Abstract
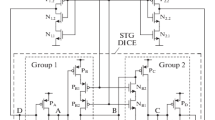
The TCAD simulation of charge collection from tracks of single nuclear particles directed along the normal to the logic matching element on STG DICE cells demonstrates their unique upset tolerance. The tracks used for simulation are directed normal to the microchip surface with the linear energy transfer (LET) ranging from 10 to 60 MeV cm2/mg. We investigate a 65-nm bulk CMOS logic matching element for use in content addressable memory and translation lookaside buffers. It is a matching element on an STG DICE cell with an exclusive OR logic element on two tristate inverters. The linear energy transfers in the range of 30–60 MeV cm2/mg on the tracks normal to the chip surface do not cause single event upsets in the STG DICE cell for LET = 60 MeV cm2/mg. In the output combinational logic of the matching element, short (up to 0.6 ns) noise voltage pulses for a LET ranging from 20 to 60 MeV cm2/mg can be found.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katunin, Yu.V., Stenin, V.Ya., and Stepanov, P.V., Modeling the characteristics of trigger elements of twophase CMOS logic, taking into account the charge sharing effect under exposure to single nuclear particles, Russ. Microelectron., 2014, vol. 43, no. 2, pp. 112–124.
Stenin, V.Ya., Simulation of the characteristics of the DICE 28-nm CMOS cells in unsteady states caused by the effect of single nuclear particles, Russ. Microelectron., 2015, vol. 44, no. 5, pp. 324–334.
Calin, T., Nicolaidis, M., and Velazco, R., Upset hardened memory design for submicron CMOS technology, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 1996, vol. 43, no. 6, pp. 2874–2878.
Stenin, V.Ya. and Stepanov, P.V., Basic memory elements using DICE cells for fault-tolerant 28 nm CMOS RAM, Russ. Microelectron., 2015, vol. 44, no. 6, pp. 368–379.
Stenin, V.Ya., Katunin, Yu.V., and Stepanov, P.V., Upset-resilient RAM on STG DICE memory elements with the spaced transistors into two groups, Russ. Microelectron., 2016, vol. 45, no. 6, pp. 419–432.
Katunin, Yu.V. and Stenin, V.Ya., Simulation of Single Event Effects in STG DICE Memory Cells, Russ. Microelectron., 2018, vol. 47, no. 1, pp. 20–33.
Narasimham, B., Bhuva, B.L., Schrimpf, R.D., Massengill, L.W., Gadlage, M.J., Holman, W.T., Witulski, A.F., Robinson, W.H., Black, J.D., Benedetto, J.M., and Eaton, P.H., Effects of guard bands and well contacts in mitigating long SETs in advanced CMOS processes, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2008, vol. 55, no. 3, pp. 1708–1713.
Warren, K.M., Stenberg, A.L., Black, J.D., Weller, R.A., Reed, R.A., Mendenhall, M.H., Schrimpf, R.D., and Massengill, L.W., Heavy ion testing and single-event upset rate prediction considerations for a DICE flip-flop, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2009, vol. 56, no. 6, pp. 3130–3137.
Loveless, T.D., Jagannathan, S., Reece, T., Chetia, J., Bhuva, B.L., McCurdy, M.W., Massengill, L.W., Wen, S.-J., Wong, R., and Rennie, D., Neutron-and proton-induced single event upsets for D-and DICEflip/ flop designs at a 40 nm technology node, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2011, vol. 58, no. 3, pp. 1008–1014.
Lilja, K., Bounasser, M., Wen, S., Wong, R., Holst, J., Gaspard, N., Jagannathan, S., Loveless, D., and Bhuva, B., Single event performance and layout optimization of flip-flops in a 28-nm bulk technology, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2013, vol. 60, no. 4, pp. 2782–2788.
Pagiamtzis, K., Azizi, N., and Najm, F.N., A soft-error tolerant content-addressable memory (CAM) using an error-correcting-match scheme, in Proceedings of the IEEE Custom International Circuits Conference, San Hose, CA, Sept. 10–13, 2006, pp. 301–304.
Abbas, S.M., Lee, S., Baeg, S., and Park, S., An efficient multiple cell upsets tolerant content-addressable memory, IEEE Trans. Comput., 2014, vol. 63, no. 8, pp. 2094–2098.
Azizi, N. and Najm, F., A family of cells to reduce the soft-error-rate in ternary-CAM, in Proceedings of the 43rd Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, CA, July 24–28, 2006, pp. 779–784.
Eftaxiopoulos, N., Axelos, N., and Pekmestzi, K., Low leakage radiation tolerant CAM/TCAM cell, in Proceedings of IEEE International On-Line Testing Symposium (IOLTS), Halkidiki, Greece, July 6–8, 2015, pp. 206–211.
Stenin, V.Ya. and Antonyuk, A.A., Design of the 65-nm CMOS comparison element for a content-addressable memory and simulation of single-event transients, in Proceedings of the 24th Telecommunications Forum, Belgrade, 2016, pp. 413–416.
Stenin, V.Ya. and Antonyuk, A.A., Design of the CMOS comparison elements on STG DICE for a content-addressable memory and simulation of singleevent transients, Telfor J., 2017, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 61–66.
Stenin, V.Ya., Antonyuk, A.A., Katunin, Yu.V., and Stepanov, P.V., Design of logical elements for the 65-nm CMOS translation lookaside buffer with compensation of single events effects, in Proceedings of the International Siberian Conference on Control and Communications, 2017, pp. 1–6.
Wang, T., Xiao, L., and Huang, Q., Simulation study of single event effect for different N-well and deep-N-well doping in 65 nm triple-well CMOS devices, in Proceedings of International Conference on Optoelectronics and Microelectronics, 2012, pp. 505–509.
Giot, D., Roche, P., Gasiot, G., Autran, J.-L., and Harboe-Sørensen, R., Heavy ion testing and 3D simulations of multiple cell upset in 65 nm standard SRAMs, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2008, vol. 55, no. 4, pp. 2048–2054.
Uznanski, S., Gasiot, G., Roche, P., Tavernier, C., and Autran, J.-L., Single event upset and multiple cell upset modeling in commercial bulk 65-nm CMOS SRAMs and flip-flops, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2010, vol. 57, no. 4, pp. 1876–1883.
Boruzdina, A.B., Sogoyan, A.V., Smolin, A.A., Ulanova, A.V., Gorbunov, M.S., Chumakov, A.I., and Boychenko, D.V., Temperature dependence of MCU sensitivity in 65 nm CMOS SRAM, IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci., 2015, vol. 62, no. 6, pp. 2860–2866.
Garg, R. and Khatri, S.P., Analysis and Design of Resilient VLSI Circuits: Mitigating Soft Errors and Process Variations, New York: Springer, 2010, pp. 194–205.
Soft Errors in Modern Electronic Systems, Nicolaidis, M., Ed., New York: Springer, 2011, pp. 35–37.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © Yu.V. Katunin, V.Ya. Stenin, 2018, published in Mikroelektronika, 2018, Vol. 47, No. 2.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katunin, Y.V., Stenin, V.Y. The Element of Matching on an STG DICE Cell for an Upset Tolerant Content Addressable Memory. Russ Microelectron 47, 142–156 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063739718020051
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063739718020051