Abstract
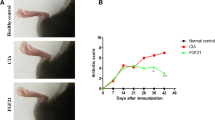
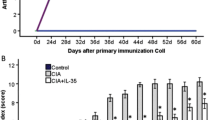
We investigated the therapeutic potential and mechanism of action of IFN-β protein for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Collagen-induced arthritis was induced in DBA/1 mice. At the first clinical sign of disease, mice were given daily injections of recombinant mouse IFN-β or saline for 7 days. Disease progression was monitored by visual clinical scoring and measurement of paw swelling. Inflammation and joint destruction were assessed histologically 8 days after the onset of arthritis. Proteoglycan depletion was determined by safranin O staining. Expression of cytokines, receptor activator of NF-κB ligand, and c-Fos was evaluated immunohistochemically. The IL-1-induced expression of IL-6, IL-8, and granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) was studied by ELISA in supernatant of RA and osteoarthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes incubated with IFN-β. We also examined the effect of IFN-β on NF-κB activity. IFN-β, at 0.25 μg/injection and higher, significantly reduced disease severity in two experiments, each using 8–10 mice per treatment group. IFN-β-treated animals displayed significantly less cartilage and bone destruction than controls, paralleled by a decreased number of positive cells of two gene products required for osteoclastogenesis, receptor activator of NF-κB ligand and c-Fos. Tumor necrosis factor α and IL-6 expression were significantly reduced, while IL-10 production was increased after IFN-β treatment. IFN-β reduced expression of IL-6, IL-8, and GM-CSF in RA and osteoarthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes, correlating with reduced NF-κB activity. The data support the view that IFN-β is a potential therapy for RA that might help to diminish both joint inflammation and destruction by cytokine modulation.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
- CIA:
-
collagen-induced arthritis
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium
- ELISA:
-
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- FCS:
-
fetal calf serum
- FLS:
-
fibroblast-like synoviocytes
- GM-CSF:
-
granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor
- HRP:
-
horseradish peroxidase
- IFN:
-
interferon
- IL:
-
interleukin
- MHC:
-
major histocompatibility complex
- NF:
-
nuclear factor
- OA:
-
osteoarthritis
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- RA:
-
rheumatoid arthritis
- RANKL:
-
receptor activator of NF-κB ligand
- TNF:
-
tumor necrosis factor.
References
van Holten J, Plater-Zyberk C, Tak PP: Interferon-beta for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis?. Arthritis Res. 2002, 4: 346-352. 10.1186/ar598.
Stark GR, Kerr IM, Williams BR, Silverman RH, Schreiber RD: How cells respond to interferons. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998, 67: 227-264. 10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.227.
De ME, De Maeyer-Guignard J: Type I interferons. Int Rev Immunol. 1998, 17: 53-73.
Tak PP, Hart BA, Kraan MC, Jonker M, Smeets TJ, Breedveld FC: The effects of interferon beta treatment on arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 1999, 38: 362-369. 10.1093/rheumatology/38.4.362.
Rep MH, Hintzen RQ, Polman CH, van Lier RA: Recombinant interferon-beta blocks proliferation but enhances interleukin-10 secretion by activated human T-cells. J Neuroimmunol. 1996, 67: 111-118. 10.1016/0165-5728(96)00060-4.
Rep MH, Schrijver HM, van Lopik T, Hintzen RQ, Roos MT, Ader HJ, Polman CH, van Lier RA: Interferon (IFN)-beta treatment enhances CD95 and interleukin 10 expression but reduces interferon-gamma producing T cells in MS patients. J Neuroimmunol. 1999, 96: 92-100. 10.1016/S0165-5728(98)00271-9.
Palmer G, Mezin F, Juge-Aubry CE, Plater-Zyberk C, Gabay C, Guerne PA: Interferon beta stimulates interleukin 1 receptor antagonist production in human articular chondrocytes and synovial fibroblasts. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004, 63: 43-49. 10.1136/ard.2002.005546.
Jungo F, Dayer JM, Modoux C, Hyka N, Burger D: IFN-beta inhibits the ability of T lymphocytes to induce TNF-alpha and IL-1beta production in monocytes upon direct cell-cell contact. Cytokine. 2001, 14: 272-282. 10.1006/cyto.2001.0884.
Yong VW, Chabot S, Stuve O, Williams G: Interferon beta in the treatment of multiple sclerosis: mechanisms of action. Neurology. 1998, 51: 682-689.
