development of uveal melanoma [5]. We suspect but cannot prove that isolated choroidal melanocytosis may predispose the affected eye to development of choroidal melanoma later in life, although at a lower frequency than the rate encountered with the complete form. Because of this risk, we are recommending that our patient be monitored at least once yearly, though he is currently examined twice yearly (once by her local ophthalmologist and once by our group).
This rare presentation of advanced unilateral retinoblastoma and contralateral isolated choroidal melanocytosis in a young child emphasizes the importance of detailed fundus mapping of the non-affected eye and has potential implications due to the increased incidence of uveal melanoma later in life.
References
Rodriguez-Galindo C, Orbach DB, VanderVeen D. Retinoblastoma. Pediatr Clin N Am. 2015;62(1):201–23.
Broaddus E, Topham A, Singh AD. Incidence of retinoblastoma in the USA: 1975-2004. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009;93(1):21–3.
Augsburger JJ, Trichopoulos N, Correa ZM, Hershberger V. Isolated choroidal melanocytosis: a distinct clinical entity? Graefe's archive for clinical and experimental ophthalmology = Albrecht von Graefes Archiv fur klinische und experimentelle Ophthalmologie. 2006;244(11):1522–7.
Gonder JR, Ezell PC, Shields JA, Augsburger JJ. Ocular melanocytosis. A study to determine the prevalence rate of ocular melanocytosis. Ophthalmology. 1982;89(8):950–2.
Velazquez N, Jones IS. Ocular and oculodermal melanocytosis associated with uveal melanoma. Ophthalmology. 1983;90(12):1472–6.
Funding
Any costs related to this publication was supported by the James J. Augsburger Ocular Oncology Fund of the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine.
Availability of data and materials
Additional data and material related to this report is available upon request but will require parental consent.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CB drafted the initial manuscript and collected the necessary data. JJA and ZMC analyzed and critically reviewed the manuscript. ZMC obtained written consent to publish. JJA and ZMC edited the patient photographs. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Institutional Review Board of the University of Cincinnati has approved an ongoing retrospective review of the Ocular Oncology Database. UC IRB number 2012–4914.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication of clinical details and clinical images was obtained from the parents of the patient. A copy of the consent form is available for review by the Editor of this journal.
Competing interests
None of the authors has any conflicts of interest pertaining to this case. Dr. Correa is a consultant for Castle Biosciences, Inc.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Brooks, C.C., Augsburger, J.J. & Correa, Z.M. Unilateral retinoblastoma with contralateral isolated choroidal Melanocytosis: case report of an unexpected presentation. BMC Ophthalmol 18, 251 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-018-0916-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-018-0916-x