Abstract
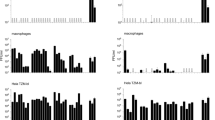
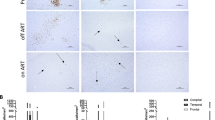
Macrophage/microglia cells are the principal targets for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) in the central nervous system (CNS). Prototype HIV-1 isolates from the CNS are macrophage (M)-tropic, non-syncytia-inducing (NSI), and use CCR5 for entry (R5 strains), but whether syncytia-inducing (SI) CXCR4-using X4 strains might play a role in macrophage/microglia infection and neuronal injury is unknown. To explore the range of features among HIV-1 primary isolates from the CNS, the authors analyzed an HIV-1 strain (TYBE) from cerebrospinal fluid of an individual with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) that was unusual because it was SI. Like other CNS isolates, HIV-1/TYBE replicated to high level in primary human macrophages, but, in contrast to CNS prototypes, TYBE used CXCR4 exclusively to infect macrophages. A functional TYBE env clone confirmed the X4 phenotype and displayed a highly charged V3 sequence typical of X4 strains. Supernatant from TYBE-infected primary human macrophages induced apoptosis of neurons. Thus, TYBE represents a novel type of CNS-derived HIV-1 isolate that is CXCR4-restricted yet replicates efficiently in macrophages and induce neuronal injury. These results demonstrate that HIV-1 variants in the CNS may possess a broader range of biological characteristics than generally appreciated, raise the possibility that X4 strains may participate in AIDS neuropathogenesis, and provide a prototype clade B HIV-1 strain that replicates efficiently in primary macrophages through the exclusive use of CXCR4 as a coreceptor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albright AV, Shieh JTC, Itoh T, Lee B, Pleasure D, O’Connor MJ, Doms RW, Gonzalez-Scarano F (1999). Microglia express CCR5, CXCR4, and CCR3, but of these, CCR5 is the principal coreceptor for human immunodefi-ciency virus type 1 dementia isolates. J Virol 73: 205–213.
Anand R, Thayer R, Srinivasan A, Nayyar S, Gardner M, Luciw P, Dandekar S (1989). Biological and molecular characterization of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1BR) from the brain of a patient with progressive dementia. Virology 168: 79–89.
Bezzi P, Domercq M, Brambilla L, Galli R, Schols D, De Clercq E, Vescovi A, Bagetta G, Kollias G, Meldolesi J, Volterra A (2001). CXCR4-activated astrocyte glutamate release via TNFalpha: amplification by microglia triggers neurotoxicity. Nat Neurosci 4: 702–710.
Brew BJ, Evans L, Byrne C, Pemberton L, Hurren L (1996). The relationship between AIDS dementia complex and the presence of macrophage tropic and non-syncytium inducing isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in the cerebrospinal fluid. J NeuroVirol 2: 152–157.
Catani MV, Corasaniti MT, Navarra M, Nistico G, Finazzi-Agro A, Melino G (2000). gp120 induces cell death in human neuroblastoma cells through the CXCR4 and CCR5 chemokine receptors. J Neurochem 74: 2373–2379.
Chen W, Sulcove J, Frank I, Jaffer S, Ozdener H, Kolson DL (2002). Development of a human neuronal cell model for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected macrophage-induced neurotoxicity: apoptosis induced by HIV type 1 primary isolates and evidence for involvement of the Bcl-2/Bcl-xL-sensitive intrinsic apoptosis pathway. J Virol 76: 9407–9419.
Cheng-Mayer C, Weiss C, Seto D, Levy JA (1989). Isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 from the brain may constitute a special group of the AIDS virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 8575–8579.
Choe W, Albright A, Sulcove J, Jaffer S, Hesselgesser J, Lavi E, Crino P, Kolson DL (2000). Functional expression of the seven-transmembrane HIV-1 co-receptor APJ in neural cells. J NeuroVirol 6 (Suppl 1): S61-S69.
Collman R, Hassan NF, Walker R, Godfrey B, Cutilli J, Hastings JC, Friedman H, Douglas SD, Nathanson N (1989). Infection of monocyte-derived macrophages with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). Monocyte-tropic and lymphocyte-tropic strains of HIV-1 show distinctive patterns of replication in a panel of cell types. J Exp Med 170: 1149–1163.
Connor RI, Sheridan KE, Ceradini D, Choe S, Landau NR (1997). Change in coreceptor use correlates with disease progression in HIV-1-infected individuals. J Exp Med 185: 621–628.
Donzella GA, Schols D, Lin SW, Este JA, Nagashima KA, Maddon PJ, Allaway GP, Sakmar TP, Henson G, De Clercq E, Moore JP (1998). AMD3100, a small molecule inhibitor of HIV-1 entry via the CXCR4 co-receptor. Nat Med 4: 72–77.
