Abstract
Purpose : To use computer-controlled, multilevel embryo morphology analysis to quantify the reduction in cytoplasmic volume from the zygote stage to the combined volume of the individual blastomeres as an expression for the degree of fragmentation.
Methods : Zygotes and their corresponding embryos from patients referred to ICSI treatment were analyzed. Sequences of digital images were taken focussing at 5-μm intervals through the zygotes and embryos. Assessment of cytoplasmic volumes and fragmentation were based on these sequences.
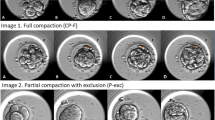
Results : The mean cytoplasmic reduction of the embryos were significant linear increasing with increasing degree of fragmentation assessed by traditional evaluation (P<0.001). Embryos scored to be highly fragmented had on average a cytoplasmic reduction of 63% larger than embryos assessed to have no fragmentation. In total, 68% of the embryos had a cytoplasmic reduction lying within their allocated fragmentation group.
Conclusion : Assessment of embryonic fragmentation based on computer-controlled, multilevel embryo analysis of the blastomere volumes expressed in relation to the volume of the preceding zygote may allow a more precise and standardized evaluation of fragmentation than the traditional fragmentation assessment.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Puissant F, Van Rysselberge M, Barlow P, Deweze J, Leroy F: Embryo scoring as a prognostic tool in IVF treatment. Hum Reprod 1987;2:705–708
Schulman A, Ben-Num I, Gethler Y, Kaneti H, Shilon M, Beyth Y: Relationship between embryo morphology and implanta-tion rate after in vitro fertilization treatment in conception cy-cles. Fertil Steril 1993;60:123–126
Giorgetti C, Terriou P, Auquier P, Hans E, Spach JL, Salzmann J, Roulier R: Embryo score to predict implantation after in-vitro fertilization: Based on 957 single embryo transfers. Hum Reprod 1995;10:2427–2431
Van Royen E, Mangelschots K, De Neubourg D, Valkenburg M, Van de Meerssche M, Ryckaert G, Eestermans W, Gerris J: Characterization of top quality embryo, a step towards single-embryo transfer. Hum Reprod 1999;14:2345–2349
Ziebe S, Lundin K, Loft A, Bergh C, Nyboe Andersen A, Selleskog U, Grøndahl C, Arce J-A: Embryo morphol-ogy and total chromosomal constitution for chromosome 13,16,18,21,22,X and Y after 3 days of culture of 144 randomly selected donated human oocytes. Hum Reprod 2003;18:2575–2581
Hill GA, Freeman M, Bastias MC, Rogers BJ, Herbert CM III, Osteens KG, Wentz AC: The influence of oocyte maturity and embryo quality on pregnancy rate in a program for in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer. Fertil Steril 1989;52:801–806
Erenus M, Zouves C, Rajamahendran P, Leung S, Fluker M, Gomel V: The effect of embryo quality on subsequent preg-nancy rates after in vitro fertilization. Fertil Steril 1991;56:707–710
Ziebe S, Petersen K, Lindenberg S, Andersen A-G, Gabrielsen A, Nyboe Andersen A: Embryo morphology or cleavage stage: How to select the best embryo for transfer after in vitro fertil-ization. Hum Reprod 1997;12:1545–1549
Steer CV, Mills CL, Tan SL, Campbell S, Edwards RG: The cumulative embryo score: A predictive embryo scoring tech-nique to select the optimal number of embryos to transfer in an in-vitro fertilization and transfer programme. Hum Reprod 1992;7:117–119
Ebner T, Yaman C, Moser M, Sommergruber M, Polz W, Tews G: Embryo fragmentation in vitro and its impact on treatment pregnancy outcome. Fertil Steril 2001;76:281–285
Roux C, Joanne C, Agnani G, Fromm M, Clavequin MC, Bresson JL: Morphometric parameters of living human in-vitro fertilization embryos; importance of asynchronous divi-sion process. Hum Reprod 1995;10:1201–1207
Goyanes VJ, Ron-Corzo A, Costas E, Maneiro E: Morphome-tric categorization of the human oocyte and early conceptus. Hum Reprod 1990;5:613–618
Hardy K, Winston RML, Handyside AH: Binucleate blas-tomeres in preimplantation human embryos in vitro: Failure of cytokinesis during early cleavage. J Rep Fertil 1993;98:549–558
Hnida C, Engenheiro E, Ziebe S: Computer controlled multi-level morphometric analysis of blastomere size as biomarker of fragmentation and multinuclearity in human embryos. Hum Reprod 2004;19:288–293
Johansson M, Hardarson T, Lundin K: There is a cutoff limit in diameter between a blastomere and a small anucleate frag-ment. J Assist Reprod Genet 2003;20:309–313
Alikani M, Cohen J, Tomkin G, Garrisi GJ, Mack C, Scott RT: Human embryo fragmentation in vitro and its implications for pregnancy and implantation. Fertil Steril 1999;71:836–842
Van Blerkom J, Davis P, Alexander S: A microscopic and biochemical study of fragmentation phenotypes in stage-appropriate human embryos. Hum Reprod 2001;16:719–729
Hardarson T, Lofman C, Coull G, Sjogren A, Hamberger L, Edwards RG: Internalization of cellular fragments in a hu-man embryo: Time-lapse recordings. Reprod Biomed Online 2002;5:36–38
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hnida, C., Ziebe, S. Total Cytoplasmic Volume as Biomarker of Fragmentation in Human Embryos. J Assist Reprod Genet 21, 335–340 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JARG.0000045473.80338.57
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JARG.0000045473.80338.57