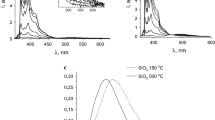
In the photostationary state, the cis/trans isomer ratio of azobenzene and 3,3′-dimethylazobenzene adsorbed in zeolite NaY increases significantly to ca. 90:10, in contrast to the reaction in cyclohexane. However, for azobenzene-4,4′-dicarboxylic acid diethyl ester the formation of the cis isomer is remarkably suppressed to ca. 30%. On the basis of ab initio MO calculations, it is suggested that electrostatic interaction between these azobenzenes and the metal ions in zeolite nanocavities regulates the cis-trans photoisomerization process. In addition, it is found that the photoisomerization behavior of azobenzenes adsorbed on silica gel is similar to that in NaY.
Similar content being viewed by others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kojima, M., Nakajoh, M., Nebashi, S. et al. Effect of metal cation on photoisomerization of azobenzenes in zeolite nanocavities. Res Chem Intermediat 30, 181–190 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1163/156856704322960754
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1163/156856704322960754