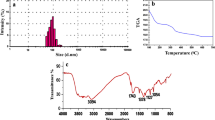
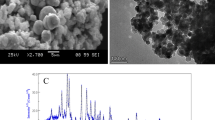
Abstract
This paper summarizes a comprehensive study concerning the acute toxicity of a commercial carbon nanomaterial consisting mostly of carbon nanotubes to larvae of Chironomidae, crustaceans Ceriodaphnia affinis, algae Scenedesmus quadricauda, and bacteria Escherichia coli. It is shown that the nucleolar organizer region (NOR) index of polytene chromosomes in the salivary gland cells of midge larvae depends on the duration of concentration and exposure. This fact is indicative of the switching on of cell adaptation pathways in response to a xenobiotic stressor to restore cell homeostasis. The investigated nanomaterial is labeled as a Class III environmentally hazardous material (moderately hazardous). Safe concentrations of the carbon nanomaterial in aquatic media are less than 2 mg/L. It is concluded that larvae of Chironomidae are the most resistant to the material of all test species, whereas Scenedesmus quadricauda and Escherichia coli are the most sensitive.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Lijima, “Helical Microtubules of Graphitic Carbon,” Nature 354, 56–58 (1991).
S. Kim, “From Carbon Fibers—to Nanotubes,” Chem. J., No. 10, 60–65 (2009).
N. H. Levi-Polyachenko, D. L. Carroll, and J. H. Stewart, “Applications of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials for Drug Delivery in Oncology,” in Medicinal Chemistry and Pharmacological Potential of Fullerenes and Carbon Nanotubes, Ed. by F. Cataldo and T. Da Ros (Springer, Berlin, 2008), pp. 223–266.
R. J. Aitken, K. S. Crely, and C. I. Tran, Nanoparticles: an Occupational Hygiene Review. HSE Research Report. http://www.hse.gov.uk/research/rrhtm/rr274.htm
P. Manchikanti and T. K. Bandopadhyay, “Nanomaterials and Effects on Biological Systems: Development of Effective Regulatory Norms,” Nanoethics 4, 77–83 (2010).
J. Hoeck, “What Is Typical for Nanotoxicology and Different from Bulk or the ‘Toxicology’,” Project NMP4-CT-2005-013968 (Eur. Commun., 2009), pp. 39–41.
A. Kahru and H.-Ch. Dubourguier, “From Ecotoxicology to Nanoecotoxicology,” Toxicology 269, 105–119 (2010).
L. E. Murr and K. M. Garza, “Natural and Anthropogenic Environmental Nanoparticulates: Their Microstructural Characterization and Respiratory Health Implications,” in Proceedings of the Workshop at Centro Stefano Franscini “Nanoparticles in the Environment: Implications and Applications”, Monte Verita, Switzerland, 2008, p. 33.
D. Y. Lyon, A. Thill, J. Rose, and P. J. Alavarez, “Ecotoxicological Impacts of Nanomaterials,” in Environmental Nanotechnology: Applications and Implications of Nanomaterials, Ed. by M. R. Weisner and J.-Y. Bottero (McGraw-Hill, New York, 2007), pp. 445–479.
C. Metcalfee, E. Bennettm, M. Chappell, J. Steevens, M. Depledge, G. Goss, S. Goudey, S. Kaczmar, N. O’Brien, and A. Picado, “Strategic Management and Assessment of Risks and Toxicity of Engineered Nanomaterials (SMARTEN),” in Nanomaterials: Risks and Benefits, Ed. by I. Linkov and J. Steevens (Springer, Dordrecht, 2009), pp. 95–102.
X. Zhu, L. Zhu, Y. Chen, and S. Tian, “Acute Toxicities of Six Manufactured Nanomaterial Suspensions to Daphnia Magna,” J. Nanopart. Res. 11, 67–75 (2009).
G. Schrantz and L. Kantiani, and D. Barcelo, “Ecotoxicity and Analysis of Nanomaterials in the Aquatic Environment,” Anal Bioanal Chem. 393, 81–95 (2009).
J. P. Cheng, E. Flahaut, and S. H. Cheng, “Effect of Carbon Nanotubes on Developing Zebrafish (Danio Rerio) Embryos,” Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 26, 708–716 (2007).
