Abstract
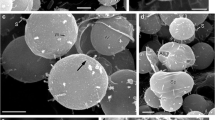
A previous molecular-genetic analysis of clonal cultures and single cells of Ostreopsis spp. that were isolated from Peter the Great Bay (the Sea of Japan) revealed three different genotypes according to the nucleotide sequences of ribosomal DNA (rDNA). Of these, Ostreopsis sp. 1 was earlier found only off the coast of Japan and described as being the most common and highly toxic. We have obtained further molecular evidence and have studied the morphological features of cells from one of the Ostreopsis strains with this genotype and some aspects of its growth at salinities of 24, 28, and 32‰. The results showed that in cells from the Russian coast of the Sea of Japan, the third apical (3') and the third precingular (3") plates do not adjoin one another, being separated by the elongated second apical (2') plate. Cells of Ostreopsis sp. 1 from the Russian coast are significantly larger than Ostreopsis sp. 1 cells with the same genotype from the coast of Japan. Salinity did not have a substantial effect on the growth of Ostreopsis sp. 1. The growth rate varied from 0.24 to 0.35 divisions per day, with maximum values at a salinity of 24‰. When salinity decreased to 24‰, the exponential growth phase was significantly extended and the maximum cell concentration doubled.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Konovalova, G.V., Dinoflagellaty (Dinophyta) dal’nevostochnykh morei Rossii i sopredel’nykh akvatorii Tikhogo okeana (Dinoflagellates (Dinophyta) of the Far Eastern Seas of Russia and Adjacent Waters of the Pacific Ocean), Vladivostok: Dalnauka, 1998.
Selina, M.S. and Levchenko, E.V., Species composition and morphology of dinoflagellates (Dinophyta) of epiphytic assemblages of Peter the Great Bay in the Sea of Japan, Russ. J. Mar. Biol., 2011, vol. 37, no. 1, pp. 23–32.
Accoroni, S., Romagnoli, T., Penna, A., et al., Ostreopsis fattorussoi sp. nov. (Dinophyceae), a new benthic toxic Ostreopsis species from the eastern Mediterranean Sea, J. Phycol., 2016, vol. 52, no. 6, pp. 1064–1084.
Accoroni, S., Romagnoli, T., Pichierri, S., et al., Morphometric analysis of Ostreopsis cf. ovata cells in relation to environmental conditions and bloom phases, Harmful Algae, 2012, vol. 19, pp. 15–22.
Adachi, M., Sako, Y., and Ishida, Y., Restriction fragment length polymorphism of ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer and 5.8S regions in Japanese Alexandrium species (Dinophyceae), J. Phycol., 1994, vol. 30, no. 5, pp. 857–863.
Aligizaki, K. and Nikolaidis, G., The presence of the potentially toxic genera Ostreopsis and Coolia (Dinophyceae) in the North Aegean Sea, Greece, Harmful Algae, 2006, vol. 5, pp. 717–730.
Bravo, I., Vila, M., Casabianca, S., et al., Life cycle stages of the benthic palytoxin-producing dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata (Dinophyceae), Harmful Algae, 2012, vol. 18, pp. 24–34.
Carnicer, O., García-Altares, M., Andree, K.B., et al., Ostreopsis cf. ovata from western Mediterranean Sea: physiological responses under different temperature and salinity conditions, Harmful Algae, 2016, vol. 57, pp. 98–108.
Chinain, M., Faust, M.A., and Paullac, S., Morphology and molecular analyses of three toxic species of Gambierdiscus (Dinophyceae): G. pacificus, sp. nov., G. australes, sp. nov., and G. polynesiensis, sp. nov., J. Phycol., 1999, vol. 35, no. 6, pp. 1282–1296.
Ciminiello, P., Dell’Aversano, C., Fattorusso, E., et al., Putative palytoxin and its new analogue, ovatoxin-a, in Ostreopsis ovata collected along the Ligurian coasts during the 2006 toxic outbreak, J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom., 2008, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 111–120.
Darriba, D., Taboada, G.L., Doallo, R., et al., jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing, Nat. Methods, 2012, vol. 9, no. 8, pp. 772–772.
