Abstract
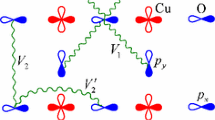
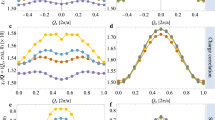
The t–t′–J–V model, one of the realistic models for studying high-T c cuprates, has been investigated to explore the hole pairing and other ground state properties using exact diagonalization (ED) technique with 2 holes in a small 8-site cluster. The role of next-nearest-neighbor (NNN) hopping and nearest-neighbor (NN) Coulomb repulsion has been considered. It appears that qualitative behavior of the ground state energies of an 8-site and 16- or 18-site cluster is similar. Results show that a small short-ranged antiferromagnetic (AF) correlation exists in the 2 hole case which is favored by large V∕t. A superconducting phase emerges at 0 ≤ V∕t ≤ 4J. Hole–hole correlation calculation also suggests that the two holes of the pair are either at |i − j| = 1 or √2. Negative t′∕t suppresses the possibility of pairing of holes. Though s-wave pairing susceptibility is dominant, pairing correlation length calculation indicates that the long range pairing, which is suitable for superconductivity, is in the d-wave channel. Both s- and d-wave pairing susceptibility gets suppressed by V∕t while d-(s-) wave susceptibility gets favored (suppressed) by t′∕t. The charge gap shows a gapped behavior while a spin-gapless region exists at small V∕t for finite t′∕t.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.W. Anderson, Science 235, 1196 (1987)
F.C. Zhang, T.M. Rice, Phys. Rev. B 37, 3709 (1988)
J. Hubbard, Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 276, 238 (1963)
F.C. Zhang et al., Supercond. Sci. Technol. 1, 36 (1988)
T.K. Lee, S.P. Feng, Phys. Rev. B 38, 11809 (1988)
S. Sorella et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 117002 (2002)
T.K. Lee et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 279702 (2002)
M. Calandra, S. Sorella, Phys. Rev. B 61, R11894 (2000)
W. Putikka, M. Luchini, T.M. Rice, Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 538 (1992)
K. Haule, G. Kotliar, Europhys. Lett. 77, 27007 (2007)
A. Himeda, T. Kato, M. Ogata, Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 117001 (2002)
M. Capello, M. Raczkowski, D. Poilblanc, Phys. Rev. B77, 224502 (2008)
P. Corboz et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 113, 046402 (2014)
D.J. Scalapino, Handbook of high temperature superconductivity, edited by J.R. Schrieffer, J.B. Brooks (Springer, New York, 2007) (Chap. 13)
R. Raimondi, J.H. Jefferson, L.F. Feiner, Phys. Rev. B 53, 8774 (1996)
K. Tanaka et al., Phys. Rev. 70, 092503 (2004)
H. Yokoyama et al., J. Phys. Soc. Jpn 82, 014070 (2013)
O. Parcollet, G. Biroli, G. Kotliar, Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 226402 (2004)
L. Spanu et al., Phys. Rev. B 77, 024510 (2008)
C.T. Shih et al., Phys. Rev. B 70, 220502 (2004)
E. Pavirini et al Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 047003 (2001)
C.T. Shih et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 227002 (2004)
N.S. Mondal, N.K. Ghosh, Pramana-J. Phys. 74, 115 (2010)
N.S. Mondal, N.K. Ghosh, Pramana-J. Phys. 74, 1009 (2010)
S. Nath, N.K. Ghosh, J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 27, 1347 (2014)
S. Nath, N.K. Ghosh, J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 27, 2871 (2014)
J.D. Sau, S. Sachdev, Phys. Rev. B 89, 075129 (2014)
A. Allais, J. Bauer, S. Sachdev, Phys. Rev. B 90, 155114 (2014)
R. Eder, J. van den Brink, G.A. Sawatzky, Phys. Rev. B 54, R732 (1996)
K. Rościszewski, A.M. Oleś, J. Phys: Condens. Matter 15, 8363 (2003)
M. Calandra, J. Merino, R.H. McKenzie, Phys. Rev. B 66, 195102 (2002)
E. Dagotto, J. Riera, Phys. Rev. B 46, 12084 (1992)
M. Bejas, A. Greco, H. Yamase, Phys. Rev B 86, 224509 (2012)
R.B. Laughlin, Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 017004 (2012)
R.B. Laughlin, Phys. Rev. B 89, 035134 (2014)
Z. Yu et al., Phys. Rev. B 96, 045110 (2017)
P.A. Leeet al., Rev. Mod. Phys. 78, 17 (2006)
W.M. Que, S.P. Bowen, C.D. Williams, J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 20, L835 (1989)
J.A. Riera, Phys. Rev. B 40, 833 (1989)
Z. Zhu et al., Sci. Rep. 4, 5419 (2014)
T. Koretsune, M. Ogata, Phys. Rev. B 72, 134513 (2005)
S. Daul, R.M. Noack, Phys. Rev. B 61, 1646 (2000)
Y. Hasegawa, D. Poilblanc, Phys. Rev. B 40, 9035 (1989)
S.M. Hayden et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 67, 3622 (1991)
S. Zhou, Z. Wang, Phys. Rev. B 70, 020501 (2004)
S. Raghu et al., Phys. Rev. B 85, 024516 (2012)
E. Plekhanov, S. Sorella, M. Fabrizio, Phys. Rev. Lett. 90, 187004 (2003)
D. Sénéchal et al., Phys. Rev. B 87, 075123 (2013)
M.A. Kastner et al., Rev. Mod. Phys. 70, 897 (1998)
S. Raghu et al., Phys. Rev. B 85, 024516 (2012)
J.A. Riera, A.P. Young, Phys. Rev. B 39, 9697 (1989)
T. Koretsune, M. Ogata, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn 74, 1390 (2005)
E. Dagotto, Rev. Mod. Phys. 66, 763 (1994)
V. Barzykin, D. Pines, Adv. Phys. 58, 1 (2009)
D.J. Scalapino, Rev. Mod. Phys. 84, 1383 (2012), references therein
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, K., Pal, P., Nath, S. et al. Hole pairing and ground state properties of high-T c superconductivity within the t–t′–J–V model. Eur. Phys. J. B 91, 64 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2018-80488-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2018-80488-y