Abstract
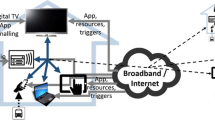
Despite the commercial onslaught of multipurpose portable devices such as integrated mobile phone-PDA combos, the need for multiple devices, with each device performing its own pre-defined and specialized function still exists today. The new generation of internet users has been expeditious in imbibing the new generation of divergent devices for their varying needs—cell phones for voice communication, pagers for text messaging and PDAs for notes. Content sources today assume that the end-device used to retrieve the content has certain minimum pre-defined capabilities. The architecture presented in this paper explores a new realm of content delivery where all the devices in a user's neighborhood of devices are united as a single entity for content delivery. This solution exploits the characteristic capabilities of these individual devices to render the retrieved content for the user; or in cases where the target devices are limited in capabilities, modifies the content to suite the capabilities of the device. A comprehensive description of the testbed we have built based on this architecture is also described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Anerousis et al., “TOPS: An architecture for telephony over packet networks,” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications (JSAC), Vol. 17,No. 1, pp. 91–108, 1999.
G. Appenzeller et al., “The mobile people architecture,” Technical Report CSL-TR–99–777, 1999.
P. Bahl and V. Padmanabhan, “RADAR: An in-building RF based user location and tracking system,” IEEE INFOCOM 2000, March 2000.
G. Banavar, J. Beck, and E. Gluzberg, “Challenges: An application model for pervasive computing,” in ACM/IEEE International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (MOBICOM 2000), Aug. 2000.
A. Beck and M. Hoffman, http://www.ietf-opes.org/documents/draft-beck-opes-irml-02.txt
J. Elson and A. Cerpa, “Internet content adaptation protocol,” IETF Draft, http://www.ietf-opes.org/documents/draft-elson-opes-icap-02.txt
S.D. Gribble et al., “The Ninja architecture for robust internet-scale systems and services,” Computer Networks, Vol. 35,No. 4, 2001.
A. Haneef and A. Ganz, “Adaptive media for divergent computing student environments,” Frontiers in Education (FIE 2002), Nov. 2002.
A. Haneef, “An adaptive multimedia content delivery middleware for mobile multi-device neighborhoods”, Masters Thesis, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Massachusetts Amherst, Sept. 2002.
B. Johanson, S. Ponnekanti, C. Sengupta, and A. Fox, “Multibrowsing: Moving web content across multiple displays,” Proceedings of Ubicomp 2001, Sep. 2001.
C. Magerkurth and T. Prante, “Towards a unifying approach to mobile computing,” SIGGROUP Bulletin, Vol. 22,No.1, pp. 16–18, 2001.
S. Marti, “Active messenger: Email filtering and mobile delivery,” Master's Thesis, MIT Media Laboratory, Speech Interface Group.
Motorola, “Motorola iRadio telematics system: Driving innovation. Revolutionizing in-car infotainment,” http://www.motorola.com/ies/telematics/htmls/ iradio/index.html
Multimedia Networks Laboratory, University of Massachusetts, Amherst, “ANMoLe HomePage,” http://dvd1.ecs.umass.edu/anmole/
J.P. Mysore and V. Vasudevan, “A reconfigurable stream orchestration mechanism for mobile users,” International Conference on Mobile Data Management (MDM 2002), Jan. 2002.
OPES BOF, http://www.ietf-opes.org/
T. Phan, K. Xu, R. Guy, and R. Bagrodia, “Handoff of application sessions across time and space,” IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC 2001), June 2001.
J. Rekimoto, “A multiple device approach for supporting whiteboard-based interactions”, in ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI '98), April 1998.
N.A. Streitz, “i-LAND: An interactive landscape for creativitiy and innovation,” in ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI '99), May 1999.
Sun Microsystems, “Free TTS 1.1—A speech synthesizer written entirely in the Java programming language,” http://freetts.sourceforge.net/docs/index.php
Tomlinson et al., “Extensible proxy services framework,” Internet Draft, http://www.ietf-opes. org/documents/draft-tomlinson-epsfw-00.txt
W3C, “Composite Capabilities/Preferences Profile Working Group Public Home Page,” http://www.w3.org/Mobile/CCPP/.
W3C, “Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) 1.1,” http://www.w3.org/TR/SOAP/
H. Wang et al. “ICEBERG: An internet-core network architecture for integrated communications,” IEEE Personal Communications: Special Issue on IP-based Mobile Telecommunication Networks, 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haneef, A.M., Ganz, A. ANMoLe—An Adaptive Multimedia Content Delivery Middleware Architecture for Heterogeneous Mobile Multi-Device Neighborhoods. Multimedia Tools and Applications 22, 171–186 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MTAP.0000011933.21474.96
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:MTAP.0000011933.21474.96