Abstract
Background
We needed to validate and calibrate our portable acuity screening tools so amblyopia could be detected quickly and effectively at school entry.
Methods
Spiral-bound flip cards and download pdf surround HOTV acuity test box with critical lines were combined with a matching card. Amblyopic patients performed critical line, then threshold acuity which was then compared to patched E-ETDRS acuity. 5 normal subjects wore Bangerter foil goggles to simulate blur for comparative validation.
Results
The 31 treated amblyopic eyes showed: logMAR HOTV = 0.97(logMAR E-ETDRS)-0.04 r2 = 0.88. All but two (6%) fell less than 2 lines difference. The five showed logMAR HOTV = 1.09 ((logMAR E-ETDRS) + .15 r2 = 0.63. The critical-line, test box was 98% efficient at screening within one line of 20/40.
Conclusion
These tools reliably detected acuity in treated amblyopic patients and Bangerter blurred normal subjects.
These free and affordable tools provide sensitive screening for amblyopia in children from public, private and home schools. Changing “pass” criteria to 4 out of 5 would improve sensitivity with somewhat slower testing for all students.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Visual acuity screening in early elementary school age is an important safety net for children with undiagnosed or persistent amblyopia that has not yet been detected by a pediatrician in the medical home. In public schools, this task is usually performed by the school nurse. Students in private schools and in home schools often lack the deliberate, scheduled vision screening of a nurse. Acuity screening is an important task and there have been several attempts to simplify this important task including making it available in locations where a computer monitor is available [1].
The Alaska Blind Child Discovery (ABCD) has attempted to eliminate amblyopia by conducting statewide photoscreening of younger children [2] and by enhancing patched monocular acuity screening for older children [3]. Two devices were developed; a quick, portable acuity chart and rolls of patches designed to facilitate affordable, clean, monocular testing. Until now, the devices lacked calibration against the industry standard visual acuity (E-ETDRS). PEDIG has done this with their EVA acuity program so we empoyed their calibration scheme in this study [4].
We validated an inexpensive Flip-card, and a free- download acuity screening tool on known amblyopic patients. Industry standard for young children employs surround HOTV optotypes [5] whereas the standard for older children is the Electronic- Early Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy Study (E-ETDRS) protocol [6]. Since HOTV optotypes are not copyright protected, they can be available for free internet download. The exhaustive validation of a screening device and calibration of an acuity test often takes a large number of patients with a wide range of disease severity. A Bangerter foil is a vinyl film with irregular surface creating graded amounts of blur (http://www.bernell.com/product/3118/).We used Bangerter foils on normal subjects to do a comparative validation and calibration confirmation study.
Methods
This cross-sectional study of patients with amblyopia, and then normals is conducted by the Alaska Blind Child Discovery with Institutional Review Board through Providence Hospital. It is compliant with HIPAA and the Declaration of Helsinki. Parents provided informed consent. Three acuity tools are compared: 1) a plastic flip card set, 2) a free computer download Adobe Acrobat file are compared with 3) the E-ETDRS protocol delivered on a calibrated M&S acuity system (Niles, Illinois). The primary outcomes were calibration of the HOTV flip card against the E-ETDRS standard and validation as a screening tool for amblyopia. The secondary outcome was how the device performed with normal subjects with Bangerter foil blur.
Flip- cards
A flip card surround HOTV set was modified to range from 20/100 down to 20/16 presented at 10-ft with age-based critical lines 20/32 and 20/40 easily identified by 4 larger cards. In addition, a near card child-calibrated for presentation at 10 in.—instead of 14 in. for adults—is added. An instruction card describes a slower threshold screening protocol and a faster age-based critical line protocol. This acuity flip card set also has a matching card with the four surround HOTV optotypes at 20/80 size and a cord for measuring 10 in. and 10 ft (Fig. 1). This set is manufactured by Precision Vision, LaSalle, Illinois. The acuity protocol used was to present a critical line with 4 random optotypes seeking 3 of 4 for pass. If not passed, then move up to the 20/100 presentations. If passed, then move to smaller (20/80) until threshold— the smallest line with at least 3 of 4 correct. If 20/100 not passed, then move to half distance (5 ft) and approximate 20/200.
