Abstract
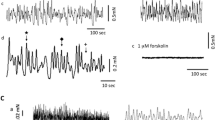
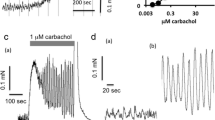
The effect of histamine on background spontaneous electrical activity of the interrelated bladder and urethra was studied in rats. The basic characteristics of pacemaker activity (action potential amplitude, average peak rise rate, peak rise time, peak half-width, rhythmogenicity frequency) were analyzed both in normal conditions and upon exposure to histamine (10–4 mol/L). A comparison of the action potential parameters in the above organs demonstrated far lower values of the amplitude (by 34.19%; p ≤ 0.001), peak rise rate (by 30.39%; p ≤ 0.01) and peak rise time (by 18%; p ≤ 0.01) at a reduced rhythmogenicity frequency. Histamine evoked a considerable increase in the amplitude and its rise rate in the bladder (by 50.59 and 56.36%, respectively; p ≤ 0.001) and rhythmogenicity frequency (by 18%; p ≤ 0.01) at a constancy of the remaining two parameters. In the urethra, no obvious changes were detected in the action potential parameters. Morphohistochemical analysis also supported the involvement of histamine in the activation of rhythmogenicity only in the bladder. Thus, histamine is not implicated in the genesis of tonic contractions in the urethra, in contrast to its activating effect on the bladder.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson, K.E. and Arner, A., Urinary bladder contraction and relaxation: physiology and pathophysiology, Physiol. Rev., 2004, vol. 84, no. 3, pp. 935–986.
McHale, N.G., Hollywood, M.A., Sergeant, G.P., Shafei, M., Thornbury, K.T., and Ward, S.M., Organization and function of ICC in the urinary tract, J. Physiol., 2006, vol. 576, pt. 3, pp. 689–694.
Brading, A.F., Spontaneous activity of lower urinary tract smooth muscles: correlation between ion channels and tissue function, J. Physiol., 2006, no. 570, pt. 1, pp. 13–22.
Fry, C.H., Meng, E., and Young, J.S., The physiological function of lower urinary tract smooth muscle, Auton. Neurosci., 2010, vol. 19, no. 154, pp. 3–13.
Drake, M.J., Harvey, I.J., and Gillespie, J.I., Autonomous activity in the isolated guinea pig bladder, Exp. Physiol., 2003, vol. 88, no. 1, pp. 19–30.
Sui, G., Fry, C.H., Malone-Lee, J., and Wu, C., Aberrant Ca2+ oscillations in smooth muscle cells from overactive human bladders, Cell Calcium, 2009, vol. 45, no. 5, pp. 456–464.
McHale, N.G., Hollywood, M.A., Sergeant, G.P., Shafei, M., Thornbury, K.T., and Ward, S., Organization and function of ICC in the urinary tract, J. Physiol., 2006, vol. 576, pt. 3, pp. 689–694.
Hashitani, H. and Edwards, F.R., Spontaneous and neurally activated depolarizations in smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig urethra, J. Physiol., 1999, vol. 514, pt. 2, pp. 459–470.
Hashitani, H., Van Helden, D.F., and Suzuki, H., Properties of spontaneous depolarizations in circular smooth muscle cells of rabbit urethra, Br. J. Pharmacol., 1996, vol. 118, no. 7, pp. 1627–1632.
Bertaccini, G., Zappia, L., Bezzi, E., and Potnezoni, D., Histamine receptors in the human ureter, Pharmac. Res. Commun., 1983, vol. 15, pp. 157–166.
Bennedito, S., Prieto, D., Rivera, L., and Costa Garcia-Saeriston, A., Mechanisms implicated in the histamine response of the ureterovesical junction, J. Urol., 1991, vol. 146, no. 1, pp. 184–187.
Neuhaus, J., Weimann, A., Stolzenburg, J.U., Dawood, W., Schwalenberg, T., and Dorschner, W., Histamine receptors in human detrusor smooth muscle cells: physiological properties and immunohistochemical representation of subtypes, World J. Urol., 2006, vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 202–209.
Bicer, F., Altuntas, C.Z., Izgi, K., Ozer, A., Kavran, M., Tuohy, V.K., and Daneshgari, F., Chronic pelvic allodynia is mediated by CCL2 through mast cells in an experimental autoimmune cystitis model, Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol., 2015, vol. 308(2), pp. 103–113.
Yilmaz, E., Batislam, E., Deniz, T., and Yuvanc, E., Histamine receptor antagonist in symptomatic treatment of renal colic accompanied by nausea: two birds with one stone, Urol. J., 2009, vol. 73, no.1, pp. 32–36.
Kazaryan, K.V., Vantsyan, V.Ts., and Simonyan, L.G., Role of histamine in regulation of spontaneous electrical activity of the rat ureter and adjacent bladder zone, Ross. Fiziol. Zh., 2011, no. 12, pp. 1319–1326.
Ugaily-Thuoesius, L., Thuiesius, O., Angelo-Khattar, M., Sabha, M., and Sivanandasinghni, P., Mast cells and histamine responses of the ureter, ultrastructural features of cell-to-cell associations and functional implications, Urol. Rev., 1988, vol. 16, pp. 287–293.
Kazaryan, K.V., Unanyan, N.G., Savayan, A.A., Piliposyan, T.A., Mkrtchyan, A.V., and Manukyan, A.M., Identification of the characteristics of spontaneous electrical activity in the rhythmogenic areas in rats, Zh. Evol. Biokhim. Fiziol., 2015, vol. 51, no. 5, pp. 340–346.
Hashitani, H., Interaction between interstitial cells and smooth muscles in the lower urinary tract and penis, J. Physiol., 2006, vol. 576, pt. 3, pp. 707–714.
Osman, F., Romics, I., Nyírády, P., Monos, E., and Nádasy, G.L., Ureteral motility, Acta Physiol. Hungarica, 2009, vol. 96, no. 4, pp. 409–426.
Sanders, K.M., Koh, S.D., and Ward, S.M., Interstitial cells of Cajal as pacemakers in the gastrointestinal tract, Ann. Rev. Physiol., 2006, vol. 68, pp. 307–343.
Bramich, N.J. and Brading, A.F., Electrical properties of smooth muscle in the guinea-pig urinary bladder, J. Physiol., 1996, vol. 492, no. 1, pp. 185–198.
Hashitani, H. and Suzuki, H., Properties of spontaneous Ca2+ transients recorded from interstitial cells of Cajal-like cells of the rabbit urethra in situ, J. Physiol., 2007, vol. 583, pp. 505–519.
McCloskey, K.D., Interstitial cells of Cajal in the urinary tract, Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology, 2002, vol. 202, pp. 233–254.
Moore, K. and Agur, A., Essential Clinical Anatomy, 3rd ed., Philadelphia, 2007, pp. 227–228.
Meliksetyan, I., The reveling of Ca2+-dependent activity of acid phosphatase in cell structures of rat brain, Morfologiya, 2007, vol. 131, pp. 77–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © K.V. c, M.A. Danielyan, R.G. Chibukhchyan, Sh.G. Margaryan, 2018, published in Zhurnal Evolyutsionnoi Biokhimii i Fiziologii, 2018, Vol. 54, No. 1, pp. 44—51.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kazaryan, K.V., Danielyan, M.A., Chibukhchyan, R.G. et al. Histamine-Mediated Regulation of Electrical Activity during the Bladder–Urethra Interaction in Rats. J Evol Biochem Phys 54, 50–58 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093018010064
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022093018010064