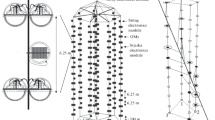
Abstract
The search for the sources of cosmic rays is a three-fold assault, using charged cosmic rays, gamma rays and neutrinos. The first conceptual ideas to detect high energy neutrinos date back to the late fifties. The long evolution towards detectors with a realistic discovery potential started in the seventies and eighties, with the pioneering works in the Pacific Ocean close to Hawaii and in Lake Baikal in Siberia. But only now, half a century after the first concepts, such a detector is in operation: IceCube at the South Pole. We do not yet know whether with IceCube we will indeed detect extraterrestrial high energy neutrinos or whether this will remain the privilege of next generation telescopes. But whatever the answer will be: the path to the present detectors was a remarkable journey. This review sketches its main milestones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi, R. et al. (IceCube Coll.) 2009. Search for point sources of high energy neutrinos with final data from AMANDA-II. Phys. Rev. D 79 : 062001
Abbasi, R. et al. (IceCube Coll.) 2010. Measurement of sound speed vs. depth in South Pole ice for neutrino astronomy. Astropart. Phys. 33 : 277
Abbasi, R. et al. (IceCube Coll.) 2011. Measurement of the atmospheric neutrino energy spectrum from 100 to 400 TeV with IceCube. Phys. Rev. D 83 : 012001
Abbasi, A. et al. (IceCube Coll.) 2011. IceCube Sensitivity for Low-Energy Neutrinos from Nearby Supernovae, Astron. Astrophys. 535 : A109
Abbasi, R. et al. (IceCube Coll.) 2011. Measurement of Acoustic Attenuation in South Pole Ice. Astropart. Phys. 34 : 382
Abbasi, R. et al. (IceCube Coll.) 2011. Constraints on the extremely-high energy neutrino flux with the IceCube 2008-2009 data. Phys. Rev. D 83 : 092003
Abbasi, A. et al. (IceCube Coll.) 2012. Neutrinos challenge Gamma Ray Burst origin of cosmic rays. Nature 484 : 351
Abbasi, A. et al. (IceCube Coll.) 2012. Background studies for acoustic neutrino detection at the South Pole. Astropart. Phys. 35 : 312
Abraham, J. et al., (Pierre Auger Coll.) 2008. Upper limit on the diffuse flux of UHE tau neutrinos from the Pierre Auger Observatory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 : 211101
Achar, C. et al. 1965. Detection of muons produced by cosmic ray neutrinos deep underground. Phys. Lett. 18 : 196
Ackermann, M. et al. (AMANDA Coll.) 2006a. Optical properties of deep glacial ice at the South Pole. J. Geophys. Res. 111 : D13203
Ackermann, M. 2006b. Searches for signals from cosmic point-like sources of high energy neutrinos in 5 years of AMANDA-II data. Ph.D. thesis, Humboldt University Berlin, http://edoc.hu-berlin.de/docviews/abstract.php?lang=ger, id=27726
Ackermann, M. et al. (AMANDA Coll.) 2006c. The IceCube prototype string in AMANDA. Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 556 : 169
Ageron, M. et al. (ANTARES Coll.) 2007. Studies of a full-scale mechanical prototype line for the ANTARES neutrino telescope and tests of a prototype instrument for deep-sea acoustic measurements. Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 581 : 695
Ageron, M. et al. (ANTARES Coll.) 2011. ANTARES : The first undersea neutrino telescope. Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 656 : 11
Aggouras, G. et al. (NESTOR Coll.) 2005a. Operation and performance of the NESTOR test detector. Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 552 : 420
Aggouras, G. et al. (NESTOR Coll.) 2005b. A measurement of the cosmic-ray muon flux with a module of the NESTOR neutrino telescope. Astropart. Phys. 23 : 377
