Abstract
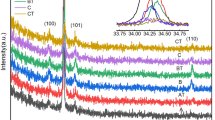
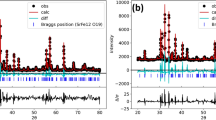
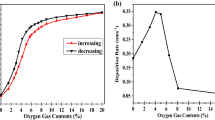
Multiphase nanopowders (NPs) and amorphous/amorphous-nanocrystalline coatings (A-NC) have been prepared by the evaporation of ceramic targets of Al2O3-Fe2O3 (0.1, 3, 5 Fe2O3 mass %) by a pulsed electron beam in vacuum. The specific surface area of NP Al2O3-Fe2O3 reached 277 m2/g. The α and γ phases Al2O3 and other nonidentified phases have been found in the composition of NP Al2O3-Fe2O3. All coatings contained an insignificant fraction of the crystalline γ phase. No secondary phases on the basis of iron have been revealed. According to transmission electron microscopy, the fine fraction of NP Al2O3-Fe2O3 consists of amorphous nanoparticles of an irregular and quasispherical shape no more than 10 nm in size which form agglomerates reaching 1.5 μm. A large fraction of NPs consists of crystal spherical nanoparticles with preferential sizes of about 10–20 nm. All NP Al2O3-Fe2O3 showed ferromagnetic behavior at room temperature. The maximum magnetic response has been established in NPs with a minimum iron content (1.1 mass %). The pulsed cathode luminescence spectra of coatings and NP Al2O3-Fe2O3 have been presented by a wide band in the wavelength range of 300–900 nm regardless of their phase composition. Phase transformations into NP AL2O3-1.1% Fe and coatings from undoped Al2O3 heated to 1400°C occur according to the following scheme: amorphous phase → γ → δ → θ → α, regardless of their initial phase composition. The threshold of thermal stability of the Γ phase in NPs and the coating of undoped Al2O3 does not exceed 830°C. For the first time, the increased thermo and optically stimulated luminescent response comparable with the response of the leading TLD-500K thermoluminescent dosimeter has been reached in A-NC coatings of undoped Al2O3.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Engelhart, W. Dreher, O. Eibl, and V. Schier, “Deposition of alumina thin film by dual magnetron sputtering: Is it γ-Al2O3?,” Acta Mater. 59, 7757–7767 (2011).
O. Zywitzki, G. Hoetzsch, F. Fietzke, and K. Goedicke, Effect of the substrate temperature on the structure and properties of Al2O3 layers reactively deposited by pulsed magnetron sputtering,” Surf. Coat. Technol. 82,1–2), 169–175 (1996).
O. Kyrylov, D. Kurapov, and J. M. Schneider, “Effect of ion irradiation during deposition on the structure of alumina thin films grown by plasma assisted chemical vapour deposition,” Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Processing 80(8), 1657–1660 (2005).
J. M. Andersson, Zs. Czigány, P. Jin, and U. Helmersson, “Microstructure of α-alumina thin films deposited at low temperatures on chromia template layers,” J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 22, 117–121 (2004).
P. Jin, G. Xu, M. Tazawa, K. Yoshimura, D. Music, J. Alami, and U. Helmersson, “Low temperature deposition of α-Al2O3 thin films by sputtering using a Cr2O3 template,” J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A. 20, 2134–2136 (2002).
J. M. Andersson, E. Wallin, U. Helmersson, U. Kreissig, and E. P. Munger, “Al2O3 thin films grown at low temperatures,” Thin Solid Films 513, 57–59 (2006).
P. Eklund, M. Sridharan, G. Singh, and J. Bottiger, “Thermal Stability and Phase Transformations of γ-/Amorphous-Al2O3,” Thin Films Plasma Processes Polym.s 6(S1), S907–S911 (2009).
X. F. Duan, N. H. Tran, N. K. Roberts, and R. N. Lamb, “Solvothermal approach for low temperature deposition of aluminium oxide thin films,” Thin Solid Films 518(15), 4290–4293 (2010).
V. Edlmayr, M. Moser, C. Walter, and C. Mitterer, “Thermal stability of sputtered Al2O3 coatings,” Surf. Coat. Technol. 204, 1576–1581 (2010).
T. Kohara, H. Tamagaki, Y. Ikari, and H. Fujii, “Deposition of a-Al2O3 hard coatings by reactive magnetron sputtering,” Surf. Coat. Technol. 185, 166–171 (2004).
