Abstract
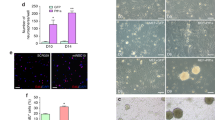
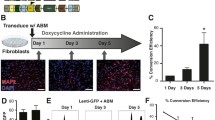
The generation of multipotent patient-specific neural precursors from human fibroblasts is one of the challenges to regenerative medicine. A recently proposed novel approach allows direct conversion of human and mouse fibroblasts into induced neuronal precursor (iNP) cells by overexpression of a single transcription factor, Sox2. In this work, we have analyzed the Sox2-induced iNP cells and evaluated the possibility of its medical application. Both mouse and human fibroblasts had pronounced morphological changes after lentiviral-mediated Sox2 overexpression. The resulting mouse and human iNP cell cultures are morphologically similar to the neuronal precursors (NPs) derived from the mouse embryonic brain. Both human and mouse iNP cells express NP molecular markers, however, differentiation of mouse iNP cells fails to produce various types of neural cells. Especially, these cells are unable to differentiate into mature neurons. In addition to Sox2, we have treated human fibroblasts with c-Myc in combination with either Ascl or Brn2. One of the produced cell lines displayed a low proliferative potential, while another intensely divided; however, cytogenetic analysis revealed their aberrant karyotype. The observed specific features of both the human and mouse iNP cells produced according to this protocol make them of limited therapeutic use. Thus, these iNP cell cultures are not completely equivalent to natural NPs. Correspondingly, we assume that the published protocol for iNP generation via Sox2 exogenous expression is poorly reproducible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heinrich, C., Blum, R., Gascon, S., Masserdotti, G., Tripathi, P., Sanchez, R., Tiedt, S., Schroeder, T., Gotz, M., and Berninger, B., Directing astroglia from the cerebral cortex into subtype specific functional neurons, Plos Biol., 2010, vol. 8, no. 5, p. å1000373.
Ieda, M., Fu, J.D., Delgado-Olguin, P., Vedantham, V., Hayashi, Y., Bruneau, B.G., and Srivastava, D., Direct reprogramming of fibroblasts into functional cardiomyocytes by defined factors, Cell, 2010, vol. 142, no. 3, pp. 375–386.
Jessberger, S. and Gage, F.H., Adult neurogenesis: bridging the gap between mice and humans, Trends Cell Biol., 2014, vol. 24, no. 10, pp. 558–563.
Keller, G., Embryonic stem cell differentiation: emergence of a new era in biology and medicine, Genes Dev., 2005, vol. 19, pp. 1129–1155.
Kruglova, A.A., Kizilova, E.A., Zhelezova, A.I., Gridina, M.M., Golubitsa, A.N., and Serov, O.L., Embryonic stem cell/fibroblast hybrid cells with near-tetraploid karyotype provide high yield of chimeras, Cell Tissue Res., 2008, vol. 334, pp. 371–380.
Marion, R.M., Strati, K., Li, H., Murga, M., Blanco, R., Ortega, S., Fernandez-Capetillo, O., Serrano, M., and Blasco, M.A., A p53-mediated DNA damage response limits reprogramming to ensure iPS cell genomic integrity, Nature, 2009, vol. 460, pp. 1149–1153.
Mouhieddine, T.H., Kobeissy, F.H., Itani, M., Nokkari, A., and Wang, K.K.W., Stem cells in neuroinjury and neurodegenerative disorders: challenges and future neurotherapeutic prospects, Neural Regen. Res., 2014, vol. 9, pp. 901–906.
Pristiazhniuk, I.E., Matveeva, N.M., Grafodatskii, A.S., Serdiukova, N.A., and Serov, O.L., Analysis of chromosome sets in interspecific embryonic stem hybrid cells of mice, Tsitologiya, 2010, vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 136–143.
Ring, K.L., Tong, L.M., Balestra, M.E., Javier, R., Andrews-Zwilling, Y., Li, G., Walker, D., Zhang, W.R., Kreitzer, A.C., and Huang, Y., Direct reprogramming of mouse and human fibroblasts into multipotent neural stem cells with a single factor, Cell Stem Cell, 2012, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 100–109.
Ruggieri, M., Riboldi, G., Brajkovic, S., Bucchia, M., Bresolin, N., Comi, G.P., and Corti, S., Induced neural stem cells: methods of reprogramming and potential therapeutic applications, Progr. Neurobiol., 2014, vol. 114, pp. 15–24.
Sasaki, M.S. and Kodama, S., Establishment and some mutational characteristics of 3T3-like near-diploid mouse cell line, J. Cellular Physiol., 1987, vol. 131, pp. 114–122.
Sekiya, S. and Suzuki, A., Direct conversion of mouse fibroblasts to hepatocyte-like cells by defined factors, Nature, 2011, vol. 475, no. 7356, pp. 390–393.
Takahashi, K. and Yamanaka, S., Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors, Cell, 2006, vol. 126, pp. 663–676.
Vierbuchen, T., Ostermeier, A., Pang, Z.P., Kokubu, Y., Sudhof, T.C., and Wernig, M., Direct conversion of fibroblasts to functional neurons by defined factors, Nature, 2010, vol. 463, no. 7284, pp. 1035–1041.
Villegas, J. and McPhaul, M., Establishment and culture of human skin fibroblasts, Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol., 2005, Unit 28.3.
Wernig, M., Meissner, A., Foreman, R., Brambrink, T., Ku, M., Hochedlinger, K., Bernstein, B.E., and Jaenisch, R., In vitro reprogramming of fibroblasts into a pluripotent ES-cell-like state, Nature, 2007, vol. 448, pp. 318–324.
Zhong, B., Watts, K.L., Gori, J.L., Wohlfahrt, M.E., Enssle, J., Adair, J.E., and Kiem, H.-P., Safeguarding nonhuman primate iPS cells with suicide genes, Mol. Ther, 2011, vol. 19, pp. 1667–1675.
Zou, Q., Yan, Q., Zhong, J., Wang, K., Sun, H., Yi, X., and Lai, L., Direct conversion of human fibroblasts into neuronal restricted progenitors, J. Biol. Chem., 2014, vol. 289, pp. 5250–5260.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © I.E. Pristyazhnyuk, T.A. Shnayder, V.S. Fishman, N.M. Matveeva, O.L. Serov, 2014, published in Vavilovskii Zhurnal Genetiki i Selektsii, 2014, Vol. 18, No. 4/3, pp. 1055–1066.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pristyazhnyuk, I.E., Shnayder, T.A., Fishman, V.S. et al. Direct conversion of somatic cells to neuronal precursors: Problems and outlooks. Russ J Genet Appl Res 5, 543–551 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079059715060106
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079059715060106