Abstract
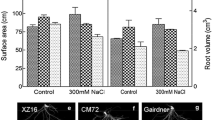
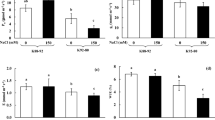
Two barley cultivars (Hordeum vulgare L., cvs. Elo and Belogorskii) differing in salt tolerance were used to study 22Na+ uptake, expression of three isoforms of the Na+/H+ antiporter HvNHX1-3, and the cellular localization of these isoforms in the elongation zone of seedling roots. During short (1 h) incubation, seedling roots of both cultivars accumulated approximately equal quantities of 22Na+. However, after 24-h incubation the content of 22Na+ in roots of a salt-tolerant variety Elo was 40% lower than in roots of the susceptible variety Belogorskii. The content of 22Na+ accumulated in shoots of cv. Elo after 24-h incubation was 6.5 times lower than in shoots of cv. Belogorskii and it was 4 times lower after the salt stress treatment. The cytochemical examination revealed that three proteins HvNHX1-3 are co-localized in the same cells of almost all root tissues; these proteins were present in the tonoplast and prevacuolar vesicles. Western blot analysis of HvNHX1-3 has shown that the content of isoforms in vacuolar membranes increased in response to salt stress in seedling roots and shoots of both cultivars, although the increase was more pronounced in the tolerant cultivar. The content of HvNHX1 in the seedlings increased in parallel with the enhanced expression of HvNHX1, whereas the increase in HvNHX2 and HvNHX3 protein content was accompanied by only slight changes in expression of respective genes. The results provide evidence that salt tolerance of barley depends on plant ability to restrict Na+ transport from the root to the shoot and relies on regulatory pathways of HvNHX1-3 expression in roots and shoots during salt stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CBD:
-
cellulose-binding domain
- Ka :
-
coefficient of 22Na+ accumulation
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- PMSF:
-
phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
References
Tester, M. and Davenport, R., Na+ Tolerance and Na+ Transport in Higher Plants, Ann. Bot., 2003, vol. 91, pp. 503–527.
Apse, M. and Blumwald, E., Minireview. Na+ Transport in Plants, FEBS Lett., 2007, vol. 581, pp. 2247–2254.
Rodríguez-Navarro, A. and Rubio, F., High-Affinity Potassium and Sodium Transport Systems in Plants, J. Exp. Bot., 2006, vol. 57, pp. 1149–1160.
Pardo, J., Cubero, B., Leidi, E., and Quintero, F., Alkali Cation Exchangers: Roles in Cellular Homeostasis and Stress Tolerance, J. Exp. Bot., 2006, vol. 57, pp. 1181–1199.
Qiu, Q., Guo, Y., Dietrich, M., Schumaker, K., and Zhu, J.-K., Regulation of SOS1, a Plasma Membrane Na+/H+ Exchanger in Arabidopsis thaliana, by SOS2 and SOS3, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2002, vol. 99, pp. 8436–8441.
Zhu, J.K., Genetic Analysis of Plant Salt Tolerance Using Arabidopsis, Plant Physiol., 2000, vol. 124, pp. 941–948.
Apse, M., Sottosanto, J., and Blumwald, E., Vacuolar Cation/H+ Exchange, Ion Homeostasis, and Leaf Development Are Altered in a T-DNA Insertional Mutant of AtNHX1, the Arabidopsis Vacuolar Na+/H+ Antiporter, Plant J., 2003, vol. 36, pp. 229–239.
Shi, H., Lee, B., Wu, S., and Zhu, J.K., Overexpression of a Plasma Membrane Na+/H+ Antiporter Gene Improves Salt Tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana, Nat. Biotech., 2003, vol. 21, pp. 81–85.
Rodriguez-Rosales, M.P., Gálvez, F.J., Huertas, R., Aranda, M.N., Baghour, M., Cagnac, O., and Venema, K., Plant NHX Cation/Proton Antiporters, Plant Sign. Behav., 2009, vol. 4, pp. 265–276.
Yokoi, S., Quintero, F., Cubero, B., Ruiz, M., Bressan, R., Hasegawa, P., and Pardo, J., Differential Expression and Function of Arabidopsis thaliana NHX Na+/H+ Antiporters in the Salt Stress Response, Plant J., 2002, vol. 30, pp. 529–539.
Zorb, C., Noll, A., Karl, S., Leib, K., Yan, F., and Schubert, S., Molecular Characterization of Na+/H+ Antiporters (ZmNHX) of Maize (Zea mays L.) and Their Expression under Salt Stress, J. Plant Physiol., 2005, vol. 162, pp. 55–66.
Venema, K., Belver, A., Marin-Manzano, C., Rodriguez-Rosales, P., and Donaire, J., A Novel Intracellular K+/H+ Antiporter Related to Na+/H+Antiporters Is Important for K+ Ion Homeostasis in Plants, J. Biol. Chem., 2003, vol. 278, pp. 22453–22459.