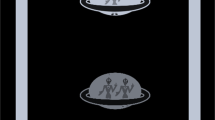
Downloaded pdf acuity
Kurt Simons, PhD designed an HOTV “top” acuity tester that allows a screener to spin the top to present optoptyes in random fashion. ABCD borrowed Dr. Simons’ simple and elegant idea with his permission. Instead of using the original design, surround, HOTV critical line optotpyes subtending 20/32 and 20/40 at ten feet were printed on an Adobe Acrobat file that can be folded into a test “box” that can be compared to a second pdf file that includes 20/80 sized match card surround HOTV and a set of instructions (Fig. 2). The protocol familiarizes the patient unpatched at 10-in. encouraging pointing to the matching card. Then the screener moves to ten feet from the unpatched child seeking sucessful match. Finally, the non-tested eye is patched and 4 random critical line optotypes are presented with pass if at least 3 of 4 are correct. Both pdf files have been loaded on the www.ABCD-Vision.org website for free download. There is also a link to a video demonstrating use: http://vimeo.com/robertarnold/hotvacuitytestkit .
Patients
Patients with treated amblyopia in one or both eyes, and already familiar with acuity testing had parental consent and then had the sound eye patched. Amblyopia was defined as best corrected visual acuity of 20/40 or less on E-ETDRS. Each used best spectacle correction and was screened at critical line 20/40 HOTV, then threshold surround HOTV was determined and then the E-ETDRS protocol was performed.
Bangerter-blurred Normals
Five normal teen female co-authors constructed blur goggles using color-coded swim goggles with a known Bangerter foil (Richmond Products, Albuquerque NM: 0.3, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 and 1.0) attached to the front of one lens. This was done to provide a range of blurred vision overlapping the screening critical line of 20/40 for Kindergarten entry and younger—or critical line 20/30 (logMAR 20/32) for students older than Kindergarten. The goggles afforded a way to discourage peeking around the Bangerter foil. Testing was performed without routine spectacles. The non-tested eye was occluded with an ABCD patch. Each subject then assessed “pass” (at least three of four correct) or “fail” (less than three of four correct) with no goggles using the ABCD 20/40 folded paper test box, and then sought threshold acuity—smallest line with at least three of four HOTV optotypes correct for each of the Bangerter goggles and with a + 1.0 trial lens for a total of 7 screening conditions each. The gold standard was later tested under each Bangerter-induced blur condition with the E-ETDRS on a subsequent day less than a month later.
Results
For the 31 amblyopic patients—aged 10.7 ± 3 years, range 6–19 years, a regression between their HOTV threshold logMAR acuity and the E-ETDRS in their worse amblyopic eye is given in Fig. 3. The etiology for these treated, residual amblyopic patients was refractive (anisometropia) in 15, strabismic in 4 and mixed mechanism in 12. Eleven were right eyes. Twelve were girls. The tested eyes had mean ± SD sphere of +1.88 ± 3.4 D with cylinder of +1.38 ± 1.57 D. The spherical equivalent of the tested amblyopic eyes was +3.42 ± 2.51 D. Just two of the 8 patients with astigmatism greater than 2 diopters had an oblique axis (> 10° from axial). Linear regression of HOTV versus E-ETDRS showed good correlation (r [2] = 0.88) with HOTV = 0.97 (E-ETDRS) -0.04 (Fig. 3).
Five normal teen females provided critical line surround HOTV, then threshold HOTV with five different Bangerter blurred goggles, then with a + 1 trial lens and additionally in their natural state (“none”). The normal subjects all corrected to better than 20/20. Visual acuity in each Bangerter blur condition, the +1 trial and in natural state was repeated on a subsequent day within 1 month with E-ETDRS. A regression of logMAR acuity with critical line identified is shown in Fig. 4.
For the 31 amblyopia patients, mean ± S.D. HOTV acuity was 0.43 ± 0.30 logMAR compared to E-ETDRS of 0.48 ± 0.29 logMAR. For the Bangerter blurred girls, the mean ± S.D. logMAR acuity for HOTV was 0.40 ± 0.25 and for E-ETDRS 0.23 ± 0.18. The difference between E-ETDRS and HOTV for the 31 amblyopic patients was 0.05 (95% C.I. -0.11, 0.25). The difference between E-ETDRS and HOTV for the Bangerter blurred normal subjects was 0.17 (95% C.I -0.03, 0.40).
A critical line screening (the pdf download) correctly sorted all but one (94%) of the amblyopic patients within 1 logMAR lines of 20/40 E-ETDRS. This one case was 20/80 E-ETDRS passing 20/40 screening HOTV. Critical line screening correctly (within one logMAR line) identified E-ETDRS acuity in the Bangerter-blurred normals in 34 of 35 (97%) of cases. The positive predictive value of the 20/40 HOTV screening was 93% for the amblyopic patients and 74% for Bangerter blurred normal subjects. The ROC curve for the amblyopic patients and the Bangerter blurred normals is given in Fig. 5.