Aguilar, J.A. et al. (ANTARES Coll.) 2011. A fast algorithm for muon track reconstruction and its application to the ANTARES neutrino telescope. Astropart. Phys. 34 : 652
Ahmad, Q. et al. (SNO Collaboration) 2001. Measurement of the charged current interactions produced by B8 neutrinos at the Sudbury Neutrino Observatory. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87 : 071301
Ahrens, J. et al. (AMANDA Coll.) 2004a. Muon track reconstruction and data selection techniques in AMANDA. Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 524 : 169
Ahrens, J. et al. (IceCube Coll.) 2004b. Sensitivity of the IceCube detector to astrophysical sources of high energy muon neutrinos. Astropart. Phys. 20 : 507
Aiello, S. et al. (NEMO Coll.) 2010. Measurement of the atmospheric muon flux with the NEMO Phase-1 detector. Astropart. Phys. 33 : 263
Allison, P. et al. 2011. Design and Initial Performance of the Askaryan Radio Array Prototype EeV Neutrino Detector at the South Pole. submitted to Astropart. Phys., arXiv:1105.2854
Alvarez-Muniz, J. and F. Halzen. 2002. Possible high-energy neutrinos from the cosmic accelerator RXJ 1713.7-3946. Astrophys. J. 576 : 233
Ameli, F. (Ed.) 2009. Proc. 3rd Int. ARENA Workshop, Univ. Rome, 2008. Nucl. Instr. Meth. Suppl. A 604
Amram, P. et al. (ANTARES Coll.) 2000. Background light in potential sites for the ANTARES undersea neutrino telescope. Astropart. Phys. 13 : 127
Amram, P. et al. (ANTARES Coll.) 2003. Sedimentation and fouling of optical surfaces at the ANTARES site. arXiv:astro-ph/0206454
Andres, E. et al. (AMANDA Coll.) 1999. The AMANDA Neutrino Telescope : Principle of Operation and First Results. Astropart. Phys. 13 : 1
Andres, E. et al. (Amanda Coll.) 2001. Results from the AMANDA high-energy neutrino detector. Nucl. Phys. Proc. Suppl. 91 : 423
ANTARES homepage : http://antares.in2p3.fr
Antonioli, P. et al. 2004. SNEWS : The supernova early warning system. New J. Phys. 6 : 114
Anzalone, A, et al. 2012. The JEM-EUSO Mission : Status and Prospects, Contributions of the JEM-EUSO Collaboration to the 32nd ICRC, Beijing 2011, arXiv:1204.5065
Araki, T. et al. 2005. (Kamland Collaboration) Experimental investigation of geologically produced antineutrinos with KamLAND. Nature 436 : 499
Askaryan, G. 1957. Hydrodynamic radiation from the tracks of ionizing particles in stable liquids. Sov. J. Atom. Energy 3 : 921
Askaryan, G. 1962. Excess negative charge of an electron-photon shower and its coherent radio emission. Sov. Phys. JETP 14 : 441
Askebjer, P. et al. (AMANDA Coll.) 1995. Optical properties of the South Pole ice at depths between 0.8 km and 1 km. Science 267 : 1147
Aslanides, E. et al. (ANTARES Coll.) 1999. A deep sea telescope for high-energy neutrinos. arXiv:astro-ph/9907432
Avronin, A. et al. (Baikal Coll.) 2009. Search for high-energy Neutrinos in the Baikal Neutrino Experiment. Astron. Lett. 35 : 650
Aynutdinov, V. et al. (Baikal Coll.) 2006a. Search for a diffuse flux of high-energy extraterrestrial neutrinos with the NT200 neutrino telescope. Astropart. Phys. 25 : 140
Aynutdinov, V. et al. (Baikal Coll.) 2006b. The BAIKAL neutrino experiment : From NT200 to NT200+. Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 567 : 433
Aynutdinov, V. et al. (Baikal Coll.) 2009. The prototype string for the km3-scale Baikal neutrino telescope. Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 602 : 227
Babson, E. et al. (DUMAND Coll.) 1990. Cosmic ray muons in the deep ocean. Phys. Rev. D 42 : 3613
Bagduev, R. et al. (Baikal Coll.) 1999. The optical module of the Baikal deep underwater neutrino telescope. Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 420 : 138