K. O. Kusk and L. Wollenberger, “Fully Defined Saltwater Medium for Cultivation of and Toxicity Testing with Marine Copepod Acartia Tonsa,” Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 18, 1564–1567 (1999).
A. A. Shvedova, V. Castranova, and E. R. Kisin, “Exposure to Carbon Nanotube Material: Assessment of Nanotube Cytotoxicity Using Human Keratinocyte Cells,” J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 66, 1909–1926 (2003).
A. M. Schrand, J. Johnson, L. Dai, S. M. Hussain, J. J. Schlager, L. Zhu, Y. Hong, and E. Osawa, “Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Carbon Nanomaterials,” in Safety of Nanoparticles, Nanostructure Science and Technology, Ed. by T. J. Webster (Springer, New York, 2009), pp. 159–187.
N. A. Monteiro-Riviere, R. J. Nemanich, and A. O. Inman, “Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube Interactions with Human Epidermal Keratinocytes,” Toxicol. Lett. 155, 377–384 (2005).
J. Kolosnjaj, H. Szwarc, and F. Moussa, “Toxicity Studies of Carbon Nanotubes,” in Bio-Applications of Nanoparticles, Ed. by C. W. Warren (Springer, New York, 2007), pp. 181–204.
A. M. Schranda, L. Daia, J. J. Schlager, S. M. Hussain, E. Osawa, “Differential Biocompatibility of Carbon Nanotubes and Nanodiamonds,” Diamond Relat. Mater. 16(12), 2118–2123 (2007).
A. K. Patlolla, S. M. Hussain, J. J. Schlager, S. Patlolla, and P. B. Tchounwou, “Comparative Study of the Clastogenicity of Functionalized and Non-Functionalized Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes in Bone Marrow Cells of Swiss-Webster Mice,” Environ. Toxicol. 25, 608–621 (2010).
A. Nel, T. Xia, L. Madler, and N. Li, “Toxic Potential of Materials at the Nano Level,” Science (Washington, DC, U.S.) 311, 622–627 (2006).
H. K. Lindberg, G. C. Falck, S. Suhonen, M. Vippola, E. Vanhala, J. Catalan, K. Savolainen, and H. Norppa, “Genotoxicity of Nanomaterials: DNA Damage and Micronuclei Induced by Carbon Nanotubes and Graphite Nanofibres in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells in Vitro,” Toxicol. Lett. 186, 166–173 (2009).
C. Yang, D. Liu, H. Yang, Z. Zhang, and Z. Xi, “Comparative Study of Cytotoxicity, Oxidative Stress and Genotoxicity Induced by Four Typical Nanomaterials: the Role of Particle Size, Shape and Composition,” J. Appl. Toxicol. 29, 69–78 (2009).
D. Pantarotto, J. P. Briand, M. Prato, and A. Bianco, “Translocation of Bioactive Peptides across Cell Membranes by Carbon Nanotubes,” Chem. Commun. (Cambridge, U. K.) 40, 16–17 (2004).
I. F. Zhimulev, Chromomeric Organization of Polytene Chromosomes (Nauka, Novosibirsk, 1994) [in Russian].
N. A. Petrova and O. K. Klishko, “On the Problem of Individual Variability of Karyotype Chironomus Plumosus: Offtype Puffs at Larva from Natural Population of Chita Oblast’,” Tsitologiya 43, 172–177 (2001).
V. A. Timoshevskii and S. A. Nazarenko, “Interphase Cytogenetics in Estimation of Genomic Mutations in Somatic Cells,” Russ. J. Gen. 41, 1–12 (2005).
W. Beermann, “Differentiation at the Level of the Chromosomes,” in Cell Differentiation and Morphogenesis (North Holland, Amsterdam 1966), pp. 24–54.
T. A. Kolesnikova, I. A. Fedorova, A. A. Gusev, and D. A. Gorin, “Acute Toxicity Analysis of Polyelectrolyte Microcapsules with Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Microcapsule Shell Components Using Aquatic Organisms,” Nanotechnol. Russ. 6, 244–255 (2011).
A. G. Tkachev and I. V. Zolotukhin, Equipment and Methods of Synthesis of Solid State Nanostructures: Monograph (Mashinostroenie-1, Moscow, 2007) [in Russian].
