Abstract
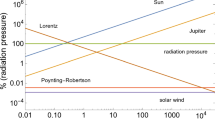
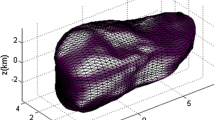
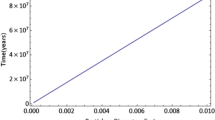
We present the values of a ratio β of the solar radiation pressure force to the solar gravity on the finite circular cylindrical grains, as functions of an aspect ratio of the cylinder and an incident angle Θ of the solar radiation. By using the resulting formula of β(Θ), the trajectory of the Kepler orbit for the rotating silicate cylinder is computed associated with a spin motion under the assumption that the spin axis is along the shortest axis of the cylinder and points to the direction perpendicular to the solar radiation. We found for the silicate cylinder grain with a mass equivalent to a sphere with a radius of 0.15 μm, and the aspect ratio of 2.0 that a heliocentric distance of the grain varies periodically with a time, having an amplitude of the fluctuation in the heliocentric distance of about 0.02 AU, where the spin velocity is 0.25 rotation/day and the initial orbit has a semi-major axis 3.0 AU and an eccentricity 0. In addition, during such a fluctuation of the heliocentric distance, the instantaneous eccentricity of the orbit also varies simultaneously from 0 to 1.6 with the rotation of the grain. This implies that the in-situ measurements of orbital elements of impact grains on the dust detector may record those instantaneous orbital elements related to the phase of the grain’s rotation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asano, S. and G. Yamamoto, Light scattering by a spheroidal particle, Appl. Optics, 14, 29–49, 1975.
Asano, S. and G. Yamamoto, Light scattering by a spheroidal particle: ettratum, Appl. Optics, 15, 2028, 1976.
Burns, J. A., P. L. Lamy, and S. Soter, Radiation forces on small particles in the solar system, Icarus, 40, 1–48, 1979.
Davis, L. Jr. and J. L. Greenstein, The polarization of starlight by aligned dust grains Astrophys. J., 114, 206–215, 1951.
Dohnanyi, J. S., Particle Dynamics, in Comet Dust, edited by J. A. M. MacDonnell, pp. 527–587, Wiley, New York, 1978.
Draine, B. T. and P. J. Flatau, Discrete dipole approximation for scattering calculation, J. Opt. Soc.Am.A,, 11, 1491–1499, 1994.
Draine, B. T. and P. J. Flatau, User Guide for the Discrete Dipole Approximation Code DDSCAT, http://www.xxx.lanl.gov/abs/astro-ph/0008151v3, 1–41, 2000.
Everhart, E., An Efficient Integrator that Uses Gauss=Radau Spacing, Dynamics of Comets: Their Origin and Evolution, Proc. of IAU Colloqu. 183, edited by A. Carusi and Gi. B. Valsecchi, pp. 185–192, Dordrecht: Reidel, Astrophysics and Space Science Library, 115, 1985.
Fujiwara, A. and A. Tsukamoto, Experimental study on the velocity of fragments in collisional breakup, Icarus, 44, 142–153, 1981.
Gold, T., Polarization of star light, Nature, 169, 322–324, 1952.
Greenberg, J. M., Interstellar Grains, in Nebulae and Interstellar Matter, edited by B. M. Middlehurst and L. H. Aller, pp. 221–364, The University of Chicago Press, Chicago & London, 1968.
Gustafson, B. A. S., Comet ejection and dynamics of nonspherical dust particles and meteoroids, Astrophys. J., 337, 945–949, 1989.
Il’in, V. B. and N. V. Voshchinnikov, Radiation pressure on nonspherical dust grains in envelopes of late-type giants, Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser, 128, 187–196, 1998.
Ishiguro, M., R. Nakamura, Y. Fujii, K. Morishige, H. Yano, H. Yasuda, S. Yokogawa, and T. Mukai, First detection of visible zodiacal dust bands from ground based observations, Astrophys. J., 511, 432–435, 1998.
Kimura, H., H. Okamoto, and T. Mukai, Radiation pressure and Poynting-Robertson effect for fluffy dust particles, Icarus, 157, 349–361, 2002.
Low, F. J., D. A. Beintema, T. N. Gautier, F. C. Gillett, C. A. Beichman, G. Neugebauer, E. Young, H. H. Aumann, N. Boggess, J. P. Emerson, H. J. Habing, M. G. Hauser, J. R. Houck, M. Rowan-Robinson, B. T. Soifer, R. G. Walker, and P. R. Wesselius, Infrared cirrus: New component of the infrared mission, Astrophys. J., 278, L19–L22, 1
Mukai, T., Spin-down Effect on an Interplanetary Dust Grain, Proc. of ISAS Lunar & Planetary Symp., 14, 169–174, 1981.
Mukai, T., Cometary dust and interplanetary particles, in Evolution of Interstellar Dust and Related Topics, edited by A. Benti, J. M. Greenberg, and S. Aiello, pp. 397–445, Elsevier Sci. Publ. Amsterdam, 1989.
Mukai, T., H. Ishimoto, T. Kozasa, J. Blum, and J. M. Greenberg, Radiation pressure forces of fluffy porous grains, Astron. Astrophys., 262, 315–320, 1992.
Paddack, S. J. and J. W Rhee, Rotational bursting of interplanetary dust particles, in Interplanetary Dust and Zodiacal Light, edited by H. Elsaesser and H. Fechtig, pp. 453–457, Lecture Notes in Physics 48, Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York, 1976.
Purcell, E. M. and C. R. Pennypacker, Scattering and absorption of light by nonspherical dielectric grains, Astrophys. J., 186, 705–714, 1973.
Reach, W. T., B. A. Franz, and J. L. Weiland, The three-dimensional structure of the zodiacal dust bands, Icarus, 127, 461–484, 1997.
Spiesman, J. W., G. M. Hauser, T. Kelsall, M. C. Lisse, H. S. Moseley, T. W. Reach, F. R. Sillverberg, W. S. Stemwedel, and L. J. Weiland, Near- and far-infrared observation of interplanetary dust bands from the COBE diffuse infrared background experiment, Astrophys. J., 442, 662–667, 1995.
Voshchinnikov, N. V. and V. B. Il’in, Radiation pressure on cylindrical particles, Opt. Spectrosc., 55, 304–306, 1983.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saklayen, M.A., Mukai, T. Orbital variation of the rotating non-spherical dust grains due to change of the solar radiation forces by shape effect. Earth Planet Sp 56, 613–620 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1186/BF03352522
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/BF03352522