Bagley, P. et al. (KM3NeT Coll.) 2008. Conceptual design report, ISBN 978-90-6488-031-5, available from : www.km3net.org
Bagley, P. et al. (KM3NeT Coll.) 2010. Technical design report, ISBN 978-90-6488-033-9, available from : www.km3net.org
Bahcall, J. 1994. Solar Neutrinos – the first thirty years. Addison-Wesley Publ. Comp., Reading
Baikal, http://baikalweb.jinr.ru
Balkanov, R. et al. (Baikal Coll.) 1997. Reconstruction of atmospheric neutrinos with the Baikal neutrino telescope NT-96. Astropart. Phys. 12 : 75
Barwick, S. et al. (ANITA Coll.) 2006. Constraints on cosmic neutrino fluxes from the ANITA experiment. Phys. Rev. Lett. 96 : 171101
Barwick, S. 2007. ARIANNA : A new concept for UHE neutrino detection. J. Phys. : Conf. Ser. 60 : 278
Bellini, G. et al. 2010 (Borexino Collaboration). Observation of Geo-Neutrinos. Phys. Lett. B 687 : 299
Belolaptikov, I. et al., The experimental limits on Q-ball flux with the Baikal deep underwater array Gyrlyanda, arXiv:astro-ph/9802223
Belotti, E. and M. Laveder. 1993. High energy neutrino detectors. Proc. 5th Int. Workshop on Neutrino Telescopes, edited by M.Baldo-Ceolin, Venice p. 275
Berezinsky, V. and G. Zatsepin. 1970. Cosmic neutrinos of superhigh energies. Yad. Fiz. 11 : 200
Berezinsky, V. and A. Smirnov. 1975. Cosmic Neutrinos of Ultra-High Energies and Detection Possibility. Astrophys. Space Sci. 32 : 461
Berezinsky, V. and O. Priludsky. 1977. High Energy Neutrinos from Supernova Explosions and Davis’ Experiment. Sov. Astron. Lett. 3 : 79
Berezinsky, V. 1990. High energy neutrino astronomy. Proc. Int. Workshop on Neutrino Telescopes, edited by M.Baldo-Ceolin, Venice, p. 125
Bergeson, H. et al. 1967. Evidence for a new production process for 1012 eV muons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 19 : 1487
Bergeson, H. G. Cassiday and M. Hendricks. 1973. Phys. Rev. Lett. 31 : 66
Bezrukov, L.B. et al. (Baikal Coll.) 1984. Progress report on Lake Baikal neutrino experiment : Site studies and stationary string. Proc. XI. Conf. on Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics, Nordkirchen, Germany, p. 550
Bezrukov, L.B. et al. 1987. Properties and test results of a photon detector based on the combination of electro-optical preamplifier and a small photomultiplier. Proc. 2nd Int. Symp. Underground Physics-87, Baksan Valley, USSR, p. 230
Blondeau, F. for the ANTARES Coll. 1998. The ANTARES demonstrator : Towards a high-energy undersea neutrino telescope. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 40 : 413
Bobisut, F. 1991. NET : a Neutrino Telescope. Proc. 3nd Int. Workshop on Neutrino Telescope, edited by M. Baldo-Ceolin, Venice, p. 387
Bogatyrev, V. 1971. On the possibility of constructing large detectors for neutrino astronomy. Sov. J. Nucl. Phys. 13 : 187
Boliev, M. et al. 1981. Limitations on parameters of neutrino oscillations according to data of the Baksan underground telescope (in Russian). Yad. Fiz. 34 : 1418
Bosetti, P. et al. (DUMAND Coll.) 1988. DUMAND II : Proposal to construct a deep-ocean laboratory for the study of high energy neutrino astrophysics and particle physics. Tech. Rep. HDC-2-88, Hawaii DUMAND Center, University of Hawaii
Bosetti, P. 1991. JULIA, Proc. Trends in Astroparticle Physcis, edited by P. Bosetti, Aachen, p. 88
Bradner, H. (Ed.) 1977. Proc. Workshop on acoustic detection of atmospheric neutrinos (DUMAND 77)
Capone, A. et al. (NEMO Coll.) 2009. Recent results and perspectives of the NEMO project. Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 602 : 47
Corstanje, A. et al. 2011. LOFAR : Detecting Cosmic Rays with a Radio Telescope, Contribution to 32nd ICRC, Beijing, 2011, arXiv:1109.5805