David, H., Laza-Martínez, A., Miguel, I., and Orive, E., Ostreopsis cf. siamensis and Ostreopsis cf. ovata from the Atlantic Iberian Peninsula: morphological and phylogenetic characterization, Harmful Algae, 2013, vol. 30, pp. 44–55.
Efimova, K.V., Orlova, T.Yu., and Brykov, Vl.A., Phylogenetic characterization of cryptic species of the marine dinoflagellate, Ostreopsis sp. Shmidt, 1902, from Russian coastal waters, the Sea of Japan, J. Biodiversity Environ. Sci., 2014, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 317–332.
Faimali, M., Giussani, V., Piazza V., et al., Toxic effects of harmful benthic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis ovata on invertebrate and vertebrate marine organisms, Mar. Environ. Res., 2012, vol. 76, pp. 97–107.
Gallitelli, M., Ungaro, N., Addante, L.M., et al., Respiratory illness as a reaction to tropical algal blooms occurring in a temperate climate, JAMA, 2005, vol. 293, pp. 2595–2600.
Giussani, V., Costa, E., Pecorino, D., et al., Effects of the harmful dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata on different life cycle stages of the common moon jellyfish Aurelia sp., Harmful Algae, 2016, vol. 57, pp. 49–58.
Granáli, E., Vidyarathna, N.K., Funari, E., et al., Can increases in temperature stimulate blooms of the toxic benthic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis ovata?, Harmful Algae, 2011, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 165–172.
Guindon, S., Dufayard, J.F., Lefort, V., et al., New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0, Syst. Biol., 2010, vol. 59, no. 3, pp. 307–321.
Hoppenrath, M., Murray, S.A., Chomérat, N., and Horiguchi, T., Marine Benthic Dinoflagellates–Unveiling Their Worldwide Biodiversity, Kleine Senckenberg-Reihe, Stuttgart, Germany: Schweizerbart, 2014, vol.54.
Kameneva, P.A., Efimova, K.V., Rybin, V.G., and Orlova, T.Yu., Detection of dinophysistoxin-1 in clonal culture of marine dinoflagellate Prorocentrum foraminosum (Faust M.A., 1993) from the Sea of Japan, Toxins, 2015, vol. 7, no. 10, pp. 3947–3959.
Mangialajo, L., Ganzin, N., Accoroni, S., et al., Trends in Ostreopsis proliferation along the Northern Mediterranean coasts, Toxicon, 2011, vol. 57, no. 3, pp. 408–420.
Monti, M., Minocci, M., Beran A., and Iveša, L., First record of Ostreopsis cf. ovata on macroalgae in the Northern Adriatic Sea, Mar. Pollut. Bull., 2007, vol. 54, no. 5, pp. 598–601.
Morton, S.L., Norris, D.R., and Bomber, J.W., Effect of temperature, salinity and light intensity on the growth and seasonality of toxic dinoflagellates associated with ciguatera, J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 1992, vol. 157, no. 1, pp. 79–90.
Nascimento, S.M., Corrêa, E.V., Menezes, M., et al., Growth and toxin profile of Ostreopsis cf. ovata (Dinophyta) from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, Harmful Algae, 2012, vol. 13, pp. 1–9.
Norris, D.R., Bomber, J.W., and Balech, E., Benthic dinoflagellates associated with ciguatera from the Florida Keys. I. Ostreopsis heptagona sp. nov., Toxic Dinoflagellates, New York: Elsevier, 1985, pp. 39–44.
Parsons, M.L., Aligizaki, K., Bottein, M.-Y.D., et al., Gambierdiscus and Ostreopsis: Reassessment of the state of knowledge of their taxonomy, geography, ecophysiology, and toxicology, Harmful Algae, 2012, vol. 14, pp. 107–129.
Penna, A., Bertozzini, E., Battocchi, C., et al., Monitoring of HAB species in the Mediterranean Sea through molecular methods, J. Plankton Res., 2007, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 19–38.
Penna, A., Fraga, S., Battocchi, C., et al., A phylogeographical study of the toxic benthic dinoflagellate genus Ostreopsis Schmidt, J. Biogeogr., 2010, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 830–841.
Penna, A., Vila, M., Fraga, S., et al., Characterization of Ostreopsis and Coolia (Dinophyceae) isolates in the western Mediterranean Sea based on morphology, toxicity and internal transcribed spacer 5.8S rDNA sequences, J. Phycol., 2005, vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 212–225.