R. Romàn, T. Hernàndez, and M. Gonzàlez, “Nano or micro grained alumina powder? A choose before sintering,” Boletín de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio 47(6), 311–318 (2008).
G. R. Karagedov and A. L. Myz, “Preparation and sintering pure nanocrystalline α-alumina powder,” J. Europ. Ceram. Soc. 32(1), 219–225 (2012).
K. Yatsui, T. Yukawa, C. Grigoriu, M. Hirai, and W. Jiang, “Synthesis of ultrafne γ-Al2O3 powders by pulsed laser ablation,” J. Nanopart. Res. 2(1), 75–83 (2000).
D. A. Dubov, Vl. Snytnikov, and V. N. Snytnikov, “The way to synthesize nanopowders of churlish oxides by means of laser evaporation,” in Collection of Scientific Papers of Novosibirsk State Technical University (Novosibirsk, 2005), No. 4(42), pp. 83–90 [in Russian].
S. P. Bardakhanov, A. I. Korchagin, N. K. Kuksanov, A. V. Lavrukhin, R. A. Salimov, S. N. Fadeev, and V. V. Cherepkov, “Use of an electron accelerator to produce nanopowders by evaporation of initial materials at atmospheric pressure,” Russ. Phys. J. 50(2), 120–124 (2007).
V. G. Il’ves, A. I. Medvedev, A. M. Murzakaev, S. Yu. Sokovnin, A. V. Spirina, and M. A. Uimin, “Physiscal characteristics of Al2O3-Al(Cu) nanopowders synthesized by target electron-beam evaporation,” Fiz. Khim. Obrab. Mater., No. 2, 65–70 (2011).
S. Schlabach, V. Szabó, D. Vollath, A. Braun, and R. Clasen, “Structure of alumina and zirconia nanoparticles synthesized by the Karlsruhe Microwave Plasma Process,” Solid State Phenom. 99–100, 191–196 (2004).
K. Jiang, K. Sarakinos, S. Konstantinidis, and J. M. Schneider, “Low temperature synthesis of α-Al2O3 films by high-power plasma-assisted chemical vapor deposition,” J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 43, 325202 (15) (2010).
D. L. Alontseva, S. N. Bratushka, A. D. Pogrebnyak, N. V. Prokhorenkova, and V. T. Shablya, “Structure and properties of coatings and modified layers synthesized by means of plasma flows,” Fiz. Inzh. Poverkhn. 5(3–4), 124–139 (2007).
A. D. Pogrebnyak, M. I. Il’yashenko, S. N. Bratushka, V. V. Ponaryadov, and N. K. Erdybaeva, “The way for forming high-dispersed state in plasma-detonating aluminum oxide coating,” Fiz. Inzh. Poverkhn. 4(1–2), 32–47 (2006).
I. Levin and D. Brandon, “Metastable Alumina Polymorphs: Crystal Structures and Transition Sequences,” J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 81(8), 1995–2012 (1998).
L. A. Krushinskaya and Ya. A. Stel’makh, “Structure and properties of aluminum oxide thick condensates synthesized by electron-beam evaporation and deposition of vapor phase in vacuum,” VANT. Ser.: Chist. Mater. Vakuum. Tekhnol. 19(6), 92–98 (2011).
E. Krumov, V. Mankov, and K. Starbova, “Nanosized columnar microstructure and related properties of electron gun deposited Al2O3 thin films,” Vacuum 76, 211–214 (2004).
H. H. Huang, Y. S. Liu, Y. M. Chen, M. C. Huang, and M. C. Wang, “Effect of oxygen pressure on the microstructure and properties of the Al2O3-SiO2 thin films deposited by E-beam evaporation,” Surf. Coat. Technol. 200, 3309–3313 (2006).
N. Yu, T. W. Simpson, P. C. McIntyre, M. Nastasi, and I. V. Mitchell, “Doping effects on the kinetics of solid phase epitaxial growth of amorphous alumina thin films on sapphire,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 67, 924–926 (1995).
V. S. Kortov, I. I. Mil’man, and S. V. Nikiforov, “Solid dosimetry,” Izv. Tomsk. Politekhn. Univ. 303(2), 35–45 (2000).
C. E. Chryssou and C. W. Pitt, “Al2O3 thin films by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition using trimethyl-amine alane (TMAA) as the Al precursor,” Appl. Phys. A 65, 469–475 (1997).