Costantini, M. and F. Vissani. 2005. Neutrinos from supernovas and supernova remnants, arXiv:astro-ph/0508152
Cowan, C. et al. 1956. Detection of the Free Neutrino : A Confirmation. Science 103 : 124
Cowsik, R. et al. 1963. Flux of atmospheric neutrinos of different types at sea level and cosmic ray neutrino experiments. in Proc. Int. Cosmic Ray Conf. 1963, Vol. 6, p. 211
Crouch, M. et al. 1978. Cosmic-ray muon fluxes deep underground. Intensity vs. depth and the neutrino-induced component. Phys. Rev. D 18 : 2239
Dagkesamanksii, R. V. Matveev and I. Zheleznykh. 2011. Prospects of radio detection of extremely high energy neutrinos bombarding the moon. Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 626 : S44
Davis Jr., R et al. 1968. A search for neutrinos from the Sun. Phys. Rev. Lett. 20 : 1205
Deneyko, A.O. et al. 1991. The tests of a prototype of an autonomous module of deep underwater neutrino telescope during October-December of 1989. Proc. 3rd Int. Workshop on Neutrino Telescopes, Venice, p. 407
De Rujula, D. and S. Glashow. 1984. Nuclearites – a novel form of cosmic radiation. Nature 312 : 734
Dirac, P. 1931. Quantised singularities in the electromagnetic field. Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. A 133 : 60
Distefano, C. 2007. Detection potential to point-like neutrino sources with the NEMO-km3 telescope. Astrophys. Space Sci. 309 : 415
Domogatsky G. and G. Zatsepin. 1965. On the experimental possibilities of the observation of neutrinos from collapsing stars. Proc. 9th Int. Conf. on Cosmic Rays, London, p. 1030
Domogatsky, G. et al. 1986. Present status of Baikal deep underwater experiment. Proc. XII. Conf. on Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics, Sendai, Japan, p. 737
Eberl, T. for the ANTARES Coll. 2011. Status and first results of the ANTARES neutrino telescope. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 66 : 457
Fargion, D. 2002. Discovering ultra high energy neutrinos by horizontal and upward tau air-showers : Evidences in terrestrial gamma flashes? Astrophys. J. 570 : 909
Fargion, D. P. De Sanctis Lucentini and M. De Santis. 2004. Tau air showers from Earth. Astrophys. J. 613 : 1285
Feinstein, F. for the ANTARES Coll. 1999. The ANTARES demonstrator towards an undersea neutrino telescope. Nucl. Phys. Proc. Suppl. 70 : 445
Fermi, E. 1934. Versuch einer Theorie der β-Strahlen. Z. Physik 88 : 161
Fernandez, E. et al. The High Energy Neutrino Astrophysics Panel, in High energy neutrino observatories, available from : www.lngs.infn.it/lngs/infn/contents/docs/pdf/panagic/henap2002.pdf
Fukuda, Y. et al. (Super-Kamiokande Coll.) 1998. Evidence for oscillation of atmospheric neutrinos. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81 : 1562
Gaisser, T. 1990. Prospects for neutrino astronomy. Proc. 2nd Workshop on Neutrino Telescopes, edited by M. Baldo-Ceolin, Venice, p. 397
Gigaton Volume Detector, Design Report (in Russian) at http://baikalweb.jinr.ru
Gorham, P. et al. 2004. Experimental limit on the cosmic diffuse ultra-high energy neutrino flux. Phys. Rev. Lett. 93 : 0041101
Gorham, P. et al. 2007. Observations of the Askaryan effect in ice. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99 : 171101
Gorham, P. et al. 2011. Observational constraints on the ultra-high energy cosmic neutrino flux from the second flight of the ANITA experiment. Erratum to Phys. Rev. D 82 : 022004
Greisen, K. 1960. Cosmic Ray Showers. Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 10 : 63
Grieder, P. 1994. DUMAND : Facts, Figures and Initial Operation. Proc. XVI Int. Conf. on Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics, Eilat, 1994
