Abstract
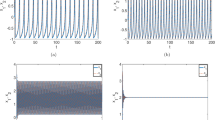
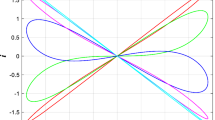
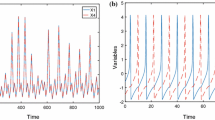
The feed-forward neural networks are the basis and have been widely applied on modern deep learning models, wherein connection strength between neurons plays a critical role in weak signal propagation and neural synchronization. In this paper, a four-variable Hindmarsh–Rose (HR) neural model is presented by introducing an additive variable as magnetic flow which changes the membrane potential via a memristor. The improved HR neurons in the feed-forward multilayer (four and eight layers) networks are investigated. The effects of electromagnetic radiation, synaptic weight and noise intensity on the propagation of the subthreshold excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC) signal and the neural synchronization are discussed. It is found that when the system is in a weak magnetic field, the subthreshold EPSC signal can be successfully transmitted to the post-layers. Moreover, the neural synchronization of each layer is affected by electromagnetic radiation in the network, and with the help of noise the constant input current will transmit to the post-layers in a stable periodic synchronous form. Our findings provide a possible mechanism for enhancing the subthreshold signal propagation and triggering the neural synchronization in the nervous system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.Q. Guo, C.G. Li, J. Comput. Neurosci. 30, 567 (2011)
G.A. Babu, S.N. Bhukya, R.S. Kumar, in Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Computer Science & Education, ICCSE 2013, (IEEE, 2013), p. 181
M. Diesmann, M.O. Gewaltig, A. Aertsen, Nature 402, 529 (1999)
S. Moldakarimov, M. Bazhenov, T.J. Sejnowski, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 112, 2545 (2015)
H.T. Wang, Y. Chen, Physica A 462, 321 (2016)
M. Masoliver, C. Masoller, Sci. Rep. 8, 8276 (2018)
Y. Yao, C. Ma, C. Wang, M. Yi, R. Gui, Phys. A 492, 1247 (2018)
L.T. Arredondo, C.A. Perez, PLoS One 12, e0186932 (2017)
M. Perc, Phys. Rev. E 72, 016207 (2005)
E. Yilmaz, M. Ozer, V. Baysal, M. Perc, Sci. Rep. 6, 30914 (2016)
X.J. Sun, J.Z. Lei, M. Perc, J. Kurths, G.R. Chen, Chaos 21, 016110 (2011)
S. Majhi, M. Perc, D. Ghosh, Chaos 27, 073109 (2017)
J. Teramae, T. Fukai, Biol. Cybern. 99, 105 (2008)
S. Goedeke, M. Diesmann, New J. Phys. 10, 15007 (2008)
Q.Y. Wang, M. Perc, Z.S. Duan, G.R. Chen, Phys. Rev. E 80, 026206 (2009)
D.Q. Guo, C.G. Li, Phys. Rev. E 79, 051921 (2009)
J. Ma, L. Mi, P. Zhou, Y. Xu, T. Hayat, Appl. Math. Comput. 307, 321 (2017)
Y. Asai, A.E.P. Villa, Brain Res. 1434, 17 (2012)
M. Yi, L.J. Yang, Phys. Rev. E 81, 061924 (2010)
M. Ge, Y. Jia, J.B. Kirunda, Y. Xu, J. Shen, L. Lu, Y. Liu, Q. Pei, X. Zhan, L. Yang, Neurocomputing 320, 60 (2018)
L. Lu, Y. Jia, J.B. Kirunda, Y. Xu, M. Ge, Q. Pei, L. Yang, Nonlinear Dyn. 95, 1673 (2019)
L.O. Chua, IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 18, 507 (1971)
J. Ma, J. Tang, Nonlinear Dyn. 89, 1569 (2017)
M. Ge, Y. Xu, Z. Zhang, Y. Peng, W. Kang, L. Yang, Y. Jia, Eur. Phys. J. Special Topics 227, 799 (2018)
J. Ma, F. Wu, C. Wang, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 31, 1650251 (2017)
Y. Xu, Y. Jia, M. Ge, L. Lu, L. Yang, X. Zhan, Neurocomputing 283, 196 (2018)
Z. Rostami, S. Jafari, M. Perc, M. Slavinec, Nonlinear Dyn. 94, 679 (2018)
M. Ge, Y. Jia, Y. Xu, L. Lu, H. Wang, Y. Zhao, Appl. Math. Comput. 352, 136 (2019)
Y. Xu, Y. Jia, H. Wang, Y. Liu, P. Wang, Y. Zhao, Nonlinear Dyn. 95, 3237 (2019)
D. Hansel, G. Mato, C. Meunier, Europhys. Lett. 23, 367 (1993)
A. Destexhe, Z.F. Mainen, T.J. Sejnowski, J. Comput. Neurosci. 1, 195 (1994)
L. Yang, Y. Jia, M. Yi, ICNC 2, 819 (2010)
X. Pei, L. Wilkens, F. Moss, Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 4679 (1996)
S. Wang, W. Wang, F. Liu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 018103 (2006)
P. Parmananda, G. Santos, M. Rivera, K. Showalter, Phys. Rev. E 71, 031110 (2005)
M. Stimberg, T. Hoch, K. Obermayer, Neurocomputing 70, 1824 (2007)
Y. Wang, J. Ma, Y. Xu, F. Wu, P. Zhou, Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 27, 1750030 (2017)
M. Ge, Y. Jia, Y. Xu, L. Yang, Nonlinear Dyn. 91, 515 (2018)
B. Bao, A. Hu, Q. Xu, H. Wu, M. Chen, Nonlinear Dyn. 92, 1695 (2018)
L.L. Lu, Y. Jia, Y. Xu, M.Y. Ge, L.J. Yang, X. Zhan, Sci. China Technol. Sci. 62, 427 (2019)
Y. Xu, Y. Jia, J.B. Kirunda, J. Shen, M. Ge, L. Lu, Q. Pei, Complexity 2018, 3012743 (2018)
Y. Yao, W. Cao, Q. Pei, C. Ma, M. Yi, Complexity 2018, 879329 (2018)
V. Berec, Chaos 86, 75 (2016)
V. Berec, Eur. Phys. J. Special Topics 225, 7 (2016)
Y. Yao, L. Yang, C. Wang, Q. Liu, R. Gui, J. Xiong, M. Yi, Complexity 2018, 5632650 (2018)
Y. Xu, Y. Jia, J. Ma, H. Tasawar, A. Ahmed, Sci. Rep. 8, 1349 (2018)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, M., Lu, L., Xu, Y. et al. Effects of electromagnetic induction on signal propagation and synchronization in multilayer Hindmarsh-Rose neural networks. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 228, 2455–2464 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2019-900006-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjst/e2019-900006-2