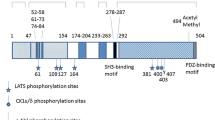
Abstract
JAK/STAT is a conserved signaling pathway in higher eukaryotes that plays a critical role in different processes of ontogenesis. This article reviews the pathway structure at the molecular level, mainly in Drosophila as a model organism. The review is focused on the data concerning the relationship between this signaling pathway and transcription machinery of higher eukaryotes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BRG1:
-
Brahma-related gene protein 1
- CBP/p300:
-
CREB binding protein and p300
- CNTFR:
-
ciliary neurotrophic factor receptor
- DOME:
-
domeless receptor of the JAK/STAT pathway in drosophila
- gp130:
-
glycoprotein 130, a cytokine receptor
- HOP:
-
hopscotch Janus kinase in drosophila
- IFN:
-
interferon
- IL:
-
interleukin
- JAK:
-
janus kinase
- LIFR:
-
leukemia inhibitory factor receptor
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
- PIAS:
-
protein inhibitors of activated STATs
- PTPs:
-
protein tyrosine phosphatases
- SOCS:
-
supressors of cytokine signaling
- STAT:
-
signal transducer and activator of transcription
- TFIID:
-
transcription factor IID
- Tyk-2:
-
tyrosine protein kinase-2
- UPD:
-
unpaired ligand family involved in JAK/STAT activation in drosophila
References
Pires-daSilva A., Sommer R.J. 2003. The evolution of signalling pathways in animal development. Nature Rev. Genet. 4, 39–49.
Lodish H., Berk A., Matsudaira P., Kaiser C.A., Krieger M., Scott M.P., Zipursky L., Darnell J.E., Jr. (Eds.). 2003. Molecular Cell Biology, 5th ed. NY: Freeman.
Li E., Hristova K. 2006. Role of receptor tyrosine kinase transmembrane domains in cell signaling and human pathologies. Biochemistry. 45, 6241–6251.
Arbouzova N.I., Zeidler M.P. 2006. JAK/STAT signalling in Drosophila: insights into conserved regulatory and cellular functions. Development. 133, 2605–2616.
Dawson M.A., Bannister A.J., Gottgens B., Foster S.D., Bartke T., Green A.R., Kouzarides T. 2009. JAK2 phosphorylates histone H3Y41 and excludes HP1alpha from chromatin. Nature. 461, 819–822.
Shi S., Larson K., Guo D., Lim S.J., Dutta P., Yan S.J., Li W.X. 2008. Drosophila STAT is required for directly maintaining HP1 localization and heterochromatin stability. Nature Cell Biol. 10, 489–496.
Wright V.M., Vogt K.L., Smythe E., Zeidler M.P. 2011. Differential activities of the Drosophila JAK/STAT pathway ligands Upd, Upd2 and Upd3. Cell Signal. 23, 920–927.
Harrison D.A., McCoon P.E., Binari R., Gilman M., Perrimon N. 1998. Drosophila unpaired encodes a secreted protein that activates the JAK signaling pathway. Genes Dev. 12, 3252–3263.
Wang Y.H., Huang M.L. 2010. Organogenesis and tumorigenesis: Insight from the JAK/STAT pathway in the Drosophila eye. Dev. Dyn. 239, 2522–2533.
Gilbert M.M., Weaver B.K., Gergen J.P., Reich N.C. 2005. A novel functional activator of the Drosophila JAK/STAT pathway, unpaired2, is revealed by an in vivo reporter of pathway activation. Mech. Dev. 122, 939–948.
Brown S., Hu N., Hombria J.C. 2001. Identification of the first invertebrate interleukin JAK/STAT receptor, the Drosophila gene domeless. Curr. Biol. 11, 1700–1705.
Binari R., Perrimon N. 1994. Stripe-specific regulation of pair-rule genes by hopscotch, a putative Jak family tyrosine kinase in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 8, 300–312.
Luo H., Dearolf C.R. 2001. The JAK/STAT pathway and Drosophila development. Bioessays. 23, 1138–1147.
Hombria J.C., Brown S. 2002. The fertile field of Drosophila Jak/STAT signalling. Curr. Biol. 12, R569–575.
Zeidler M.P., Bach E.A., Perrimon N. 2000. The roles of the Drosophila JAK/STAT pathway. Oncogene. 19, 2598–2606.
Yamaoka K., Saharinen P., Pesu M., Holt V.E., Silvennoinen O., O’Shea J.J. 2004. The Janus kinases (Jaks). Genome Biol. 5, 253.
Usacheva A., Kotenko S., Witte M.M., Colamonici O.R. 2002. Two distinct domains within the N-terminal region of Janus kinase 1 interact with cytokine receptors. J. Immunol. 169, 1302–1308.
Ekas L.A., Cardozo T.J., Flaherty M.S., McMillan E.A., Gonsalves F.C., Bach E.A. 2010. Characterization of a dominant-active STAT that promotes tumorigenesis in Drosophila. Dev. Biol. 344, 621–636.
