Abstract
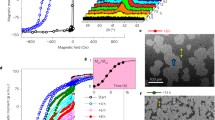
For FeCr/IrMn bilayers, the exchange bias training effect and the magnetization reversal mechanism are correlated to each other and depend on the composition of the ferromagnetic layer. For high Fe contents, the asymmetric magnetization reversal is observed. During the training effect, both exchange field and coercivity decrease monotonically, suggesting a type I training effect. For low Fe contents, the domain wall depinning takes place for the two hysteresis loop branches. Only exchange field diminution happens in the training effect. The coercivity almost does not change in the process, corresponding to a type II training effect. It is suggested that the motion of antiferromagnetic spins is modified by the magnetization reversal mechanism in the ferromagnetic layer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.H. Meiklejohn, C.P. Bean, Phys. Rev. 102, 1413 (1956)
see, e.g., J. Nogués, I.K. Schuller, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 192, 203 (1999)
A.E. Berkowitz, K. Takano, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 200, 552 (1999)
D. Paccard et al., Phys. Status Solidi 16, 301 (1966)
H. Xi et al., Phys. Rev. B 64, 184416 (2001)
K. Zhang et al., J. Appl. Phys. 89, 6910 (2001)
K. Zhang et al., J. Appl. Phys. 91, 6902 (2002)
A. Hochstrat et al., Phys. Rev. B 66, 092409 (2002)
Ch. Binek, Phys. Rev. B 70, 014421 (2004)
S. Brems et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 157202 (2005)
S. Brems et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 067201 (2007)
Ch. Binek et al., Phys. Rev. Lett 96, 067201 (2006)
M.S. Lund, C. Leighton, Phys. Rev. B. 76, 104433 (2007)
S. Polisetty et al., Phys. Rev B 76, 184423 (2007)
T. Hauet et al., Phys. Rev B 76, 144423 (2007)
A. Paul et al., Phys. Rev B 76, 184424 (2007)
M.K. Chan et al., Phys. Rev B 77, 014420 (2008)
M. Fecioru-Morariu et al., Phys. Rev B 77, 054441 (2008)
Z. Shi et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 222504 (2008)
S. Polisetty et al., Phys. Rev. B 78, 184426 (2008)
J. Ventura et al., Phys. Rev. B 77, 184404 (2008)
A.G. Biternas et al., Phys. Rev. B 80, 134419 (2009)
P. Biagioni et al., Phys. Rev. B 80, 134401 (2009)
T. Suzuki et al., IEEE Trans. Magn. 28, 2754 (1992)
A. Fnidikia et al., Physica B 363, 271 (2005)
K. Tarafder et al., J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 20, 445201 (2008)
D.V. Ratnam, W.R. Buessem, J. Appl. Phys. 43, 1291 (1972)
S.M. Zhou, C.L. Chien, Phys. Rev. B 63, 104406 (2001)
R. Shan et al., Phys. Rev. B 71, 064402 (2005)
C. Papusoi Jr., J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 195, 708 (1999)
L. Sun et al., Phys. Rev. B 71, 012417 (2005)
T. Ambrose et al., Phys. Rev. B 56, 83 (1997)
B. Beckmann et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 187201 (2003)
A. Hoffmann, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, 097203 (2004)
Z. Shi et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 122507 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Z., Qiu, X.P., Zhu, J.T. et al. Composition-controlled exchange bias training effect in FeCr/IrMn bilayers. Eur. Phys. J. B 84, 173–176 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2011-20808-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjb/e2011-20808-3