Ossege LM, Sindern E, Patzold T, Malin JP: Immunomodulatory effects of interferon-beta-1b in patients with multiple sclerosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2001, 1: 1085-1100. 10.1016/S1567-5769(01)00039-X.
Triantaphyllopoulos KA, Williams RO, Tailor H, Chernajovsky Y: Amelioration of collagen-induced arthritis and suppression of interferon-gamma, interleukin-12, and tumor necrosis factor alpha production by interferon-beta gene therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42: 90-99. 10.1002/1529-0131(199901)42:1<90::AID-ANR12>3.0.CO;2-A.
Sundel RP, Wallace CA, Zurakowski Boston D: Pilot trial of interferon beta-1a in JRA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44: s272-
Smeets TJ, Dayer JM, Kraan MC, Versendaal J, Chicheportiche R, Breedveld FC, Tak PP: The effects of interferon-beta treatment of synovial inflammation and expression of metalloproteinases in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43: 270-274. 10.1002/1529-0131(200002)43:2<270::AID-ANR5>3.0.CO;2-H.
Takayanagi H, Kim S, Matsuo K, Suzuki H, Suzuki T, Sato K, Yokochi T, Oda H, Nakamura K, Ida N, Wagner EF, Taniguchi T: RANKL maintains bone homeostasis through c-Fos-dependent induction of interferon-beta. Nature. 2002, 416: 744-749. 10.1038/416744a.
Alliston T, Derynck R: Medicine: interfering with bone remodelling. Nature. 2002, 416: 686-687. 10.1038/416686a.
Tak PP, Firestein GS: NF-kappaB: a key role in inflammatory diseases. J Clin Invest. 2001, 107: 7-11.
Gerlag DM, Ransone L, Tak PP, Han Z, Palanki M, Barbosa MS, Boyle D, Manning AM, Firestein GS: The effect of a T cell-specific NF-kappa B inhibitor on in vitro cytokine production and collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol. 2000, 165: 1652-1658.
Plater-Zyberk C, Buckton J, Thompson S, Spaull J, Zanders E, Papworth J, Life PF: Amelioration of arthritis in two murine models using antibodies to oncostatin M. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44: 2697-2702. 10.1002/1529-0131(200111)44:11<2697::AID-ART450>3.0.CO;2-#.
Williams RO, Feldmann M, Maini RN: Anti-tumor necrosis factor ameliorates joint disease in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992, 89: 9784-9788.
Dudler J, Renggli-Zulliger N, Busso N, Lotz M, So A: Effect of interleukin 17 on proteoglycan degradation in murine knee joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000, 59: 529-532. 10.1136/ard.59.7.529.
Tak PP, Smeets TJ, Daha MR, Kluin PM, Meijers KA, Brand R, Meiders AE, Breedveld FC: Analysis of the synovial cell infiltrate in early rheumatoid synovial tissue in relation to local disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40: 217-225.
Thurkow EW, van der Heijden IM, Breedveld FC, Smeets TJ, Daha MR, Kluin PM, Meinders AE, Tak PP: Increased expression of IL-15 in the synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis compared with patients with Yersinia-induced arthritis and osteoarthritis. J Pathol. 1997, 181: 444-450. 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199704)181:4<444::AID-PATH778>3.3.CO;2-F.
Dayer JM, Beutler B, Cerami A: Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor stimulates collagenase and prostaglandin E2 production by human synovial cells and dermal fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1985, 162: 2163-2168. 10.1084/jem.162.6.2163.
Firestein GS: Cytokine networks in rheumatoid arthritis: implications for therapy. Agents Actions Suppl. 1995, 47: 37-51.
Moore KW, O'Garra A, de Waal MR, Vieira P, Mosmann TR: Interleukin-10. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993, 11: 165-190. 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.001121.
Wei XQ, Leung BP, Arthur HM, McInnes IB, Liew FY: Reduced incidence and severity of collagen-induced arthritis in mice lacking IL-18. J Immunol. 2001, 166: 517-521.
Buchwalder PA, Buclin T, Trinchard I, Munafo A, Biollaz J: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of IFN-beta 1a in healthy volunteers. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2000, 20: 857-866. 10.1089/10799900050163226.
Miyazaki T, Katagiri H, Kanegae Y, Takayanagi H, Sawada Y, Yamamoto A, Pando MP, Asano T, Verma IM, Oda H, Nakamura K, Tanaka S: Reciprocal role of ERK and NF-kappaB pathways in survival and activation of osteoclasts. J Cell Biol. 2000, 148: 333-342. 10.1083/jcb.148.2.333.