Receiver-operator characteristic (ROC) curve for surround HOTV flip card and test box screening in amblyopic patients and in Bangerter foil blurred normal subjects. Amblyopia is defined as E-ETDRS visual acuity of 20/40 or worse. Points on the curve correspond to passing that given level of HOTV visual acuity with at least 3 of 4 correct
Using the HOTV and E-ETDRS scales, the Bangerter foil goggles produced a degradation in visual acuity shown in Table 1. Demographics of the amblyopic children are given in Table 2.
Discussion
This paper addresses two questions: 1) are the surround HOTV flip card and the paper critical line “box” valid for school screening? and 2) can blur by Bangerter filter enhance acuity screen calibration and validation?
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) publishes an evidence-based, age- approriate series of vision screening techniques aimed at detecting amblyopia early when therapy is most effective. Instrument-based screening (photoscreening) can accurately detect amblyopia risk factors in toddlers, but it is preferrable for the instrument referral criteria to be deliberately set for high specificity (catch the most severe cases but not over-refer mild cases) [7]. In order for early specific screening to work [8], more sensitive methods for amblyopia detection must be applied in older children their first school years. A sensitive test makes sure no child with substantial amblyopia can inadvertantly pass the screening. School nurses therefore need an acuity screening tool that will not miss a case of amblyopia worse than 20/40. AAP recommends patching the non-tested eye so no child can peek.
The school nurse is hoping to quickly find children with amblyopia—ideally on school entry—so the visiual disorder will not result in permanent, lifetime vision impairment. School nurses should also identify those children with acuity consistent with good school performance (ie better than 20/30). It is less critical for the school nurse to differentiate between acuity of 20/80, 20/100 and 20/150—under each circumstance that student would need referral. In both the amblyopic patients and the Bangerter-blurred teens, a strong correlation was found for acuity in the better ranges. As a result, the ABCD surround HOTV flip chart—employing the critical line or threshold protocols—and the free downloaded critical-line folded “box” should serve their purpose well. Parents of home-schooled children can, and should, screen their students if this has not been done in a recent pediatrician, well-child examination. For private schools lacking a school nurse, parents, staff, or even upper classmen could perform screening for the early elementary grades. We found the critical line screening to take less than 90 s while threshold patched surround HOTV took 3–4 min. E-ETDRS took 4–7 min in the teens and the older, treated amblyopia patients.
In the amblyopic patients using critical-line screening, two patients passing had worse E-ETDRS acuity (20/50 and 20/80). One patient who failed 20/40 critical line actually had 20/40 E-ETDRS acuity. The advantage of critical line screening is that it takes much less time than threshold screening. The deficiency of critical line/matching is the possibility of correctly guessing. The chance a patient can guess 3 of four matching HOTV optotypes correctly (13/256) is about one in 20. The sensitivity of our test would increase by requiring 4 of 5 correct at critical line; only about 1 in 39 could pass by guessing. This would lengthen the time of testing somewhat.
For the normal girls, the Bangerter foil goggles provided substantial range of blur. The HOTV acuity mean was a line worse than the E-ETDRS, while for the amblyopic patients, the mean HOTV threshold acuity was almost a logMAR line better. The Bangerter blurred patients performed less consistently for higher levels of blur. It may be that the effect on acuity as a result of treated amblyopia may differ from that of Bangerter blur [9].
The Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group (PEDIG) compared a repeat, computer-presented surround HOTV patched protocol (EVA) to E-ETDRS and found similarities to our study [4]. The HOTV slightly over-estimated visual acuity by 0.68 logMAR especially for those with amblyopia and less for eyes better than 0.3 logMAR. We found 0.5 lines with our amblyopic patients and 1.7 lines with Bangerter blurred normals. The E-ETDRS was found reliable in older children [6]. Crowded Kay picture acuity has been correlated with ETDRS [10]. The VIPS study found non-copyrighted HOTV and copyrighted LEA Symbols similar for a large number of young, pre-school Headstart students; however, the critical line for HOTV is one logMAR line larger than for LEA Symbols [11].
