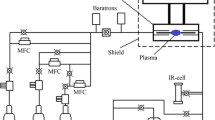
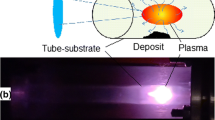
Abstract
The main operating modes of a radiofrequency induction plasma torch with a vortex stabilization of the atmospheric-pressure gas discharge at have been studied in an argon-hydrogen mixture in the range of Ar/H2 = 12–4. The dependences of the electron temperature Te and number density ne on the Ar/H2 ratio have been experimentally studied. It has been found that the electron temperature and concentration in pure argon plasma are 0.88 eV and 7.6 × 1014 cm−3, respectively. When the Ar/H2 ratio decreases, the electron temperature decreases to 0.42 eV, and the electron number density is 8 × 1012 cm−3. The calorimetric method used to estimate the gas temperature Tg, has given a value of 2500 K. The process of BCl3 reduction with hydrogen has been studied at the implemented operating modes of the induction plasma torch. The main products of the reduction of boron trichloride are a polycrystalline boron powder and dichloroborane. The morphology of boron and its phase composition and impurities have been studied. The average particle size of the boron powder is 200 nm.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Reed, T.B., J. Appl. Phys., 1961, vol. 32, p. 821.
Eckert, H.U., Report SAMSO-TR-227, Los Angeles: Space and Missile Systems Organization, 1972.
Mazin, V.I., RU Patent 2233563, 2004.
Frolov, V., Matveev, I., Ivanov, D., Zverev, S., Ushin, B., and Petrov, G., Rom. J. Phys., 2011, vol. 56, p. 36.
Matveev, I., Matveyeva, S., and Zverev, S., IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., 2014, vol. 42, p. 3891.
Vetrov, S.I., Spitsyn, A.V., Shuvaev, D.A., and Yanchenkov, S.V., Plasma Phys. Rep., 2006, vol. 32, p. 418.
Gol’dfarb, V.M. and Dresvin, S.V., Teplofiz. Vys. Temp., 1995, vol. 3, p. 333.
Isola, L.M., Gómez, B.J., and Guerra, V., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2010, vol. 43, p. 01520.
Greene, B.R., Clemens, N.T., Varghese, P.L., Bouslog, S.A., and Del Papa, S.V., 55th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Grapevine, Texas, 9–13 January 2017, AIAA SciTech Forum, (AIAA 2017-0394).
Laux, C.O., Spence, T.G., Kruger, C.H., and Zare, R.N., Plasma Sources Sci. Technol., 2003, vol. 12, p. 125.
Diana, M., Russo, G., and Mario, L., Proceedings of International Round Table on Study and Applications of Transport Phenomena in Thermal Plasmas, Bonnet, C. Ed., Odeillo: CNRS, 1975, Rep. 1.8.
Cueilleron, J. and Cruiziat, B., Bull. Soc. Chim. Fr., 1973, vol. 4, p. 1207.
Murdoch, H.D. and Hamblyn, S.M.L., US Patent 3625846, 1971.
Kelina, I.Yu., Ershova, N.I., Arakcheev, A.V., et al., Refract. Ind. Ceram., 2004, vol. 45, p. P. 185.
Rusanov, V.D. and Fridman, A.A., Physics of Chemically Active Plasma, Boca Raton: CRC, 2007.
Han, G. and Cho, G., Appl. Sci. Converg. Technol., 2017, vol. 26, p. 201.
Zhu, X.-M. and Pu, Y.-K., Plasma Sources Sci. Technol., 2008, vol. 17, p. 024002.
Iordanova, E., de Vries, N., Guillemier, M., and Mvan der Mullen J.J., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2008, vol. 41, p. 015208.
Bityurin, V.A., Grigorenko, A.V., Efimov, A.V., Klimov, A.I., Korshunov, O.V., Kutuzov, D.S., and Chinnov, V.F., High Temp., 2014, vol. 52, p. P. 31.
Raizer, Y.P., Gas Discharge Physics, Berlin: Spriger, 1991.
Nester, S.A., Potapkin, B.V., Levitskii, A.A., Rusanov, V.D., Trusov, B.G., and Fridman, A.A., Kinetiko-statisticheskoe modelirovanie khimicheskikh reaktsii v gazovom razryade (Kinetic–Statistical Modeling of Chemical Reactions in Gas Discharge), Moscow: TsNII Atominform, 1988.
Fridman, A., Plasma Chemistry, New York: Cambridge Univ. Press, 2008.
Tsvetkov, Yu.V. and Panfilov, S.A., Nizkotemperaturnaya plazma v protsessakh vosstanovleniya (Low-Temperature Plasma in Reduction Processes), Moscow: Nauka, 1980.
Lannin, J.S., Solid State Commun., 1978, vol. 25, p. 363.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, grant no. 17-13-01027). Authors thank the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (project no. 0095-2016-0006) for providing analytical equipment for characterization of the material.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated by V. Avdeeva
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kornev, R.A., Sennikov, P.G., Shabarova, L.V. et al. Reduction of Boron Trichloride in Atmospheric-Pressure Argon–Hydrogen Radiofrequency Induction Plasma. High Energy Chem 53, 246–253 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S001814391903010X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S001814391903010X