Ohnishi, M., Fukada-Tanaka, S., Hoshino, A., Takada, J., Inagaki, Y., and Iida, S., Characterization of a Novel Na+/H+ Antiporter Gene InNHX2 and Comparison of InNHX2 with InNHX1, Which Is Responsible for Blue Flower Coloration by Increasing the Vacuolar pH in the Japanese Morning Glory, Plant Cell Physiol., 2005, vol. 46, pp. 259–267.
Nakamura, N., Tanaka, S., Teko, Y., Mitsui, K., and Kanazawa, H., Four Na+/H+ Exchanger Isoforms Are Distributed to Golgi and Post-Golgi Compartments and Are Involved in Organelle pH Regulation, J. Biol. Chem., 2005, vol. 280, pp. 1561–1572.
Fukuda, A., Chiba, K., Maeda, M., Nakamura, A., Maeshima, M., and Tanaka, Y., Effect of Salt and Osmotic Stresses on the Expression of Genes for the Vacuolar H+-Pyrophosphatase, H+-ATPase Subunit A, and Na+/H+ Antiporter from Barley, Plant Sci., 2004, vol. 169, pp. 959–965.
Vasekina, A.V., Ershov, P.V., Reshetova, O.S., Tikhonova, T.V., Lunin, V.G., Trofimova, M.S., and Babakov, A.V., Vacuolar Na+/H+ Antiporter from Barley: Its Identification and Reaction to Salt Stress, Biokhimiya, 2005, vol. 70, pp. 123–132.
Ershov, P.V., Vasekina, A.V., Voblikova, V.D., Taranov, V.V., Roslyakova, T.V., and Babakov, A.V., Identification of K+/H+ Antiporter Homolog in Barley: Expression in Cultivars with Different Tolerance to NaCl, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2007, vol. 54, pp. 16–24.
Roslyakova, T.V., Lazareva, E.M., Kononenko, N.V., and Babakov, A.V., New HvNHX3 Isoform of Vacuolar Na+/H+ Antiporter from Barley: Expression and Immunological Location, Biokhimiya, 2009, vol. 74, pp. 549–556.
Wu, C.A., Yang, G.D., Meng, Q.W., and Zheng, C.C., The Cotton GhNHX1 Gene Encoding a Novel Putative Tonoplast Na+/H+-Antiporter Plays an Important Role in Salt Stress, Plant Cell Physiol., 2004, vol. 45, pp. 600–607.
Saqib, M., Zorb, C., Rengel, Z., and Schubert, S., The Expression of the Endogenous Vacuolar Na+/H+ Antiporters in Roots and Shoots Correlates Positively with the Salt Resistance of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), Plant Sci., 2005, vol. 169, pp. 959–965.
Leonova, T.G., Goncharova, E.A., Khodorenko, A.V., and Babakov, A.V., Characteristics of Salt-Tolerant and Salt-Susceptible Cultivars of Barley, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2005, vol. 52, pp. 774–778.
Ershov, P.V., Reshetova, O.S., Trofimova, M.S., and Babakov, A.V., Activity of Ion Transporters and Salt Tolerance in Barley, Russ. J. Plant Physiol., 2005, vol. 52, pp. 765–773.
Lunin, V.G., Sharapova, N.E., Tikhonova, T.V., Poletaeva, N.N., Galushkina, Z.M., Aksenova, E.I., Grabko, V.I., Velikodvorskaya, G.A., Lavrova, N.V., and Anan’ina, Yu.V., In Vivo Investigation of Immunogenic Patterns of Recombinant Cellulose-Binding Domain in Anaerocellum thermophilum, Mol. Genet. Mikrobiol. Virusol., 2009, vol. 24, pp. 21–26.
Chen, Z., Pottosin, I., Cuin, T., Fuglsang, A., Tester, M., Jha, D., Zepeda-Jazo, I., Zhou, M., Palmgren, M., Newman, I., and Shabala, S., Root Plasma Membrane Transporters Controlling K+/Na+ Homeostasis in Salt-Stressed Barley, Plant Physiol., 2007, vol. 145, pp. 1714–1725.
Davenport, R., James, R.A., Zakrisson-Plogander, A., Tester, M., and Munns, R., Control of Sodium Transport in Durum Wheat, Plant Physiol., 2005, vol. 137, pp. 807–818.
Hamada, A., Shono, M., Xia, T., Ohta, M., Hayashi, Y., Tanaka, A., and Hayakawa, T., Isolation and Characterization of a Na+/H+ Antiporter Gene from the Halophyte Atriplex gmelini, Plant Mol. Biol., 2001, vol. 46, pp. 35–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © T.V. Roslyakova, O.V. Molchan, A.V. Vasekina, E.M. Lazareva, A.I. Sokolik, V.M. Yurin, A.H. de Boer, A.V. Babakov, 2011, published in Fiziologiya Rastenii, 2011, Vol. 58, No.1, pp. 28–39.
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roslyakova, T.V., Molchan, O.V., Vasekina, A.V. et al. Salt tolerance of barley: Relations between expression of isoforms of vacuolar Na+/H+-antiporter and 22Na+ accumulation. Russ J Plant Physiol 58, 24–35 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443711010158
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443711010158