Bangerter and convex lenses have been used to compare acuity as early as 1984 [12]. Our Bangerter foils were placed on color-coded swim goggles to assure non-peeking and to enable proper identification of each blur severity. The goggles themselves may have added a non-uniform amount of blur evidenced by the non-linear degree of acuity with Bangerter foil power. Future efforts may employ a better form of no-peek frame for the Bangerter foils. The PEDIG group assessed the degree of acuity degradation due to strong Bangerter filters on the spectacles over the sound eye of patients in a clinical trial [13, 14]. They found that Bangerter 0.2 decreased acuity 5.1 lines while Bangerter 0.3 decreased acuity 4.8 lines. In comparison, we found Bangerter 0.3 on goggles to reduce acuity 5.6 lines. Similar to PEDIG, we did not find a linear relationship between acuity degradation and weaker Bangerter stated power (Table 1) [15]. We also suspect our different swim goggles may independently have had variable effect on acuity—but this does not adversely effect a validation / calibration study in which we seek to degrade normal acuity graded amounts equally for comparison between two threshold and one acuity critical line testing methods.
We did not complete an expensive large, multi-center trial of low pre-screening prevalence preschool children. Weaknesses of our study are the lack of a population-based screening with three acuity charts age-appropriate pre-schoolers with confirmatory exams on each- ther referred and the pass- with sufficient numbers to yield a large number of referrals from which to calibrate each tool, and to determine sensitivity and specificity as a screening tool. We did not check test re-Test reliability. We housed the Bangerter foils in color-coded swim goggles- and these may have variably degraded acuity. We included children older than pre-school age. Multi-center, population –based vision screening validation is prohibitively expensive for many of the manufactureres, and we lacked the millions of federal dollars needed to carry out a more ideal, multi-year study.
We saved time and money. Strengths of our study were comparing methodology with PEDIG acuity test calibration [4], the demonstration of a novel method for attaining a larger number of paired comparisons by variably blurring cooperative normal subjects, and the presentation of a receiver operator characteristic curve comparing our relatively inexpensive clinical trails to calibrate and validate pediatric vision screening devices.
A recent proposed set of guidelines suggest 20/50 screening for children age 3 and 20/40 for children aged 4 and 5 years old [16]; the Flip card can accomplish this though the pre-printed instruction follow existing AAP guidelines.
Conclusion
These affordable, portable surround HOTV screening methods seemed to perform well on amblyopia patients. These critical line screening methods are inexpensive and can be quickly used by school nurses, private school staff and home school parents with a small chance of missing a child with amblyopia. Using critical line with 4 out of 5 needed to pass instead of 3 of 4 would improve sensitivity. Bangerter blur may be a way to facilitate acuity validation using normal subjects to approximate more profound levels of amblyopia.
Abbreviations
- AAP:
-
American Academy of Pediatrics
- ATS:
-
Amblyopia Treatment Studies – controled multicenter amblyopia studies performed by PEDIG
- C.I.:
-
Confidence interval
- D:
-
Diopter
- E-ETDRS:
-
Electronic Early Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy Study- uniform visual acuity optotype presentation on computer utilizing ten capital letters.
- EVA:
-
Electronic visual acuity- paradigm of presentation of surrounded HOTV optotypes developed for the PEDIG ATS
- HIPAA:
-
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996
- HOTV:
-
Uniform optotype for visual acuity testing with bilaterally symmetric capical letters
- LEA:
-
Pediatric optotypes developed and marketed by Lea Hyvarinen, MD.
- logMAR Base:
-
10 logarithm of minimum angle of resolution- a measure of the size of an optotype viewed at a given distance.
- Pdf:
-
Portable Document Format (Adobe Acrobat).
- PEDIG:
-
Pediatric Eye Disease Investigator Group.
- ROC:
-
Receiver operator characteristic- plot of the relationship between sensitivity and specificity at various referral criteria for a screening test.
- SD:
-
Standard deviation.
- VIPS:
-
Vision in Preschoolers Study.
References
Longmuir SQ, Pfeifer W, Shah SS, Olson R. Validity of a layperson-administered web-based vision screening test. J AAPOS. 2015;19(1):29–32.
Leman RE, Clausen MM, Bates J, Stark L, Arnold KK, Arnold RW. A comparison of patched HOTV visual acuity and photoscreening. J Sch Nurs. 2006;22(4):237–43.
Clausen MM, Armitage MD, Arnold RW. Overcoming barriers to pediatric visual acuity screening through education plus provision of materials. J AAPOS. 2009;13(2):151–4.
Birch EE, Strauber SF, Beck RW, Holmes JM. Comparison of the amblyopia treatment study HOTV and the electronic-early treatment of diabetic retinopathy study visual acuity protocols in amblyopic children aged 5 to 11 years. J AAPOS. 2009;13(1):75–8.
Moke PS, Turpin AH, Beck RW, et al. Computerized method of visual acuity testing: adaptation of the amblyopia treatment study visual acuity testing protocol. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001;132(6):903–9.