Missbach M, Jeschke M, Feyen J, Muller K, Glatt M, Green J, Susa M: A novel inhibitor of the tyrosine kinase Src suppresses phosphorylation of its major cellular substrates and reduces bone resorption in vitro and in rodent models in vivo. Bone. 1999, 24: 437-449. 10.1016/S8756-3282(99)00020-4.
Chiusaroli R, Sanjay A, Hendriksen K, Engsig MT, Horne WC, Gu H, Baron R: Deletion of the gene encoding c-Cbl alters the ability of osteoclasts to migrate, delaying resorption and ossification of cartilage during the development of long bones. Dev Biol. 2003, 261: 537-547. 10.1016/S0012-1606(03)00299-9.
Berger LC, Hawley RG: Interferon-beta interrupts interleukin-6-dependent signaling events in myeloma cells. Blood. 1997, 89: 261-271.
Pilling D, Akbar AN, Girdlestone J, Orteu CH, Borthwick NJ, Amft N, Scheel-Toellner D, Buckley CD, Salmon M: Interferon-beta mediates stromal cell rescue of T cells from apoptosis. Eur J Immunol. 1999, 29: 1041-1050. 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199903)29:03<1041::AID-IMMU1041>3.0.CO;2-#.
Van Weyenbergh J, Wietzerbin J, Rouillard D, Barral-Netto M, Liblau R: Treatment of multiple sclerosis patients with interferon-beta primes monocyte-derived macrophages for apoptotic cell death. J Leukoc Biol. 2001, 70: 745-748.
Joosten LA, Helsen MM, van De Loo FA, van Den Berg WB: Anti-cytokine treatment of established type II collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1 mice. A comparative study using anti-TNF alpha, anti-IL-1 alpha/beta, and IL-1Ra. Arthritis Rheum. 1996, 39: 797-809.
Moreland LW, Schiff MH, Baumgartner SW, Tindall EA, Fleischmann RM, Bulpitt KJ, Weaver AL, Keystone EC, Furst DE, Meas PJ, Ruderman EM, Horwitz DA, Arkfeld DG, Garrison L, Burge DJ, Blosch CM, Lange ML, MacDonnell ND, Weinblatt ME: Etanercept therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1999, 130: 478-486.
Weinblatt ME, Kremer JM, Bankhurst AD, Bulpitt KJ, Fleischmann RM, Fox RI, Jackson CG, Lange M, Burge DJ: A trial of etanercept, a recombinant tumor necrosis factor receptor:Fc fusion protein, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving methotrexate. N Engl J Med. 1999, 340: 253-259. 10.1056/NEJM199901283400401.
Nishimoto N, Yoshizaki K, Maeda K, Kuritani T, Deguchi H, Sato B, Imai N, Suemura M, Kakehi T, Takagi N, Kishimoto T: Toxicity, pharmacokinetics, and dose-finding study of repetitive treatment with the humanized anti-interleukin 6 receptor antibody MRA in rheumatoid arthritis. Phase I/II clinical study. J Rheumatol. 2003, 30: 1426-1435.
van Roon JA, Lafeber FP, Bijlsma JW: Synergistic activity of interleukin-4 and interleukin-10 in suppression of inflammation and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44: 3-12. 10.1002/1529-0131(200101)44:1<3::AID-ANR2>3.0.CO;2-U.
Maini R, Paulus H, Breedveld F, Moreland LW, William St Clair E, Russel A: rHUIL-10 in subjects with active rheumatoid arthritis (RA): a phase I and cytokine response study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40: s224-
Genovese M, Chakravaty E, Krishnan E, Moreland LW: A randomized, controlled trial of interferon-β-1a in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a pilot study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2004, 6: R73-R77. 10.1186/ar1026.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Competing interests
Dr Tak has received support from Serono for a separate clinical study investigating the use of interferon-β in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Mrs Sattonet-Roche is an employee of Serono. Dr Plater-Zyberk is a former employee of Serono. Dr van Holten has received a research grant from the Serono Pharmaceutical Research Institute.
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Holten, J., Reedquist, K., Sattonet-Roche, P. et al. Treatment with recombinant interferon-β reduces inflammation and slows cartilage destruction in the collagen-induced arthritis model of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 6, R239 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1186/ar1165
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/ar1165