Abstract.
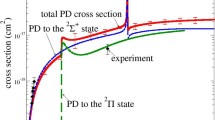
The electronic and geometric structures and photodissociation dynamics of the chromium trimer ion, Cr3 +, were investigated by photodissociation spectroscopy in the photon-energy range from 1.32 to 5.52 eV. The branching fractions of the product ions, Cr+ and Cr2 +, exhibit stepwise changes at the threshold energies for dissociation into Cr++Cr2, Cr+Cr2 +, Cr++2Cr, and Cr*+Cr2 +. It is noted that Cr2 + is produced even above the threshold for atomization; the excess energy is redistributed to produce a fragment atom, Cr*, in an excited state. The photodissociation action spectrum is well explained by a mixture of simulated spectra for two nearly-degenerate structural isomers identified by density functional calculations: those having a metastable C2v structure and the most stable structure slightly distorted from the C2v one. The barrier height between the two isomers which is lower than the zero-point energy suggests that Cr3 + has an intrinsically floppy structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.L. Michalopoulos, M.E. Geusic, S.G. Hansen, D.E. Powers, R.E. Smalley J. Phys. Chem. 86, 3914 (1982)
V.E. Bondybey, J.H. English, Chem. Phys. Lett. 94, 443 (1983)
M.M. Goodgame, W.A. Goddard III, Phys. Rev. Lett. 54, 661 (1985)
N. Desmarais, F.A. Reuse, S.N. Khanna, J. Chem. Phys. 112, 5576 (2000)
G.L. Gutsev, C.W. Bauschlicher Jr, J. Phys. Chem. A 107, 4755 (2003)
N.E. Schultz, Y Zhao, D.G. Truhlar, J. Phys. Chem. A 109, 4388 (2005)
H. Cheng, L.S. Wang, Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 51 (1996)
A. Terasaki, S. Minemoto, T. Kondow, J. Chem. Phys. 117, 7520 (2002)
K. Tono, A. Terasaki, T. Ohta, T. Kondow, J. Chem. Phys. 123, 174314 (2005)
C.-X. Su, P.B. Armentrout, J. Chem. Phys. 99, 6506 (1993)
T. Majima, K. Tono, A. Terasaki, T. Kondow, unpublished
C.-X. Su, D.A. Hales, P.B. Armentrout, Chem. Phys. Lett. 201, 199 (1993)
M.J. Frisch et al., Gaussian 03, Revision B.04, Gaussian, Inc., Pittsburgh PA, 2003
A.D. Becke, Phys. Rev. A 38, 3098 (1988)
C. Lee, W. Yang, R.G. Parr, Phys. Rev. B 37, 785 (1988)
S. Yanagisawa, T. Tsuneda, K. Hirao, J. Chem. Phys. 112, 545 (2000)
C.J. Barden, J.C. Rienstra-Kiracofe, H.F. Schaefer III, J. Chem. Phys. 113, 690 (2000)
R.E. Stratmann, G.E. Scuseria, M.J. Frisch, J. Chem. Phys. 109, 8218 (1998)
R. Bauernschmitt, R. Ahlrichs, Chem. Phys. Lett. 256, 454 (1996)
M.E. Casida, C. Jamorski, K.C. Casida, D.R. Salahub, J. Chem. Phys. 108, 4439 (1998)
K.E. Edgecombe, A.D. Becke, Chem. Phys. Lett. 244, 427 (1995)
S.M. Casey, D.G. Leopold, J. Phys. Chem. 97, 816 (1993)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Majima, T., Tono, K., Terasaki, A. et al. Photodissociation spectroscopy of the chromium trimer ion. Eur. Phys. J. D 43, 23–26 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2007-00061-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2007-00061-5