Gusev G. and I. Zhelesnykh. 1983. On the possibility of detection of neutrinos and muons on the basis of radio radiation of cascades in natural dielectric media. JETP Lett. 38 : 611
Halzen, F. and J.G. Learned. 1988. High Energy Neutrino Detection in Deep Polar Ice. in Proc. 5th Int. Symp. on Very High-Energy Cosmic-Ray Interactions, Lodz, Poland
Halzen, F. and J. Learned. 1993. High energy neutrino astronomy : towards a 1 km3 detector. Proc. 5th Int. Workshop on Neutrino Telescopes, edited by Milla Baldo-Ceolin, Venice, p. 483
Halzen, F. 1995. Ice fishing for neutrinos, http://icecube.berkeley.edu/amanda/ice-fishing.html
Halzen, F. 1998. Antarctic Dreams, http://www.exploratorium.edu/origins/antarctica/tools/dreams1.html
Halzen, F. and D. Hooper. 2005. High energy neutrinos from the TeV blazar 1ES 1959+650. Astropart. Phys. 23 : 537
Harwit, M. 1981. Cosmic Discovery, Basic Books Inc., New York
Heisenberg, W. 1936. Zur Theorie der Schauerbildung in der Höhenstrahlung. Z. Physik 101 : 533
Hess, V. 1912. Über die Bedeutung der durchdringenden Strahlung bei sieben Freiluftballonfahrten. Phys. Z. 12 : 998
IceCube, http://www.icecube.wisc.edu/
IceCube : a Kilometer-Scale Neutrino Observatory. 1999. A Proposal to the National Science Foundation. The U.S. institutions of the IceCube Collaboration
JEM-EUSO homepage : http://jemeuso.riken.jp/en/index.html
Johannson, S. 1991. Detection of High Energy Neutrinos. Proc. XXIIth ICRC, Dublin, p. 552
Kampert, K.-H. and A.A. Watson. 2012. Extensive air showers and ultra high-energy cosmic rays : a historical review. Eur. Phys. J. H 37 : 359-412
Kappes, A. et al. 2007. Potential neutrino signals from galactic gamma-ray sources. Astrophys. J. 656 : 870
Karaevsky, S. et al. 1993. Sea Acoustic Detection of Cosmic Objects (SADCO). Proc. 23rd ICRC, Calgary, Vol. 4, p. 550
Katz, U. and C. Spiering. 2012. High-energy neutrino astrophysics : Status and perspectives, to be published in Progress in Particle and Nuclear Physics, arXiv: 1111-0507
Kistler, M. and J. Beacom. 2006. Guaranteed and prospective galactic TeV neutrino sources. Phys. Rev. D 74 : 063007
Kotzer, P. (Ed.) 1976. DUMAND-75, Proc. 1975 Summer DUMAND Study, Western Washington State College, Bellingham, WA
Kowalski, M. 2005. Measuring diffuse neutrino fluxes with IceCube. J. Cosm. Astropart. Phys. 0505 : 010
Kravchenko, I. et al. 2006. RICE limits on the diffuse ultra-high energy neutrino flux. Phys. Rev. D 73 : 082002
Krishnaswamy, M. et al. 1971. The Kolar Gold Fields Neutrino Experiment. I. The Interactions of Cosmic Ray Neutrinos. Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. A 323 : 489
Kropp, W. and M. Crouch. 1991. Some Reminiscences of the CWI Atmospheric Neutrino Experiment, in Neutrinos and Other Matter (Selected Works of Frederick Reines). World Scientific, p. 226
Kurahashi, N. J. Vandenbroucke and G. Gratta. 2010. Phys. Rev. D 82 : 073006
Latridou, P. (Ed.) 2010. Proc. fourth Int. ARENA Workshop, 2010, Nantes. Nucl. Instr. Meth. 62 (2012)
Learned, J. (Ed.) 1979a. DUMAND-1979. Proc. of Khabarovsk and Lake Baikal Summer Workshops
Learned, J. 1979b. Acoustic radiation by charged atomic particles in liquids : An analysis. Phys. Rev. D 19 : 3239
Learned, J. 1990. Future of high energy neutrino astronomy. Proc. 2nd Int. Workshop on Neutrino Telescope, edited by M. Baldo-Ceolin, Venice, p. 103
Learned, J. and S. Pakvasa. 1995. Detecting ν τ Oscillations at PeV Energies. Astropart. Phys. 3 : 276
Lehtinen, N. et al. 2002. Sensitivity of an underwater acoustic array to ultra-high energy neutrinos. Astropart. Phys. 17 : 279