Ihle J.N. 2001. The Stat family in cytokine signaling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 13, 211–217.
Calo V., Migliavacca M., Bazan V., Macaluso M., Buscemi M., Gebbia N., Russo A. 2003. STAT proteins: from normal control of cellular events to tumorigenesis. J. Cell Physiol. 197, 157–168.
Li B., Zhang G.S., Dai C.W., Pei M.F. 2005. The activation of JAK/STAT signal pathway in hypereosinophilic syndrome and the patients therapeutic response to imatinib. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 85, 448–452.
Horvath C.M. 2000. STAT proteins and transcriptional responses to extracellular signals. Trends Biochem. Sci. 25, 496–502.
Levy D.E., Darnell J.E., Jr. 2002. Stats: transcriptional control and biological impact. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 3, 651–662.
Shuai K. 1999. The STAT family of proteins in cytokine signaling. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 71, 405–422.
Collum R.G., Brutsaert S., Lee G., Schindler C. 2000. A Stat3-interacting protein (StIP1) regulates cytokine signal transduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97, 10120–10125.
Sadzak I., Schiff M., Gattermeier I., Glinitzer R., Sauer I., Saalmuller A., Yang E., Schaljo B., Kovarik P. 2008. Recruitment of Stat1 to chromatin is required for interferon-induced serine phosphorylation of Stat1 transactivation domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105, 8944–8949.
Greenhalgh C.J., Hilton D.J. 2001. Negative regulation of cytokine signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 70, 348–356.
Baeg G.H., Zhou R., Perrimon N. 2005. Genomewide RNAi analysis of JAK/STAT signaling components in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 19, 1861–1870.
Stec W.J., Zeidler M.P. 2011. Drosophila SOCS proteins. J. Signal. Transduct. 2011, 894510. doi 10.1155/2011/894510
Alexander W.S. 2002. Suppressors of cytokine signalling (SOCS) in the immune system. Nature Rev. Immunol. 2, 410–416.
Callus B.A., Mathey-Prevot B. 2002. SOCS36E, a novel Drosophila SOCS protein, suppresses JAK/STAT and EGF-R signalling in the imaginal wing disc. Oncogene. 21, 4812–4821.
Rawlings J.S., Rosler K.M., Harrison D.A. 2004. The JAK/STAT signaling pathway. J. Cell. Sci. 117, 1281–1283.
Rogers R.S., Horvath C.M., Matunis M.J. 2003. SUMO modification of STAT1 and its role in PIAS-mediated inhibition of gene activation. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 30091–30097.
Betz A., Lampen N., Martinek S., Young M.W., Darnell J.E., Jr. 2001. A Drosophila PIAS homologue negatively regulates stat92E. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98, 9563–9568.
Lohi O., Lehto V.P. 2001. STAM/EAST/Hbp adapter proteins-integrators of signalling pathways. FEBS Lett. 508, 287–290.
Icardi L., De Bosscher K., Tavernier J. 2012. The HAT/HDAC interplay: multilevel control of STAT signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 23, 283–291.
Shuai K. 2000. Modulation of STAT signaling by STAT-interacting proteins. Oncogene. 19, 2638–2644.
Cantwell C.A., Sterneck E., Johnson P.F. 1998. Interleukin-6-specific activation of the C/EBPdelta gene in hepatocytes is mediated by Stat3 and Sp1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 2108–2117.
Zhang X., Wrzeszczynska M.H., Horvath C.M., Darnell J.E., Jr. 1999. Interacting regions in Stat3 and c-Jun that participate in cooperative transcriptional activation. Mol. Cell Biol. 19, 7138–7146.
Ohmori Y., Schreiber R.D., Hamilton T.A. 1997. Synergy between interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in transcriptional activation is mediated by cooperation between signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 and nuclear factor kappaB. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 14899–14907.
Qureshi S.A., Salditt-Georgieff M., Darnell J.E., Jr. 1995. Tyrosine-phosphorylated Stat1 and Stat2 plus a 48-kDa protein all contact DNA in forming interferon-stimulated-gene factor 3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 92, 3829–3833.
Goenka S., Boothby M. 2006. Selective potentiation of Stat-dependent gene expression by collaborator of Stat6 (CoaSt6), a transcriptional cofactor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103, 4210–4215.
Kwon M.C., Koo B.K., Moon J.S., et al. 2008. Crif1 is a novel transcriptional coactivator of STAT3. EMBO J. 27, 642–653.
Bhattacharya S., Eckner R., Grossman S., Oldread E., Arany Z., D’Andrea A., Livingston D.M. 1996. Cooperation of Stat2 and p300/CBP in signalling induced by interferon-alpha. Nature. 383, 344–347.
Pfitzner E., Jahne R., Wissler M., Stoecklin E., Groner B. 1998. p300/CREB-binding protein enhances the prolactin-mediated transcriptional induction through direct interaction with the transactivation domain of Stat5, but does not participate in the Stat5-mediated suppression of the glucocorticoid response. Mol. Endocrinol. 12, 1582–1593.