Procedure of Determination of Toxicity of Water and Water Extracts from Soils, Precipitates of Wastewaters, Wastes by the Mortality and Change in Fecundity of Ceriodaphnia, FR.1.39.2007.03221 (AKVAROS, Moscow, 2007).
Procedure of Determination of Toxicity of Water, Water Extracts from Soils, Precipitates of Wastewaters and Wastes by the Change in the Level of Fluorescence of Chlorophill and Number of Algae Cells, FR.1.39.2007.03223 (AKVAROS, Moscow, 2007).
Procedure of Determination of Toxicity of Water, Water Extracts from Soils, Precipitates of Wastewaters and Wastes by the Change in the Intensity of Bacterial Bioluminescence according to “Ekolyum” Test System, PND F T 14.1:2:3:4.11-04 16.1:2.3:3.8-04 (Moscow, 2004).
Estimation of Safety of Nanomaterials in Vitro and in Model Systems in Vivo: Methodical Recommendations (Fed. Tsentr Gig. Epidemiol. Rospotrebnadzora, Moscow, 2009).
On Confirmation of Criteria of Relation of Dangerous Wastes to the Class of Danger for Environment, Directive No. 511 (MPR Ross., 2001)
N. B. Il’inskaya and M. S. Iordan, “Procedure of Determination of Stage of Physiological Maturity of Larvae of Chironomids of IV Age on Structure and Size of Blastodisks,” in Proceedings of the 9th Meeting of Workgroup on Project No. 18 “Species and Its Productivity in Areal”, Vilnius, Lithuania, 1975, pp. 17–22.
Methodical Directions. Verification of Observations on Estimation of Level of Toxic Contamination of Bottom Sediments on the Basis of Biotesting. Methods of Toxicological Estimation of Contamination of Fresh-Water Ecosystems, RD 52.24.635-2002 (Rosgidromet, Moscow, 2003).
A. V. Korosov and N. M. Kalinkina, Quantitative Methods of Ecological Toxicology (Petrozavodsk. Gos. Univ., Karel. Nauchn. Tsentr, Petrozavodsk, 2003) [in Russian].
S. Yu. Demin, Extended Abstract of Candidate’s Dissertation in Biology (Leningrad, 1989) [in Russian].
J. C. Stockert, “The Normalized Balbiani Size as a Quatitave Parametår for Transcription Activity in Polytene Chromosomes,” Biol. Zentralbl. 109, 139–146 (1990).
I. A. Fedorova, “Methodical Approaches to Analysis of Toxicological and Cytogenetical Effects of Cholinotropic Preparations on Chironomus Larvae (Diptera) in Vivo in Acute Experiment,” Biomed. Radioelektron., No. 12, 58–65 (2009).
O. V. Zatsepina, “Modern Considerations on Properties and Functions of Nucleolus: Nucleolus as Target of Stress Actions on Cells,” Tsitologiya 49, 748–749 (2007).
FKKO—Federal Classification Catalogue of Wastes. http://www.fkko.ru
S. Kang, M. Herzberg, D. F. Rodrigues, and M. Elimelech, “Antibacterial Effects of Carbon Nanotubes: Size Does Matter!,” Langmuir 24, 6409–6413 (2008).
S. Kang, S. M. Mauter, and M. Elimelech, “Microbial Cytotoxicity of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials: Implications for River Water and Wastewater Effluent,” Environ. Sci. Technol. 43, 2648–2653 (2009).
C. D. Vecitis, K. R. Zodrow, S. Kang, and M. Elimelech, “Electronic-Structure-Dependent Bacterial Cytotoxicity of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes,” ACS Nano 4, 5471–5479 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.A. Gusev, I.A. Fedorova, A.G. Tkachev, A.Yu. Godymchuk, D.V. Kuznetsov, I.A. Polyakova, 2012, published in Rossiiskie Nanotekhnologii, 2012, Vol. 7, Nos. 9–10.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gusev, A.A., Fedorova, I.A., Tkachev, A.G. et al. Acute toxic and cytogenetic effects of carbon nanotubes on aquatic organisms and bacteria. Nanotechnol Russia 7, 509–516 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078012050060
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1995078012050060