Abstract
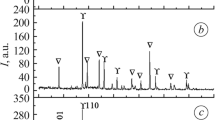
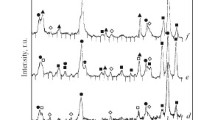
The effect the means of synthesis have on the texture, phase composition, redox properties, and catalytic activity of binary oxide systems with the composition Ce0.5Zr0.5O2 are studied. The obtained samples are characterized via BET, SEM, DTA, XRD, and Raman spectroscopy. A comparative analysis is performed of the physicochemical properties of biomorphic systems Ce0.5Zr0.5O2 obtained using wood sawdust and cellulose as templates and the properties of binary oxides of the same composition obtained by template-free means. The catalytic properties of the obtained oxide systems Ce0.5Zr0.5O2 are studied in the reaction of carbon black oxidation. It is shown that the texture of the oxide depends on the means of synthesis. When biotemplates are used, fragile porous systems form from thin binary oxide plates containing micro-, meso-, and macropores. Oxide obtained via coprecipitation consists of dense agglomerates with pores around 30 Å in size. In supercritical water, nanoparticles of metal oxide form that are loosely agglomerated. The intermediate spaces between them act as pores more than 100 Å in size. A system of single-phase pseudocubic modification is obtained using a cellulose template. The crystal lattices of all the obtained systems contain a great many defects. It is shown that the system prepared via synthesis in supercritical water has the best oxygen-exchange properties. A comparative analysis is performed of the effect the physicochemical properties of the samples have on their activity in the catalytic oxidation of carbon black.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Kaspar, P. Fornasiero, G. Balducci, et al., Inorg. Chim. 349, 217 (2003).
Z. C. Kang, J. Alloys Compd. 408, 1103 (2006).
R. Crisostomo, R. Neto, and M. Schmal, Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 450, 131 (2013).
D. R. Sellick, A. Ara, and T. Garcia, et al., Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 132–133, 98 (2013).
B. Wang, X.-d. Wu, R. Ran, Zh.-ch. Si, and D. Wenga, J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem. 356, 100 (2012).
B. Kh. Vu, E. W. Shin, J.-M. Ha, et al., Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 443–444, 59 (2012).
J. P. Cuif, G. Blanchard, O. Touret, et al., SAE 970463 (1997).
G. Vlaic, R. di Monte, P. Fornasiero, et al., J. Catal. 182, 378 (1999).
M. Yashima, K. Morimoto, N. Ishizawa, and M. Yoshimura, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 76, 2865 (1993).
R. di Monte and J. Kaspar, J. Mater. Chem. 15, 633 (2005).
J. Cao, C. R. Rambo, and H. Sieber, Ceram. Int. 30, 1967 (2004).
C. R. Rambo, J. Cao, and H. Sieber, Mater. Chem. Phys. 87, 345 (2004).
A. A. Galkin, B. G. Kostyuk, N. N. Kuznetsova, A. O. Turakulova, V. V. Lunin, and M. Polyakov, Kinet. Catal. 42, 154 (2001).
J.-R. Kim, W.-J. Myeong, and S.-K. Ihm, Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 71, 57 (2007).
A. I. Kozlov, D. H. Kim, A. Yezerets, et al., J. Catal. 209, 417 (2002).
B. K. Vua, E. W. Shina, J. M. Hab, et al., Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 443–444, 59 (2012).
J.-R. Kim, W.-J. Myeong, and S.-K. Ihm, J. Catal. 263, 123 (2009).
A. O. Turakulova, N. V. Zaletova, and V. V. Lunin, Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 84, 1309 (2010).
G. Vlaic, R. D. Monte, P. Fornasiero, et al., J. Catal. 182, 378 (1999).
L. Cao, L. Pan, C. Ni, Z. Yuana, and S. Wang, Fuel Process. Technol. 91, 306 (2010).
B. Rivas, R. Lopez-Fonseca, M. A. Gutierrez-Ortiz, and J. I. Gutierrez-Ortiz, Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 101, 317 (2011).
I. Atribak, N. Guillen-Hurtado, A. Bueno-Lupez, and A. Garcna-Garcna, Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 7706 (2010).
W. Huang, J. Yang, Ch. Wang, et al., Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 2349 (2012).
A. Trovarelli, F. Zamar, J. Llorka, et al., J. Catal. 169, 490 (1997).
S. Damyanova, B. Pawelec, K. Arishtirova, et al., Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 337, 86 (2008).
G.-f. Li, Q. Wanga, B. Zhao, and R.-x. Zhou, Fuel 92, 360 (2012).
I. Kosacki, T. Suzuki, H. U. Anderson, and P. Colomban, Solid State Ionics 149, 99 (2002).
H. C. Yao and Y. F. Yuyao, J. Catal. 86, 254 (1984).
Z. Yuan, C. Ni, C. Zhang, et al., Catal. Today 146, 124 (2009).
M. Daturi, E. Finocchio, C. Binet, et al., J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 9186 (2000).
J. Kaspar, P. Fornasiero, and M. Graziani, Catal. Today 50, 285 (1999).
B. R. Stanmore, J. F. Brilhac, and P. Gilot, Carbon 39, 2247 (2001).
P. Miceli, S. Bensaid, N. Russo, and D. Fino, Chem. Eng. J. 278, 190 (2015).
P. A. Kumar, M. D. Tanwar, S. Bensaid, et al., Chem. Eng. J. 207–208, 258 (2012).
S. Bensaid, N. Russo, and N. Fino, Catal. Today 216, 57 (2013).
P. Miceli, S. Bensaid, N. Russo, and D. Fino, Nanoscale Res. Lett. 9, 254 (2014).
E. Aneggi, C. Leitenburg, G. Dolcetti, and A. Trovarelli, Catal. Today 114, 40 (2006).
X. Wu, D. Liu, K. Li, J. Li, and D. Weng, Catal. Commun. 8, 1274 (2007).
E. Aneggi, M. Boaro, C. Leitenburg, et al., Catal. Today 112, 94 (2006).
E. Saab, E. Abi-Aad, M. N. Bokova, et al., Carbon 45, 561 (2007).
B. A. Setten, J. M. Schouten, M. Makkee, and J. A. Moulijn, Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 28, 253 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.N. Kharlanov, A.O. Turakulova, A.V. Levanov, V.V. Lunin, 2018, published in Zhurnal Fizicheskoi Khimii, 2018, Vol. 92, No. 4, pp. 577–588.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kharlanov, A.N., Turakulova, A.O., Levanov, A.V. et al. Dependence of the Physicochemical and Catalytic Properties of Ce0.5Zr0.5O2 Oxide on the Means of Synthesis. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. 92, 678–688 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S003602441804012X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S003602441804012X