Yu. A. Kotov, S. Yu. Sokovnin, V. G. Il’ves, and C. K. Rhee, RF Patent 2353573 B82B 3/00, Byull. Izobret., No. 12 (2009).
S. G. Mikhailov, V. V. Osipov, and V. I. Solomonov, “Pulse cathodoluminescent KLAVI 1 AU device for matter analyzing,” Prib. Tekhn. Eksperim., No. 3, 164–165 (2001).
I. I. Mil’man, E. V. Moiseikin, S. V. Nikiforov, S. V. Solov’ev, I. G. Revkov, and E. N. Litovchenko, “Role of deep traps in luminescence of α-Al2O3:C anion-defect crystals,” Fiz. Tverd. Tela 50(11), 1991–1995 (2008).
A. K. Ladavos and T. V. Bakas, “The Al2O3-Fe2O3 mixed oxidic system, I. Preparation and characterization,” React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 73(2), 223–228 (2001).
S. Yu. Sokovnin, V. G. Il’ves, and S. V. Pryanichnikov, “Structure and magnetic properties of ZnO nanopowders doped by ferrum,” Zh. Tekh. Fiz. (2013) (in press).
C. Oprea and V. Ionescu, “TEM and XRD investigation of Fe2O3-Al2O3 system,” Ovidius Univ. Ann. Chem. 20(2), 222–226 (2009).
A. D. Pogrebnyak, Yu. N. Tyurin, Yu. F. Ivanov, A. P. Kobzev, O. P. Kul’ment’eva, and M. V. Il’yashenko, “The way to produce and investigate structure and properties of Al2O3 plasma-detonating coatings,” Pis’ma Zh. Tekh. Fiz. 26(21), 3–60 (2000).
R. Nakamura, T. Shudo, A. Hirata, M. Ishimaruand, and H. Nakajima, “Nanovoid formation through the annealing of amorphous Al2O3 and WO3 films,” Scripta Mater. 64, 197–200 (2011).
R. Nakamura, M. Ishimaru, A. Hirata, K. Sato, M. Tane, H. Kimizuka, T. Shudo, T. J. Konno and H. Nakajima, “Enhancement of nanovoid formation in annealed amorphous Al2O3 including W,” J. Appl. Phys. 110, 064324 (7) (2011).
E. Yu. Svetkina, “Mechanical-chemical variations of Al2O3 under vibration,” Vopr. Khim. Khim. Tekhnol., No. 4, 36–41 (2003).
R. S. Gates, S. M. Hsu, and E. E. Klaus, “Tribochemical mechanism of alumina with water,” Tribol. Trans 32(3), 357–363 (1989).
E. S. Astapova, E. B. Pivchenko, and E. A. Vanina, “Transition α γ for aluminum oxide in corundum ceramic caused by neutron radiation,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk 376(5), 611–614 (2001).
Z. Zhou, H. Guo, M. Abbas, and S. Gong, “Effect of water vapor on the phase transformation of alumina grown on NiAl at 95°C,” Corrosion Sci. 53, 2943–2947 (2011).
F. Pan, C. Song, X. J. Liu, Y. C. Yang, and F. Zeng, “Ferromagnetism and possible application in spintronics of transition-metal doped ZnO films,” Mater. Sci. Eng. 62, 1–35 (2008).
T. Dietl, “A ten-year perspective on dilute magnetic semiconductors and oxides,” Nature Mater. 9, 965–974 (2010).
J. M. D. Coye and S. Chambers, “Oxide dilute magnetic semiconductors-fact or fiction?,” MRS Bull. 33, 1053–1058 (2008).
J. M. D. Coey, “d0 Ferromagnetism,” Solid State Sci. 7, 660–667 (2005).
A. Sundaresan, R. Bhargavi, N. Rangarajan, U. Sid- desh, and C. N. R. Rao, “Ferromagnetism as a universal feature of nanoparticles of the otherwise nonmagnetic oxides,” Phys. Rev. B 74(16), 161304 (4) (2006).
Y. L. Zheng, C. M. Zhen, X. Q. Wang, L. Ma, X. L. Li, and D. L. Hou, “Room-temperature ferromagnetism observed in alumina films,” Solid State Sci. 13(8), 1516–1519 (2011).
V. G. Il’ves and S. Yu. Sokovnin, “The way to synthesize ZnO and Zn-ZnO nanopowders by means of pulse electron beam evaporation in low pressure gas,” Ross. Nanotekhnol. 6(1–2), 20–26 (2011).