Edinger AL, Hoffman TL, Sharron M, Lee B, Yi Y, Choe W, Kolson DL, Mitrovic B, Zhou Y, Faulds D, Collman RG, Hesselgesser J, Horuk R, Doms RW (1998). An orphan seven-transmembrane domain receptor expressed widely in the brain functions as a coreceptor for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and simian immunodeficiency virus. J Virol 72: 7934–7940.
Ellis RJ, Gamst AC, Capparelli E, Spector SA, Hsia K, Wolfson T, Abramson I, Grant I, McCutchan JA (2000). Cerebrospinal fluid HIV RNA originates from both local CNS and systemic sources. Neurology 54: 927–936.
Gartner S, Markovits P, Markovitz DM, Betts RF, Popovic M (1986). Virus isolation from and identification of HTLV-III/LAV-producing cells in brain tissue from a patient with AIDS. JAMA 256: 2365–2371.
Giulian D, Vaca K, Noonan CA (1990). Secretion of neurotoxins by mononuclear phagocytes infected with HIV-1. Science 250: 1593–1596.
Gorry PR, Bristol G, Zack JA, Ritola K, Swanstrom R, Birch CJ, Bell JE, Bannert N, Crawford K, Wang H, Schols D, De Clercq E, Kunstman K, Wolinsky SM, Gabuzda D (2001). Macrophage tropism of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates from brain and lymphoid tissues predicts neurotropism independent of coreceptor specificity. J Virol 75: 10073–10089.
Groenink M, Fouchier RAM, Broersen S, Baker CH, Koot M, van’t Wout AB, Huisman HG, Miedema F, Tersmette M, Schuitemaker H (1993). Relation of phenotype evolution of HIV-1 to envelope V2 configuration. Science 260: 1513–1516.
Haas DW, Clough LA, Johnson BW, Harris VL, Spearman P, Wilkinson GR, Fletcher CV, Fiscus S, Raffanti S, Donlon R, McKinsey J, Nicotera J, Schmidt D, Shoup RE, Kates RE, Lloyd RM Jr, Larder B (2000). Evidence of a source of HIV type 1 within the central nervous system by ultraintensive sampling of cerebrospinal fluid and plasma. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 16: 1491–1502.
He JL, Chen YZ, Farzan M, Choe HY, Ohagen A, Gartner S, Busciglio J, Yang XY, Hofmann W, Newman W, Mackay CR, Sodroski J, Gabuzda D (1997). CCR3 and CCR5 are co-receptors for HIV-1 infection of microglia. Nature 385: 645–649.
Hesselgesser J, Taub D, Baskar P, Greenberg M, Hoxie J, Kolson DL, Horuk R (1998). Neuronal apoptosis induced by HIV-1 gp120 and the chemokine SDF-1α is mediated by the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Curr Biol 8: 595–598.
Kaul M, Garden GA, Lipton SA (2001). Pathways to neuronal injury and apoptosis in HIV-associated dementia. Nature 410: 988–994.
Koyanagi Y, Miles S, Mitsuyasu RT, Merrill JE, Vinters HV, Chen ISY (1987). Dual infection of the central nervous system by AIDS viruses with distinct cellular tropisms. Science 236: 819–822.
Lavi E, Strizki JM, Ulrich AM, Zhang W, Fu L, Wang Q, O’Connor M, Hoxie JA, Gonzalez-Scarano F (1997). CXCR-4 (Fusin), a co-receptor for the type 1 human immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1), is expressed in the human brain in a variety of cell types, including microglia and neurons. Am J Pathol 151: 1035–1042.
Llanes C, Collman RG, Hrin R, Kolson DL (1995). Acetylcholinesterase expression in NTera 2 human neuronal cells: a model for developmental expression in the nervous system. J Neuroscience Res 42: 791–802.
Masciotra S, Owen SM, Rudolph D, Yang C, Wang B, Saksena N, Spira T, Dhawan S, Lal RB (2002). Temporal relationship between V1V2 variation, macrophage replication, and coreceptor adaptation during HIV-1 disease progression. AIDS 16: 1887–1898.
Meucci O, Fatatis A, Simen AA, Bushell TJ, Gray PW, Miller RJ (1998). Chemokines regulate hippocampal neuronal signaling and gp120 neurotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 14500–14505.
Ohagen A, Ghosh S, He J, Huang K, Chen Y, Yuan M, Osathanondh R, Gartner S, Shi B, Shaw G, Gabuzda D (1999). Apoptosis induced by infection of primary brain cultures with diverse human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates: evidence for a role of the envelope. J Virol 73: 897–906.
Pang S, Vinters HV, Akashi T, O’Brien WA, Chen ISY (1991). HIV-1 env sequence variation in brain tissue of patients with AIDS-related neurologic disease. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 4: 1082–1092.