Zhang J.J., Vinkemeier U., Gu W., Chakravarti D., Horvath C.M., Darnell J.E., Jr. 1996. Two contact regions between Stat1 and CBP/p300 in interferon gamma signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 93, 15092–15096.
Valineva T., Yang J., Palovuori R., Silvennoinen O. 2005. The transcriptional co-activator protein p100 recruits histone acetyltransferase activity to STAT6 and mediates interaction between the CREB-binding protein and STAT6. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 14989–14996.
Zhu M., John S., Berg M., Leonard W.J. 1999. Functional association of Nmi with Stat5 and Stat1 in IL-2- and IFNgamma-mediated signaling. Cell. 96, 121–130.
Paulson M., Press C., Smith E., Tanese N.. Levy D.E. 2002. IFN-Stimulated transcription through a TBP-free acetyltransferase complex escapes viral shutoff. Nature Cell. Biol. 4, 140–147.
Horvath C.M., Stark G.R., Kerr I.M., Darnell J.E., Jr. 1996. Interactions between STAT and non-STAT proteins in the interferon-stimulated gene factor 3 transcription complex. Mol. Cell Biol. 16, 6957–6964.
Martinez-Moczygemba M., Gutch M.J., French D.L., Reich N.C. 1997. Distinct STAT structure promotes interaction of STAT2 with the p48 subunit of the interferon-alpha-stimulated transcription factor ISGF3. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 20070–20076.
Stocklin E., Wissler M., Gouilleux F., Groner B. 1996. Functional interactions between Stat5 and the glucocorticoid receptor. Nature. 383, 726–728.
Huang M., Qian F., Hu Y., Ang C., Li Z., Wen Z. 2002. Chromatin-remodelling factor BRG1 selectively activates a subset of interferon-alpha-inducible genes. Nature Cell. Biol. 4, 774–781.
Giraud S., Hurlstone A., Avril S., Coqueret O. 2004. Implication of BRG1 and cdk9 in the STAT3-mediated activation of the p21waf1 gene. Oncogene. 23, 7391–7398.
Ni Z., Karaskov E., Yu T., Callaghan S.M., Der S., Park D.S., Xu Z., Pattenden S.G., Bremner R. 2005. Apical role for BRG1 in cytokine-induced promoter assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 102, 14611–14616.
Zhang Y., Cheng M.B., Zhang Y.J., Zhong X., Dai H., Ya L., Wu N.H., Shen Y.F. 2010. A switch from hBrm to Brg1 at IFN gamma-activated sequences mediates the activation of human genes. Cell Res. 20, 1345–1360.
Letimier F.A., Passin N., Gasparian S., Bianchi E., Rogge L. 2007. Chromatin remodeling by the SWI/SNF-like BAF complex and STAT4 activation synergistically induce IL-12Rbeta2 expression during human Th1 cell differentiation. EMBO J. 26, 1292–1302.
Zhang F., Boothby M. 2006. T helper type 1-specific Brg1 recruitment and remodeling of nucleosomes positioned at the IFN-gamma promoter are Stat4 dependent. J. Exp. Med. 203, 1493–1505.
Xu R., Spencer V.A., Bissell M.J. 2007. Extracellular matrix-regulated gene expression requires cooperation of SWI/SNF and transcription factors. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 14992–14999.
Wurster A.L., Pazin M.J. 2008. BRG1-mediated chromatin remodeling regulates differentiation and gene expression of T helper cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 28, 7274–7285.
Snyder M., He W., Zhang J.J. 2005. The DNA replication factor MCM5 is essential for Stat1-mediated transcriptional activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 102, 14539–14544.
Muller P., Kuttenkeuler D., Gesellchen V., Zeidler M.P., Boutros M. 2005. Identification of JAK/STAT signalling components by genome-wide RNA interference. Nature. 436, 871–875.
Panov V.V., Kuzmina J.L., Doronin S.A., Kopantseva M.R., Nabirochkina E.N., Georgieva S.G., Vorobyeva N.E., Shidlovskii Y.V. 2012. Transcription co-activator SAYP mediates the action of STAT activator. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, 2445–2453.
Vorobyeva N.E., Soshnikova N.V., Nikolenko J.V., Kuzmina J.L., Nabirochkina E.N., Georgieva S.G.. Shidlovskii Y.V. 2009. Transcription coactivator SAYP combines chromatin remodeler Brahma and transcription initiation factor TFIID into a single supercomplex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106, 11049–11054.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.V. Shaposhnikov, I.F. Komar’kov, L.A. Lebedeva, Yu.V. Shidlovskii, 2013, published in Molekulyarnaya Biologiya, 2013, Vol. 47, No. 3, pp. 388–397.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaposhnikov, A.V., Komar’kov, I.F., Lebedeva, L.A. et al. Molecular components of JAK/STAT signaling pathway and its interaction with transcription machinery. Mol Biol 47, 343–351 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893313030126
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893313030126