Lorenz, E. and R. Wagner. 2012. Very-high energy gamma-ray astronomy. A 23-year success story. Eur. Phys. J. H 37 : 459-513
Lowder, D. et al. 1991. Observation of muons using the polar ice cap as a Cherenkov detector. Nature 353 : 331
Mannheim, K. R. Protheroe and J. Rachen. 2001. On the cosmic ray bound for models of extragalactic neutrino production. Phys. Rev. D 63 : 023003
Markov, M.A. 1960a. On High Energy Neutrino Physics. in : Proc. 10th ICHEP, Rochester, p. 578
Markov, M. and I. Zheleznykh. 1960b. On High Energy Neutrino Physics in Cosmic Rays, in the Collection on High Energy Neutrino Physics, Dubna, p. 17
Markov, M. and I. Zheleznykh. 1961. On high energy neutrino physics in cosmic rays. Nucl. Phys. 27 : 385
Markov, M. 1993. Rasmyshlyaja o fisikakh, o fisike, o mire (contemplating on physics, physicists and the world, in Russian), Nauka, p. 76
McDonald, A. et al. 2004. Astrophysical neutrino telescopes. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 75 : 293
Morlino, G. P. Blasi and E. Amato. 2009. Gamma rays and neutrinos from supernova remnant RXJ 1713.7.3946. Astropart. Phys. 31 : 376
Morse, R. 1993. The AMANDA Astronomy Project, Proc. 5th Int. Workshop on Neutrino Telescope, edited by M. Baldo-Ceolin, Venice, p. 309
Nahnhauer, R. and S. Boeser. (Eds.) 2006. Proc. Int. ARENA Workshop, Zeuthen 2005, World Sci. Publ. Co. PTE LTD, Singapore
Nahnhauer, R. A. Rostovtsev and D. Tosi. 2008. Permafrost - an alternative target material for ultra high energy neutrino detection? Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 29 : 29
Nahnhauer, R. 2010. Acoustic particle detection – from early ideas to future benefits. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 662 : 20
Nahnhauer, R. 2012. Acoustic detetction of ultra-high energy neutrinos : a snapshot. to appear in Nucl. Instrum. Meth. (to be published)
Narisimham, V. 2004. Perspectives of Experimental Neutrino Physics in India. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. A 70 : 11
NESTOR, http://www.nestor.noa.gr/
Nishikawa, K. 1992. Proc. 4th Int. Workshop on Neutrino Telescopes, edited by M. Baldo-Ceolin, Venice, p. 337
Osborne, J. S. Said and A. Wolfendale. 1965. The energy spectra of cosmic ray neutrinos at ground level in the range 1–1000 GeV. Proc. Phys. Soc. 86 : 93
Pauli, W. 1930. Liebe radioaktive Damen und Herren Letter printed in Physics Today (1978) 31 : 72
Pierre Auger. Observatory homepage : http://www.auger.org
Pistilli, P. 1988. SINGAO : a very large telescope for neutrino and gamma astronomy and cosmic ray studies. Proc. Int. Workshop on Neutrino Telescope, edited by M. Baldo-Ceolin, p. 316
Price, B. 1996. Comparison of optical, radio, and acoustical detectors for ultrahigh-energy neutrinos. Astropart. Phys. 5 : 43
Reimer, A. M. Böttcher and S. Postnikov. 2005. Neutrino emission in the hadronic synchrotron mirror model : the “orphan” TeV flare from 1ES 1959+650. Astrophys. J. 630 : 186
Reines, F. 1960. Neutrino Interactions. Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 10 : 1
Reines, F. et al. 1965. Evidence for high-energy cosmic-ray neutrino interactions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 15 : 9
Reines, F. 1981. Closing summary ν-81, in : Proc. 30th Int. Conf. on Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics, edited by V. Peterson, Vol. 2, p. 496
Resvanis, L. et al. (NESTOR Coll.) 1994. NESTOR : A neutrino particle astrophysics underwater laboratory for the Mediterranean. Nucl. Phys. Proc. Suppl. 35 : 294
Roberts, A. (Ed.) 1976. DUMAND-76, Proc. 1976 Summer DUMAND Workshop. University of Hawaii, Honolulu, HI
Roberts, A. and G. Wilkins. (Eds.) 1978. DUMAND-78, Proc. 1978 Summer DUMAND Study
