Abstract
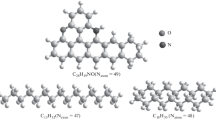
The molecular mechanics method MM+ was used to examine the structure and properties of the inverse water-in-oil emulsion. The energies EMMB of intermolecular interactions between molecules were calculated for 3M + nH2O systems constituted by molecules of asphaltenes, paraffins, and naphthenes, such as M = C28H19NO, C15H32, and C18H30, which model the structure of oil macrocomponents, and water molecules at n = 0–70. It was shown that the energy EMMB of interaction of H2O molecules with asphaltene molecules exceeds that with paraffin and naphthene molecules. The values of EMMB were calculated for systems of paraffin and naphthene molecules with H2O molecules. A mechanism was suggested by which an inverse emulsion is formed. The mechanism is based on the stage that yields cores composed of water molecules, around which asphaltene molecules are coordinated, with molecules of naphthenes and paraffins forming an external layer. A conclusion is made that the molecular mechanics method MM+ can be used to model the structure of a water-in-oil inverse emulsion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khadzhiev, S.N., Neftekhimiya, 2011, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 3–16
Khadzhiev, S.N., Petrol. Chem., 2011, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 1–15.
Khadzhiev, S.N., Kadiev, Kh.M., and Kadieva, M.Kh., Petrol. Chem., 2014, vol. 54, no. 5, pp. 323–346.
Bellussi, G., Rispoli, G., Landoni, A., Millini, R., Molinari, D., Montanari, E., Moscotti, D., and Pollesel, P., J. Catal., 2013, no. 308, pp. 189–200.
Kim, S.-H., Kim, K.-D., and Lee, Y.-K., J. Catal., 2017, no. 347, pp. 127–137.
Syunyaev, Z.I., Safieva, R.Z., and Syunyaev, R.Z., Neftyanye dispersnye sistemy (Dispersed Petroleum Systems), Moscow: Khimiya, 1990.
Safieva, R.Z., Fizikokhimiya nefti. Fiziko-khimicheskie osnovy pererabotki nefti (Physical Chemistry of Oil. Physicochemical Foundations of Oil Processing), Moscow: Khimiya, 1998.
Svarovskaya, N.A., Vinokurov, V.A., and Kolesnikov, I.M., Predstavlenie o strukture neftyanykh sistem. Uchebnoe posobie (Insight into Structure of Oil Systems, Text Book), Moscow: Izd. Neft’ i gaz, Ross. Gos. Univ. Nefti i Gaza im. I.M. Gubkina, 2006.
Kadiev, Kh.M., Gyul’maliev, A.M., Kadieva, M.Kh., and Khadzhiev, S.N., Petrol. Chem., 2018, vol. 58, no. 10, pp. 849–854.
Kronberg, B., Costas, M., and Silveston, R., J. Dispersion Sci. Technol., 1994, vol. 15, pp. 333–351.
Maibaum, L., Dinner, A.R., and Chandler, D., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, vol. 108, pp. 6778–6781.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © Kh.M. Kadiev, A.M. Gyul’maliev, M.Kh. Kadieva, S.N. Khadzhiev, 2018, published in Zhurnal Prikladnoi Khimii, 2018, Vol. 91, No. 11, pp. 1573−1578.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kadiev, K.M., Gyul’maliev, A.M., Kadieva, M.K. et al. Modeling the Structure of Water-in-Oil Inverse Emulsion. Russ J Appl Chem 91, 1779–1784 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070427218110071
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1070427218110071