Abstract
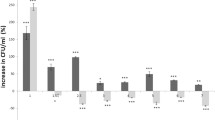
Shiga toxin 2 (Stx2)-converting bacteriophages ca n infect and lysogenized other bacteria in vivo and in vitro, and thus contribute to the genotypic heterogeneity of infected host. However, the global transcription patterns accompanying the lysogenic infection of Escherichia coli coli host have not been clearly resolved. In this study, we compared the gene expression profiles of Stx2 phage ΦMin27(Δstx::cat) converted and naïve E. coli MG1655 hosts using microarray analyses. It was identified that conversion by ΦMin27(Δstx::cat) had a direct effect on the global expression of bacterial host genes as 166 genes were found to be differentially expressed (104 up-regulated and 62 down-regulated). These genes were predominantly responsible for bacterial central metabolism, transport and transcription. It was shown that in addition to the down-regulation of genes involved in synthesis of Thi an d protein transporters, expression of genes associated with bacterial energy production (e.g., fadABDEHIJL, aceK and acnA) were also suppressed. Conversely, a significantly larger number of genes were up-regulated, including transport genes, flagellar synthesis genes (fliDESTZ) and acid resistant genes (e.g., gadEW, hdeABD and adiY). Our study also discovered conversion of ΦMin27(Δstx::cat) could change host physiological character. The converted cells had increased acid tolerance at low pH and promoted swimming motility on semisolid agar surface compared to the uninfected bacterial host.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gyles C.L. 2007. Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli: An overview. J. Anim. Sci. 85, 45–62.
O’Brien A.D., Newland J.W., Miller S.F., Holmes R.K., Smith H.W., Formal S.B. 1984. Shiga-like toxin-converting phages from Escherichia coli strains that cause hemorrhagic colitis or infantile diarrhea. Science. 226, 694–696.
Gamage S.D., Strasser J.E., Chalk C.L., Weiss A.A. 2003. Nonpathogenic Escherichia coli can contribute to the production of Shiga toxin. Infect. Immun. 71, 3107–3115.
Cornick N.A., Helgerson A.F., Mai V., Ritchie J.M., Acheson D.W. 2006. In vivo transduction of an Stx-encoding phage in ruminants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 5086–5088.
Heuvelink A.E., VandeKar N.C., Meis J.F., Monnens L.A., Melchers W.J. 1995. Characterization of verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli O157 isolates from patients with haemolytic uraemic syndrome in Western Europe. Epidemiol. Infect. 115, 1–14.
Thomas A., Cheasty T., Chart H., Rowe B. 1994. Isolation of Vero cytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli sero-types O9ab:H- and O101: H- carrying VT2 variant gene sequences from a patient with haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 13, 1074–1076.
Herold S., Karch H., Schmidt H. 2004. Shiga toxin-encoding bacteriophages: Genomes in motion. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 294, 115–121.
Schmidt H. 2001. Shiga-toxin-converting bacteriophages. Res. Microbiol. 152, 687–695.
Allison, H.E. 2007. Stx-phages: Drivers and mediators of the evolution of STEC and STEC-like pathogens. Future. Microbiol. 2, 165–174.
James C.E., Stanley K.N., Allison H.E., Flint H.J., Stewart C.S., Sharp R.J., Saunders J.R., McCarthy A.J. 2001. Lytic and lysogenic infection of diverse Escherichia coli and Shigella strains with a verocytotoxigenic bacteriophage. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67, 4335–4337.
Muniesa M., Blanco J.E., Simãn M.D., Serra-Moreno R., Blanch A.R., Jofre J. 2004. Diversity of stx2 converting bacteriophages induced from Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains isolated from cattle. Microbiology. 150, 2959–2971.
Mühldorfer I., Hacker J., Keusch G.T., Acheson D.W., Tschäpe H., Kane A.V., Ritter A., Ölschläger T., Dono-hue-rolfe A. 1996. Regulation of the Shiga-like toxin II operon in Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 64, 495–502.
Wagner P.L., Acheson D.W., Waldor M.K. 2001. Human neutrophils and their products induce Shiga toxin production by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 69, 1934–1937.
Letellier L., Plancon L., Bonhivers M., Boulanger P. 1999. Phage DNA transport across membranes. Res. Microbiol. 150, 499–505.
Nash H.A. 1981. Integration and excision of bacteriophage lambda: The mechanism of conservation site specific recombination. Annu. Rev. Genet. 15, 143–167.
Harrington C.A., Rosenow C., Retief J. 2000. Monitoring gene expression using DNA microarrays. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 3, 285–291.
Osterhout R.E., Figueroa I.A., Keasling J.D., Arkin A.P. 2007. Global analysis of host response to induction of a latent bacteriophage. BMC Microbiol. 7, 82–93.
Herold S., Siebert J., Huber A., Schmidt H. 2005. Global expression of prophage genes in Escherichia coli O157:H7 strain EDL933 in response to norfloxacin. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 49, 931–944.
Karlsson F., Malmborg-Hager A.C., Albrekt A.S., Borrebaeck C.A. 2005. Genome-wide comparison of phage M13-infected vs. uninfected Escherichia coli. Can. J. Microbiol. 51, 29–35.