Pleasure SJ, Page C, Lee VM-Y (1992). Pure, postmitotic, polarized human neurons derived from NTera 2 cells provide a system for expressing exogenous proteins in terminally differentiated neurons. J Neurosci 12: 1802–1815.
Rana S, Besson G, Cook DG, Rucker J, Smyth RJ, Yi Y, Turner JD, Guo H-H, Du J-G, Peiper SC, Lavi E, Samson M, Libert F, Liesnard C, Vassart G, Doms RW, Parmentier M, Collman RG (1997). Role of CCR5 in infection of primary macrophages and lymphocytes by M-tropic strains of HIV: Resistance to patient-derived and prototype isolates resulting from the Δccr5 mutation. J Virol 71: 3219–3227.
Rizzuto CD, Wyatt R, Hernandez-Ramos N, Sun Y, Kwong PD, Hendrickson WA, Sodroski J (1998). A conserved HIV gp120 glycoprotein structure involved in chemokine receptor binding. Science 280: 1949–1953.
Simmons G, Reeves JD, McKnight A, Dejucq N, Hibbitts S, Power CA, Aarons E, Schols D, De Clercq E, Proudfoot AE, Clapham PR (1998). CXCR4 as a functional coreceptor for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of primary macrophages. J Virol 72: 8453–8457.
Singh A, Besson G, Mobasher A, Collman RG (1999). Patterns of chemokine receptor fusion cofactor utilization by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 variants from the lungs and blood. J Virol 73: 6680–6690.
Vallat AV, de Girolami U, He JL, Mhashilkar A, Marasco W, Shi B, Gray F, Bell J, Keohane C, Smith TW, Gabuzda D (1998). Localization of HIV-1 co-receptors CCR5 and CXCR4 in the brain of children with AIDS. Am J Pathol 152: 167–178.
Verani A, Pesenti E, Polo S, Tresoldi E, Scarlatti G, Lusso P, Siccardi AG, Vercelli D (1998). CXCR4 is a functional coreceptor for infection of human macrophages by CXCR4-dependent primary HIV-1 isolates. J Immunol 161: 2084–2088.
Westmoreland SV, Rottman JB, Williams KC, Lackner AA, Sasseville VG (1998). Chemokine receptor expression on resident and inflammatory cells in the brain of macaques with simian immunodeficiency virus encephalitis. Am J Pathol 152: 659–665.
Xiong HG, Zeng YC, Zheng JL, Thylin M, Gendelman HE (1999). Soluble HIV-1 infected macrophage secretory products mediate blockade of long-term potentiation: a mechanism for cognitive dysfunction in HIV-1-associated dementia. J NeuroVirol 5: 519–528.
Yi Y, Isaacs SN, Williams DA, Frank I, Schols D, De Clercq E, Kolson DL, Collman RG (1999). Role of CXCR4 in cell-cell fusion and infection of monocytederived macrophages by primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) strains: two distinct mechanisms of HIV-1 dual tropism. J Virol 73: 7117–7125.
Yi Y, Rana S, Turner JD, Gaddis N, Collman RG (1998). CXCR-4 is expressed by primary macrophages and supports CCR5-independent infection by dual-tropic but not T-tropic isolates of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol 72: 772–779.
Younkin DP, Tang C-M, Hardy M, Reddy UR, Shi Q-Y, Pleasure SJ, Lee VM-Y, Pleasure D (1993). Inducible expression of neuronal glutamate receptor channels in the NT2 human cell line. Neurobiology 90: 2174–2178.
Zheng J, Ghorpade A, Niemann D, Cotter RL, Thylin MR, Epstein L, Swartz JM, Shepard RB, Liu X, Nukuna A, Gendelman HE (1999a). Lymphotropic virions affect chemokine receptor-mediated neural signaling and apoptosis: implications for human immunodeficiency virus type 1-associated dementia. J Virol 73: 8256–8267.
Zheng J, Thylin MR, Ghorpade A, Xiong H, Persidsky Y, Cotter R, Niemann D, Che M, Zeng YC, Gelbard HA, Shepard RB, Swartz JM, Gendelman HE (1999b). Intracellular CXCR4 signaling, neuronal apoptosis and neuropathogenic mechanisms of HIV-1-associated dementia. J Neuroimmunol 98: 185–200.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by NIH grants to R.G.C. and D.L.K.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, Y., Chen, W., Frank, I. et al. An unusual syncytia-inducing human immunodeficiency virus type 1 primary isolate from the central nervous system that is restricted to CXCR4, replicates efficiently in macrophages, and induces neuronal apoptosis. Journal of NeuroVirology 9, 432–441 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1080/13550280390218706
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/13550280390218706