Abstract
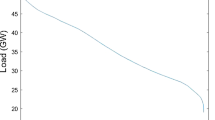
Europe is pursuing an aggressive programme to increase its share of renewable energy source (RES). However, the integration of intermittent RES (wind and photovoltaic) in the electrical system requires either maintaining in operation thermal backup systems or providing a substantial amount of electricity storage. We analyze the Italian electricity data for the year 2013 provided by the transmission system operator TERNA. The present level of intermittent RES power is scaled-up to a level at which it generates an amount of electricity equal to the annual demand. While a substantial reduction of the energy annually produced by fossil backup systems (and the associated CO2 emission) with respect to the no-RES case is possible in many scenarios considered here, the backup power is generally only marginally reduced below the value in the absence of RES. The strategy proposed is based on the combination of a modest amount of storage (0.5-5TWh) and base-load power (6-15GW, to be used during the seasons of low RES production). In this way the non-RES installed power can be reduced from ∼ 50 GW to less than 15GW and could be covered by a combination of biomass and nuclear energy without any CO2 emission.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A strategy for smart, sustainable and inclusive growth, European Commission communication COM (2010) 2020 final
Ministero dello sviluppo economico, Strategia Energetica Nazionale: per un’energia più competitiva e sostenibile, www.sviluppoeconomico.gov.it/images/stories/normativa/20130314_Strategia_Energetica_Nazionale.pdf
F. Wagner, Eur. Phys. J. Plus 129, 20 (2014)
TERNA Dati statistici sull’energia elettrica in Italia 2013, www.terna.it/default/Home/SISTEMA_ELETTRICO/statistiche/dati_statistici.aspx
www.terna.it/default/Home/SISTEMA_ELETTRICO/dispacciamento/Previsione_Prod_Eolica.aspx and www.terna.it/default/Home/SISTEMA_ELETTRICO/transparency_report/Generation/trasparency_rep_actual_ generation.aspx
TERNA, Dati di esercizio, Rapporti mensili, www.terna.it/default/Home/SISTEMA_ELETTRICO/dispacciamento/dati_esercizio/rapporto_mensile.aspx
Eurelectric, Hydro in Europe: Powering renewables. Full report (2011) www.eurelectric.org/media/26690/hydro_report_final-2011-160-0011-01-e.pdf
M. Gimeno-Gutiérrez, R. Lacal-Arántegui, Assessment of the European potential for pumped hydropower energy storage, Report EUR 25940 EN ISBN 978-92-79-29511-9 (2013)
TERNA, Piano di sviluppo 2015, www.terna.it/default/Home/SISTEMA_ELETTRICO/piano_sviluppo_rete/Piano_di_Sviluppo_2015.aspx
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Romanelli, F. Strategies for the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources in the electrical system. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 131, 53 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2016-16053-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/i2016-16053-3