Liangke Su., Yaxian Y., Chengping L. 2008. Construction of a stx2 deletion mutant of Shiga toxin 2 phage ΦMin27 and its infectious properties. Acta Microbiol. Sinica. 48, 1227–1233.
Blattner F.R., Plunkett G.III., Bloch C.A., Perna N.T., Burland V., Riley M., Collado-Vides J., Glasner J.D., Rode C.K., Mayhew G.F., Gregor J., Davis N.W., Kirkpatrick H.A., Goeden M.A., Rose D.J., Mau B., Shao Y. 1997. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science. 277, 1453–1474.
Schmidt H., Bielaszewska M., Karch H. 1999. Transduction of enteric Escherichia coli isolates with a derivative of Shiga toxin 2-encoding bacteriophage Φ3538 isolated from Escherichia coli O157:H7. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65, 3855–3861.
Livak K.J., Schmittgen T.D. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 —Δ0394;Ct method. Methods. 25, 402–408.
Castanie-Cornet M.P., Penfound T.A., Smith D., Elliott J.F., Foster J.W. 1999. Control of acid resistance in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 181, 3525–3535.
Gãmez-Gãmez J.M., Manfredi C., Alonso J.C., Blázquez J. 2007. A novel role for RecA under non-stress: promotion of swarming motility in Escherichia coli K-12. BMC. Biol. 5, 1–15.
Zorzano M.P., Hochberg D., Cuevas M.T., Gãmez-Gãmez J.M. 2005. Reaction-diffusion model for pattern formation in E. coli swarming colonies with slime. Phys. Rev. E. Stat. Nonlin. Soft. Matter. Phys. 71, 031908.
Boucher D.J., Adler B., Boyce J.D. 2005. The Pasteurella multocida nrfE gene is upregulated during infection and is essential for nitrite reduction but not for virulence. J. Bacteriol. 187, 2278–2285.
Mao H., Cremer P.S., Manson M.D. 2003. A sensitive, versatile microfluidic assay for bacterial chemotaxis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 100, 5449–5454.
Tucker D.L., Tucker N., Conway T. 2002. Gene expression profiling of the pH response in Escherichia coli. J. Bacterial. 184, 6551–6558.
Hommais F., Krin E., Coppee J.Y., Lacroix C., Yeramian E., Danchin A., Bertin P. 2004. GadE (YhiE): A novel activator involved in the response to acid environment in Escherichia coli. Microbiology. 150, 61–72.
Kieboom J., Abee T. 2006. Arginine-dependent acid resistance in Salmonella enteric serovar Typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 188, 5650–5653.
Horn P.B.V., Backstrom A., Stewart V., Begley T.P. 1993. Structural genes for thiamine biosynthetic enzymes (thiCEFGH) in Escherichia coli K-12. J. Bacteriol. 175, 982–992.
Higgins C.F. 2001. ABC transporters: Physiology, structure and mechanism—an overview. Res. Microbiol. 152, 205–210.
Cho B.K., Knight E.M., Palsson B. 2006. Transcriptional regulation of the fad regulon genes of Escherichia coli by ArcA. Microbiology. 152, 2207–2219.
Reed L.J. 1953. Metabolic functions of thiamine and lipoic acid. Physiol Rev. 33, 544–559.
Friedman D.A., Olson E.R., Georgopoulos C.G., Tilly K., Herskowitz I., Banuett F. 1984. Interactions of bacteriophage and host macromolecules in the growth of bacteriophage 7n. Microbiol. Rev. 48, 299–325.
Miller H.I., Nash N.A. 1981. Direct role of the himA gene product in phage 7n integration. Nature. 290, 523–526.
Willenbrock H., Petersen A., Sekse C., Kiil K., Wasteson Y., Ussery D.W. 2006. Design of a seven-genome Escherichia coli microarray for comparative genomic profiling. J. Bacteriol. 188, 7713–7721.
Wolfe A.J., Berg H.C. 1989. Migration of bacteria in semisolid agar. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 86, 6973–6977.
Garrity L.F., Ordal G.W. 1995. Chemotaxis in Bacillus subtilis: How bacteria monitor environmental signals. Pharmacol. Ther. 68, 87–104.
Parkinson J.S., Parker S.R., Talbert P.B., Houts S.E. 1983. Interactions between chemotaxis genes and flagellar genes in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 155, 265–274.
Blair D.F. 1995. How bacteria sense and swim. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 49, 489–522.
Tucker D.L., Tucker N., Conway T. 2002. Gene expression profiling of the pH response in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 184, 6551–6558.
Molina P.M., Parma A.E., Sanz M.E. 2003. Survival in acidic and alcoholic medium of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7 and non-O157:H7 isolated in Argentina. BMC Microbiol. 3, 1–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article was submitted by the authors in English
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, L.K., Lu, C.P., Wang, Y. et al. Lysogenic infection of a Shiga toxin 2-converting bacteriophage changes host gene expression, enhances host acid resistance and motility. Mol Biol 44, 54–66 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893310010085
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893310010085