Abstract
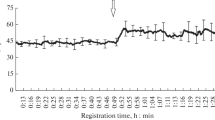
The changes in heart rate and circadian cardiac rhythm of crayfish Pontastacus leptodactylus Esch. kept in a lightning regime that is close to natural under optimal or low pH values were studied. The heart rate was registered in real time using an original noninvasive fiberoptic method. Upon acidification, disorders in circadian cardiac rhythm and organism reaction (by heart rate) in the suspension test were detected. The characteristics of cardiac activity are considered criteria for estimating the crayfish’s functional state at normal and stress conditions caused by the changes in the quality of the environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baevskii, P.M. and Berseneva, A.L., Otsenka adaptatsionnykh vozmozhnostei organizma i risk razvitiya zabolevanii (Assessment of Adaptive Capacity of the Body and the Risk of Disease Development), Moscow: Meditsina, 1997.
Vinogradov, G.A., Komov, V.T., and Matei, V.E., Functional Basis of the Effect of Low pH on Fish and Crayfish, in Fiziologicheskie i biokhimicheskie aspekty toksikologii presnovodnykh zhivotnykh (Physiological and Biochemical Aspects of Toxicology of Freshwater Animals), Borok: Inst. Biol. Vnutr. Vod Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1984, pp. 147–190.
Moiseenko, T.I., Effects of Acidification on Aquatic Ecosystems, Russ. J. Ecol., 2005, vol. 36, no. 2, pp. 93–102.
Udalova, G.P., Kholodkevich, S.V., Sladkova, S.V., et al., Study of Circadian Activity in the Crayfish Pontastacus leptodactylus during Their Multimonth Stay in the River Water Flow, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 2009, vol. 45, no. 3, pp. 304–312.
Fedotov, V.P., Kholodkevich, S.V., and Strochilo, A.G., Heart Activity of the Crayfish Astacus astacus in Various Functional States, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 2002, vol. 38, no. 1, pp. 36–4.
Fedotov, V.P., Kholodkevich S.V., Udalova G.P. Crayfish Heart Activity in Awake, Rest and “Animal” Hypnosis, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 2006, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 41–48.
Fedotov, V.P., Shumilova, T.E., Kholodkevich, S.V., and Strochilo, A.G., Noninvasive Method for Estimating the Parameters of Functioning of the Heart of Crustaceans, in Mater. Region. Soveshch. Mezhdunar. Assotsiatsii Astakologov (Proc. Regional Conf. Int. Association of Astacologists,) Astrakhan’, 2002, pp. 49–57.
Kholodkevich, S.V., Real-Time Bioelectronic Monitoring of Toxicity of Natural and Waste Waters, Ekol. Khim., 2007, vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 223–232.
Kholodkevich, S.V., Ivanov, A.V., Kornienko, E.L., and Kurakin, A.S., Method of Biological Monitoring of the Environment (Options) and the System for Its Implementation, RF Patent No. 2308720 C1, Byull. Izorbet., 2007, no. 29.
Tsukerzis, Ya.M., Rechnye raki (Crayfish), Vilnus: Mokslas, 1989.
Aagaard, A., Warman, C.G., and Depledge, M.H., The Use of Cardiac Monitoring in the Assessment of Mercury Toxicity in the Subtropical Pebble Crab Gsetice depressus (Brachyura: Grapsidae; Varuninae), Sci. Mar., 2000, vol. 64, no. 4, pp. 381–386.
Allison, V., Dunham, D.W., and Harvey, H.H., Low pH Alter Response to the Crayfish Cambarus bartoni, Can. J. Zool., 1992, vol. 70, no. 2, pp. 2416–2420.
Appelberg, M., Changes in Haemolymph Ion Concentrations of Astacus astacus L. and Pacifastacus lenticulus (Dana) after Exposure to Low pH and Aluminium, Hydrobiologia, 1985, vol. 121, pp. 19–25.
Bamber, S.D. and Depledge, M.H., Evaluation of Changes in the Adaptive Physiology of Shore Crabs (Carcinus maenas) as an Indicator of Pollution in Estuarine Environments, Mar. Biol. (Berlin), 1997, vol. 129, no. 3, pp. 667–672.
Depledge, M.H., Aagaard, A., and Gyorkos, P., Assessment of Trace Metal Toxicity using Molecular, Physiological and Behavioural Biomarkers, Mar. Pol. Bull., 1995, vol. 31, nos. 1–3, pp. 19–27.
Depledge, M.H. and Andersen, B.B., A Computer-Aided Physiological Monitoring System for Continuous, Long-Term Recording of Cardiac Activity in Selected Invertebrates, Comp. Biochem. Physiol., 1990, vol. 96A, no. 4, pp. 473–477.
Di Stefano, R.J., Neves, R.J., Helfrich, L.A., and Lewis, M.C., Response of the Crayfish Cambarus bartonii bartonii to Acid Exposure in Southern Appalachian Streams, Can. J. Zool., 1991, vol. 89, pp. 1585–1591.
Ehrenfeld, J., Aspects of Ionic Transport Mechanisms in Crayfish Astacus leptodactylus, J. Exp. Biol., 1974, vol. 61, pp. 57–70.
Fingerman, M. and Lago, A.D., Endogenous Twenty-Four Hour Rhythms of Locomotor Activity and Oxygen Consumption in the Crayfish Orconectes clypeatus, Amer. Midland. Natur., 1957, vol. 58, pp. 383–393.
France, R.L., Comparative Tolerance to Low pH of Three Life Stages of the Crayfish Orconektes virilisi, Can. J. Zool., 1984, vol. 62, pp. 2360–2363.
Kholodkevich, S.V., Ivanov, A.V., Kurakin, A.S., et al., Real Time Biomonitoring of Surface Water Toxicity Level at Water Supply Stations, J. Environ. Bioindicators, 2008, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 23–34.
McMahon, B.R., Physiological Adaptation to Environment, in Biology of Freshwater Crayfish, Oxford: Blackwell Science, 2002, pp. 327–376.
Newcombe, K.J., The pH Tolerance of the Crayfish Parastacoides tasmanicus (Erichson) (Decapoda, Parastacidae), Crustaceana, 1975, vol. 29, no. 3, pp. 231–234.
Nikinmaa, M., Jarvenpaa, T., Westman, K., Soivio, A., Effect of Hypoxia and Acidification on the Haemolymph pH Values and Ion Concentration in the Freshwater Crayfish Astacus astacus L., Finish Fisheries Res., 1983, vol. 5, pp. 17–22.
Styrishave, B., Rasmusson, A.D. and Depledge, M.H., The Influence of Bulk and Trace Metals on the Circadian Rhythmicity of Heart Rates in Freshwater Crayfish Astacus astacus, Mar. Poll. Bull., 1995, vol. 31, pp. 87–92.
Tierney, A.J. and Atema, J., Effects of Acidification on the Behavioral Response of Crayfishes (Orconektes virilisi and Procambarus acutus) to Chemical Stimuli, Aquat. Toxicol., 1986, vol. 9, pp. 1–11.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Udalova, G.P., Kholodkevich, S.V., Fedotov, V.P. et al. Changes in heart rate and circadian cardiac rhythm as physiological biomarkers for estimation of functional state of crayfish Pontastacus leptodactylus Esch. upon acidification of the environment. Inland Water Biol 5, 119–127 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082912010166
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995082912010166