S. Yu. Sokovnin, V. G. Il’ves, A. I. Medvedev, A. M. Murzakaev, and M. A. Uimin, “Pulse electron evaporation of ZnO-Zn nanopowders doped by cuprum,” in Proc. 4th All-Russian Conf. on Nanomaterials (A. Baikov Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Science, Moscow, March 1–4, 2011), pp. 128, 574.
S. Yu. Sokovnin and V. G. Il’ves, The Way to Use Pulse Electron Beam for Synthesizing Metal Oxide Powders (Ural Brunch RAS, Yekaterinburg, 2011) [in Russian].
V. G. Il’ves and S.Yu. Sokovnin, “The way to produce and investigate properties of CeO2 nanopowders,” Ross. Nanotekhnol. 7(3–4), 7–16 (2012).
V. G. Il’ves and S. Yu. Sokovnin, “Magnetic properties of ZnS nanopowders synthesized by means of pulse electron beam,” in Interuniversity Collection of Papers “Problems of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry (Ural State Tech. Univ., Yekaterinburg, 2010), Issue 26, pp. 237–242 [in Russian].
T. K. Kundu, M. Mukherjee, and D. Chakravorty, “Growth of nano-α-Fe2O3 in a titania matrix by the sol-gel route,” J. Mater. Sci. 33, 1759–1763 (1998).
M. Tadic, D. Markovic, V. Spasojevic, V. Kusigerski, M. Remskar, J. Pirnat, and Z. Jaglicic, “Synthesis and magnetic properties of concentrated α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles in a silica matric,” J. Alloys Compounds 441(1–2), 291–296 (2007).
I. Sakamoto, S. Honda, H. Tanoue, N. Hayashi, and H. Yamane, “Structural and magnetic properties of Fe ion implanted Al2O3,” Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B: Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 148(1–4), 1039–1043 (1999).
D. S. Xue, Y. L. Ma Y. Huang, P. H. Zhou, Z. P. Niu, F. S. Li, R. Job, and W. R. Fahrner, “Magnetic properties of pure Fe-Al2O3 nanocomposites,” J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 22, 1817–1820 (2003).
N. M. Dempsey, L. Ranno, D. Givord, J. Gonzalo, R. Serna, G. T. Fei, A. K. Petford-Long, R. C. Doole, and D. E. Hole, “Magnetic behavior of Fe:Al2O3 nanocomposite films produced by pulsed laser deposition,” J. Appl. Phys. 90(12), 6268–6274 (2001).
R. Ramesh, K. Ashok, G. M. Bhalero, S. Ponnusamy, and C. Muthamizhchelvan, “Synthesis and properties of α-Fe2O3 nanorods,” Cryst. Res. Technol. 45(9), 965–968 (2010).
J. Wu, S. Mao, Z. G. Ye, Z. Xie, and L. Zheng, “Room-temperature weak ferromagnetism induced by point defects in alpha-Fe2O3,” Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2(6), 1561–1564 (2010).
G. Schimanke and M. Martin, “In situ XRD study of the phase transition of nanocrystalline maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) to hematite (α-Fe2O3),” Solid State Ionics 136–137, 1235–1240 (2000).
G. Ennas, G. Marongiu, A. Musinu, A. Falqui, P. Ballirano, and R. Caminiti, “Characterization of Nanocrystalline g-Fe2O3 Prepared by Wet Chemical Method,” J. Mater. Res. 14, 1570–1575 (1999).
O. Kido, Y. Higashino, K. Kamitsuji, M. Kurumada, T. Sato, Y. Kimura, H. Suzuki, Y. Saito, and C. Kaito, “Phase Transition Temperature of γ-Fe2O3 Ultrafine Particle,” J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 73, 2014–2016 (2004).
B. B. Straumal, A. A. Myatiev, P. B. Straumal, A. A. Mazilkin, S. G. Protasova, E. Gering, and B. Baretzky, “Grain boundary layers in nanocrystalline ferromagnetic zinc oxide,” Pis’ma Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 92(6), 438–443 (2010).
B. B. Straumal, A. A. Mazilkin, S. G. Protasova, A. A. Myatiev, P. B. Straumal, G. Schütz, P. A. van Aken, E. Goering, and B. Baretzky, “Magnetization study of nanograined pure and Mn-doped ZnO films: Formation of a ferromagnetic grain-boundary foam,” Phys. Rev. B 79, 205206(6) (2009).