Pezzolesi, L., Guerrini, F., Ciminiello, P., et al., Influence of temperature and salinity on Ostreopsis cf. ovata growth and evaluation of toxin content through HR LC-MS and biological assays, Water Resour., 2012, vol. 46, no. 1, pp. 82–92.
Pistocchi, R., Pezzolesi, L., Guerrini, F., et al., A review on the effects of environmental conditions on growth and toxin production of Ostreopsis ovata, Toxicon, 2011, vol. 57, no. 3, pp. 421–428.
Rhodes, L., World-wide occurrence of the toxic dinoflagellate genus Ostreopsis Schmidt, Toxicon, 2011, vol. 57, no. 3, pp. 400–407.
Sato, S., Nishimura, T., Uehara, K., et al., Phylogeography of Ostreopsis along west Pacific coast, with special reference to a novel clade from Japan, PLoS One, 2011, vol. 6, no. 12, p. e27983.
Selina, M.S., Morozova,T.V., Vyshkvartsev, D.I., and Orlova, T.Yu., Seasonal dynamics and spatial distribution of epiphytic dinoflagellates in Peter the Great Bay (Sea of Japan) with special emphasis on Ostreopsis species, Harmful Algae, 2014, vol. 32, pp. 1–10.
Selina, M.S. and Orlova, T.Yu., First occurrence of the genus Ostreopsis (Dinophyceae) in the Sea of Japan, Bot. Mar., 2010, vol. 53, pp. 243–249.
Suzuki, T., Watanabe, R., Uchida, H., et al., LC-MS/MS analysis of novel ovatoxin isomers in several Ostreopsis strains collected in Japan, Harmful Algae, 2012, vol. 20, pp. 81–91.
Tanimoto, Y., Yamaguchi, H., Yoshimatsu, T., et al., Effects of temperature, salinity and their interaction on growth of toxic Ostreopsis sp. 1 and Ostreopsis sp. 6 (Dinophyceae) isolated from Japanese coastal waters, Fish. Sci. (Tokyo, Jpn.), 2013, vol. 79, no. 2, pp. 285–291.
Tawong, W., Nishimura, T., Sakanari, H., et al., Distribution and molecular phylogeny of the dinoflagellate genus Ostreopsis in Thailand, Harmful Algae, 2014, vol. 37, pp. 160–171.
Tindall, D.R. and Morton, S.L., Community dynamics and physiology of epiphytic/benthic dinoflagellates associated with ciguatera, in Physiological Ecology of Harmful Algal Blooms, NATO ASI Series, Ser. G: Ecological Science, vol. 41, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1998, pp. 293–313.
Totti, C., Accoroni, S., Cerino F., et al., Ostreopsis ovata bloom along the Conero Riviera (northern Adriatic Sea): relationships with environmental conditions and substrata, Harmful Algae, 2010, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 233–239.
Tubaro, A., Durando, P., Del Favero, G., et al., Case definitions for human poisonings postulated to palytoxins exposure, Toxicon, 2011, vol. 57, no. 3, pp. 478–495.
Verma, A., Hoppenrath, M., Dorantes-Aranda, J.J., et al., Molecular and phylogenetic characterization of Ostreopsis (Dinophyceae) and the description of a new species, Ostreopsis rhodesae sp. nov., from a subtropical Australian lagoon, Harmful Algae, 2016, vol. 60, pp. 116–130.
Yamaguchi, H., Yoshimatsu, T., Tanimoto, Y., et al., Effects of temperature, salinity and their interaction on growth of the benthic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata (Dinophyceae) from Japanese coastal waters, Phycol. Res., 2012, vol. 60, no. 4, pp. 297–304.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © M.S. Selina, T.V. Morozova, N.A. Aizdaicher, K.V. Efimova, 2018, published in Biologiya Morya.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selina, M.S., Morozova, T.V., Aizdaicher, N.A. et al. The Morphological, Genetic and Physiological Characteristics of a Benthic Dinoflagellate of the Genus Ostreopsis Isolated from Coastal Waters of the Northwestern Sea of Japan. Russ J Mar Biol 44, 14–24 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063074018010091
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063074018010091