Roberts, A. 1992. The birth of high-energy neutrino astronomy : A personal history of the DUMAND project. Rev. Mod. Phys. 64 : 259
Rubakov, V. 1981. Superheavy monopoles and proton decay. JETP Lett. 33 : 644
Saltzberg, D. et al. 2001. Observation of the Askaryan effect : Coherent microwave Cherenkov emission from charge asymmetry in high energy particle cascades. Phys. Rev. Lett. : 2802
Sasaki, M. Y. Asaoha and M. Jobashi. 2003. Detecting very high energy neutrinos by the Telescope Array. Astropart. Phys. 19 : 37
Scholten, O. et al. 2008. Improved flux limits for neutrinos with energies above 1022 ev from observations with the Westerbork Synthesis Radio Telescope. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103 : 191301
Sobel, H. 1988. The GRANDE facility for the study of astrophysical sources and high-energy particle interactions. Proc. Int. Workshop on Neutrino Telescope, edited by M. Baldo-Ceolin, Venice, 233
Sokalski, I. and C. Spiering. (Eds.) (Baikal Coll.) 1992. The Baikal Neutrino Telescope NT-200. Tech. Rep. Baikal-92-03, DESY/INR
Spiering, C. 2011. Neutrino Detectors under Water and Ice, Landolt-Bornstein, New Series I, 21B2, 6.2. Springer Verlag
Stecker, F.W. 2005. A note on high energy neutrinos from AGN cores. Phys. Rev. D 72 : 107301
Stenger, V. and J. Learned. 1992a. AGN Event Rates in DUMAND II, Proc. Workshop High Energy Neutrino Astrophysics, World Scientific, 288
Stenger, V. et al. (Eds.) 1992b. Proc. Workshop High Energy Neutrino Astrophysics, World Scientific
Svoboda, R. et al. 1987 (IMB Coll.). An upper limit on the flux of extraterrestrial neutrinos. Astrophys. J. 315 : 420
Taiuti, M. et al. (NEMO Coll.) 2011. The NEMO project : A status report. Nucl. Instr. Meth. A 626 : S25
Thompson, L. and S. Danahe. (Eds.) 2006. Proc. 2nd Int. ARENA Workshop, Univ. Northumbria. J. Phys. : Conf. Ser. 81
Uberall, H. and C. Cowan. 1965. Proposal to detect cosmic-ray neutrinos through the Cerenkov light of produced muons. Proc. CERN Conf. on Experimental Neutrino Physics, edited by C. Franzinetti, CERN, Vol. 496, pp. 65–32
van Aller, G. et al. 1986. A 35-cm Diameter Photomultiplier. Helve. Physica Acta 59 : 1119
Volkova, L. and G. Zatsepin. 1965. Energetic spectra of muon and electron neutrinos in the atmosphere. Isv. AN USSR, Phys. Ser. 29 : 1749
Waxman, E. and J. Bahcall. 1999. High-energy neutrinos from astrophysical sources : An upper bound. Phys. Rev. D 59 : 023002
Weekes, T.C. et al. 1989. Observation of TeV gamma rays from the Crab nebula using the atmospheric Cerenkov imaging technique. Astrophys. J. 342 : 379
Wiebusch, C. 1995. The detection of faint light in deep underwater neutrino telescopes, Ph.D. thesis, report PITHA 95/37 (Univ. Aachen)
Wischnewski, R. et al. 1993. The Lake Baikal Telescope NT-36 – a first deep underwater multi-string array. Proc. 3rd Int. NESTOR Workshop, Pylos, Greece, p. 213
Zatsepin, G. and V. Kuzmin. 1961. Neutrino production in the atmosphere. Sov. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. (JETP) 41 : 385
Zheleznykh, I. 1988. Prospects for large scale detectors of super high-energy neutrinos (1015 to 1020 eV). Proc. 13rd Int. Conf. Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics, p. 528
Zheleznykh, I. 2006. Early years of high-energy neutrino physics in cosmic rays and neutrino astronomy. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 21S1 : 1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spiering, C. Towards high-energy neutrino astronomy. EPJ H 37, 515–565 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjh/e2012-30014-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjh/e2012-30014-2