K. Sato and L. Bergqvist, J. Kudrnovsky, P. H. Dederichs, O. Eriksson, I. Turek, B. Sanyal, G. Bouzerar, H. Katayama-Yoshida, V. A. Dinh, T. Fukushima, H. Kizaki, and R. Zeller, “First-principles theory of dilute magnetic semiconductors,” Rev. Mod. Phys. 82(2), 1633–1690 (2010).
L. I. Burova, N. S. Perov, A. S. Semisalova, V. A. Kulbachinskii, V. G. Kytin, V. V. Roddatis, A. L. Vasiliev, and A. R. Kaul, “Effect of the nanostructure on room temperature ferromagnetism and resistivity of undoped ZnO thin films grown by chemical vapor deposition,” Thin Solid Films 520, 4580–4585 (2012).
D. Gao, Z. Zhang, J. Fu, Y. Xu, J. Qi, and D. Xue, “Room temperature ferromagnetism of pure ZnO nanoparticles,” J. Appl. Phys. 105(4), 113928(4) (2009).
Y. L. Zheng, C. M. Zhen, X. Q. Wang, X. L. Li, and D. L. Hou, “Room-temperature ferromagnetismobserved in alumina films,” Solid State Sci. 13(8), 1516–1519 (2011).
A. Sundaresan, R. Bhargavi, N. Rangarajan, U. Siddesh, and C. N. R. Rao, “Ferromagnetism as a universal feature of nanoparticles of the otherwise nonmagnetic oxides,” Phys. Rev. B, Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 74(16), 161306(6) (2006).
S. Yu. Sokovnin and V. G. Il’ves, “Properties of nanopowders and coatings base on aluminum oxide synthesized by electron beam evaporation,” Ross. Nanotekhnol. (2013) (in press).
M. W. Blair, L. G. Jacobsohn, S. C. Tornga, O. Ugurlu, B. L. Bennett, E. G. Yukihara, and R. E. Muenchausen, “Nanophosphor aluminum oxide: Luminescence response of a potential dosimetric material,” J. Luminescence 130, 825–831 (2010).
P. Mancosu, M. C. Cantone, I. Veronese, and A. Giussani, “Spatial distribution of beta extremity doses in nuclear medicine: a feasibility study with thin α-Al2O3:C TLDs,” Phys. Med. 26, 44–48 (2010).
J. E. Villarreal-Barajas, L. Escobar-Alarcón, E. Camps, P. R. Gonzales, and E. Villagran, “Thermoluminescence response of aluminum oxide thin films to beta-particle and UV radiation,” Superficies y Vacío 13, 126–129 (2001).
G. P. Summers, “Thermoluminescence in single crystal α-Al2O3,” Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 8(1–2), 69–80 (1984).
T. S. Bessonova, M. P. Stanislavskii, A. I. Sobko, and V. Ya. Khaimov-Mal’kov, “Concentration relationship of radiation-optical effects in ruby,” J. Prikl. Spektroskop. 27(2), 238–243.
A. I. Surdo, V. S. Kortov, and F. F. Sharafutdinov, “Luminescence of anion-defective corundum with titanium impurity,” Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 84, 261–264 (1999).
Ya. A. Valbis, P. A. Kulis, L. N. Raiskaya, V. A. Sandu- lenko, M. E. Springis, and Z. Z. Eromanov, “Recombination luminescence of α-Al2O3 crystals with admixture of IV group elements,” in Collection of Scientific Works of Latvian State University “Thermoactivating Spectroscopy for Defects in Ion Crystals” (Riga, 1983), pp. 126–144 [in Russian].
R. S. Zhou and R. L. Snyder, “Structures and transformation mechanisms of the η, and γ transition aluminas,” Acta Cryst. 47, 617–630 (1991).
E. G. Yukihara and S. W. S. McKeever, Optically Stimulated Luminescence: Fundamentals and Applications (Jonn Wiley and Sons, Chichester, 2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © S.Yu. Sokovnin, V.G. Il’ves, A.I. Surdo, I.I. Mil’man, M.I. Vlasov, 2013, published in Rossiiskie Nanotekhnologii, 2013, Vol. 8, Nos. 7–8.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sokovnin, S.Y., Il’ves, V.G., Surdo, A.I. et al. Effect of iron doping on the properties of nanopowders and coatings on the basis of Al2O3 produced by pulsed electron beam evaporation. Nanotechnol Russia 8, 466–481 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078013040186
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078013040186