Abstract.
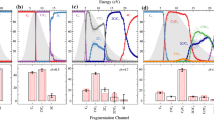
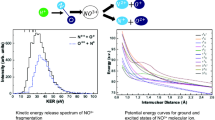
We report on experimental and theoretical efforts designed to understand the fragmentation of small carbon clusters. Experimentally, a new detection system for high velocity fragments has been recently developed allowing the fragmentation of high velocity clusters to be totally recorded [1]. Results for the branching ratios of deexcitation of C5 and C9 formed by electron capture in high velocity \( {\rm{C}}_5^ + ,\;{\rm{C}}_9^ + + {\rm{He}} \)collisions are presented. Theoretically, the dissociation dynamics of C5 has been investigated using a kinematical model based on the statistical theory of Weisskopf. In this model various structural quantities (geometries, dissociation energies, harmonic frequencies), are required for both the parent cluster and the fragments. They have been calculated within DFT and coupled-cluster formalisms for Cn up to n = 9. In all cases, a strong correlation between measured branching ratios and calculated dissociation energies is observed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinet, G., Chabot, M., Wohrer, K. et al. Fragmentation of neutral Cn clusters (n ≤ 9): experimental and theoretical investigations. Eur. Phys. J. D 24, 149 –152 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2003-00102-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/e2003-00102-1