Cotter SA, Chu RH, Chandler DL, et al. Reliability of the electronic early treatment diabetic retinopathy study testing protocol in children 7 to <13 years old. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003;136(4):655–61.
Miller JM, Lessin HR, AAP. Instrument-based pediatric vision screening policy statement. Pediatrics. 2012;130(5):983–6.
Silbert DI, Matta NS, Brubaker A. Flip chart visual acuity screening for Amblyopia risk factors compared to the PlusoptiX A09 Photoscreener,Tests performed by a lay screener. Binocul Vis Strabolog Q Simms-Romano. 2013;28(4):222–8.
Perez GM, Archer SM, Artal P. Optical characterization of Bangerter foils. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51(1):609–13.
Shah N, Laidlaw D, Rashid S, Hysi P. Validation of printed and computerized crowded Kay picture logMAR test against gold standard ETDRS acuity test chart measurements in adult and amblyopic paediatric subjects. Eye (London). 2012;26(4):593–600.
VIPS. Effect of age using lea Symbons or HOTV for preschool vision screening. Optom Vis Sci. 2010;87(2):87–95.
Mitsuyu M, Zimmer EM. Bangerter occlusives versus spherical convex lenses in the evaluation of visual acuity by visually evoked cortical potentials. Dev Ophthalmol. 1984;9:115–22.
Rutstein RP, Foster NC, Cotter SA, et al. Visual acuity through Bangerter filters in nonamblyopic eyes. J AAPOS. 2011;15(2):131–4.
Rutstein RP, Quinn GE, Lazar EL, et al. A randomized trial comparing Bangerter filters and patching for the treatment of moderate amblyopia in children. Ophthalmology. 2010;117(5):998–1004. e1006
Odell NV, Leske DA, Hatt SR, Adams WE, Holmes JM. The effect of Bangerter filters on optotype acuity, Vernier acuity, and contrast sensitivity. J AAPOS. 2008;12(6):555–9.
Cotter SA, Cyert LA, Miller JM, Quinn GE. National Expert Panel to the National Center for Children's V, eye H. Vision screening for children 36 to <72 months: recommended practices. Optom Vis Sci. 2015;92(1):6–16.
Acknowledgements
M. Diane Armitage, certified orthoptist died 2014; this was the last of her many contributions to vision screening and amblyopia research.
Kurt Simons, Ph.D. devised an amblyopia “top” for random presentation of critical-line 4-optotype vision screening. ABCD appreciates his willingness for the development of a paper-version of his “top.”
Funding
Walmart Alaska has given ABCD two unrestricted grants. Otherwise ABCD is self funded.
Availability of data and materials
The raw data for this study, de-identified- is available for download from http://www.abcd-vision.org/references/Amblyope%20Bangerter%20de-ID%20data.pdf
Financial disclosure
ABCD has received discount vision screening technology from several vendors. ABCD has received unrestricted grants from Walmart-Alaska. Dr. Arnold is Lead Concept Designer for Glacier Medical Software that markets ROP-Check NICU monitoring software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MTW contributed to construction of materials, collecting data, serving as research subject, data collection, initial writing and editing. AT contributed to construction of materials, collecting data, serving as research subject, data collection, initial writing and editing. CT contributed to construction of materials, collecting data, serving as research subject, data collection, initial writing and editing. LA contributed to construction of materials, collecting data, serving as research subject, data collection, initial writing and editing. LTW contributed to construction of materials, collecting data, serving as research subject, data collection, initial writing and editing. DA contributed to training in vision testing, patient recruiting, collecting data, serving as research subject, data collection, initial writing and editing. RA contributed to obtaining IRB approval, funding, design of study, construction of materials, collecting data, serving as research subject, data collection, statistical analysis, graphic arts, initial writing and editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Alaska Blind Child Discovery project obatained IRB approval from Providence Hospital for ongoing, observational study of non-invasive objective and sensory vision screening methods. Study is HIPAA compatible with HIPAA and the Declarations of Helsinki. Parents and legal guardians for patients in this study gave written, informed consent.
Consent for publication
School nurses, and parents of Fig. 1 gave consent to share the image for the purpose of education.
Competing interests
Alaska Blind Child Discovery has received discounted vision screening technology from several vendors. Dr. Arnold is an investigator and protocol developer for PEDIG. No author or ABCD receives royalties from Precision Vision.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Tsao Wu, M., Armitage, M.D., Trujillo, C. et al. Portable acuity screening for any school: validation of patched HOTV with amblyopic patients and Bangerter normals. BMC Ophthalmol 17, 232 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-017-0624-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-017-0624-y