Abstract
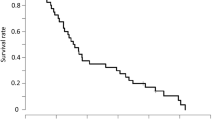
Purpose: The purpose of this phase II multi-institutional study was to define the efficacy and toxicity of infusional 5-FU in combination with PALA and leucovorin in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Patients and methods: Patients were required to have histologically confirmed colorectal cancer with distant metastases. The treatment regimen consisted of 5-FU 2600 mg/m2 as a 24-hours continuous infusion given once a week, concurrently with leucovorin (LV) at 500 mg/m2 as a 24-hour continuous infusion. PALA was administered 24 hours prior to 5-FU/LV at a dose of 250 mg/m2 iv over 15 minutes weekly. Patients were continued on the assigned treatment regimen until progression of disease, unacceptable toxicity, or the patient declined further therapy. Results: This study accrued 28 patients and all were eligible and evaluable for toxicity. Four patients had inadequate assessment of response and are considered non-responders. There was one complete response and five partial responses for an overall response rate of 6/28 or 21% (95% confidence interval 8–41%). Estimated median survival was 17.4 months (95% confidence interval 13.3–20.5 months). One patient died of a treatment related infection. This patient also had grade 4 diarrhea and vomiting. Conclusion: The combination of 5-FU, leucovorin, and PALA in the doses and schedule used here, produces a response rate similar to other modulated schedules of 5-FU with similar survival and toxicity profiles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heidelberger C, Chaudhuri NK, Danneberg P, Mooren D, Griesbach L, Duschinsky R, Schnitzer RJ, Pleven E, Scheiner J: Fluorinated pyrimidines: A new class of tumor inhibitory compounds. Nature 179: 663–666, 1957
Martin DS, Kemeny NE: Modulation of fluorouracil by N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-asparate: A review. Seminars in Oncology 19: (2) (Suppl 3): 49–55, 1992
Ullman B, Lee M, Martin DW Jr, Santi DV: Cytotoxicity of 5-fluoro-2_-deoxyuridine: Requirement for reduced folate cofactors and antagonism by methotrexate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75: 980–983, 1978
Evans RM, Laskin JD, Hakala MT: Effect of excess folates and deoxyinosine on the activity and site of action of 5-fluorouracil. Cancer Res 41: 3288–3295, 1981
Houghton JA, Maroda SJ, Jr, Philips JO, Houghton PJ: Biochemical determinants of responsiveness to 5-fluorouracil and its derivatives in xenografts of human colorectal adenocarcinomas in mice. Cancer Res. 41: 144–149, 1981
Berger SH, HakalaMT: Relationship of dUMP and free FdUMP pools to inhibition of thymidylate synthetase by 5-fluorouracil. Mol Pharmacol 25: 303–309, 1984
Advanced Colorectal Cancer Meta-Analysis Project. Modulation of fluorouracil by leucovorin in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: Evidence in terms of response rate. Journal of Clinical Oncology 10: 896–903, 1992
Piedbois P, Michiels S, for the Meta-Analysis Group in Cancer: Survival benefit of 5FU/LV over 5FU bolus in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: An updated meta-analysis based on 2,751 patients. Proceedings ASCO 22: 294, #1180 2003 (abstract)
Ardalan B, Glazer RI, Kensler TW, Jayaram HN, Pham TV, MacDonald JS, Cooney DA: Synergistic effect of 5-fluorouracil and N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-asparate on cell growth and ribonucleic acid synthesis in a human mammary carcinoma. Biochem Pharmacol 30: 2045–2049, 1981
Spiegelman S, Sawyer R, Nayak R, Ritzi E, Stolfi R, Martin D: Improving the anti-tumor activity of 5-fluorouracil by increasing its incorporation into RNA via metabolic modulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77: 4966–4970, 1980
Martin DS, Stolfi RL, Sawyer RC, Spiegelman S, Casper ES, Young CW: Therapeutic utility of utilizing low doses of N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartic acid in combination with 5-Fluorouracil: A murine study with clinical relevance. Cancer Res 43: 2317–2321, 1983
Peters GJ, Laurensse E, Lankelma J, LeyvaA, PinedoHM:Separation of several 5-fluorouracil metabolites in various melanoma cell lines. Evidence for the synthesis of 5-fluorouracilnucleotide sugars. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncology 20: 1425–1431, 1984
Major PP, Egan EM, Sargent L, Kufe DW: Modulation of 5-FU metabolism in human MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol 8: 87–91, 1982
Grem JL. King SA, O'Dwyer PJ, Leyland-Jones B: Biochemistry and clinical activity of N-(Phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate: A review. Cancer Research 48: 4441–4454, 1988
Grem JL, McAtee N, Steinberg SM, Hamilton JM, Murphy RF, Drake J, Chisena T, Balis F, Cysyk R, Arbuck SG, Sorensen JM, Chen AP, Goldstein L, Jordan E, Setser A, Goldspiel B, DeCarvalho M, Allegra CJ: A phase I study of continuous infusion 5-fluorouracil plus calcium leucovorin in combination with N-(Phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate in metastatic gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Research 53: 4828–4836, 1993
Myers CE, Diasio R, Eliot HM, Chabner BA: Pharmacokinetics of the fluoropyrimidines: Implications for their clinical use. Cancer Treatment Rev 3: 175–183, 1976
Fraile RJ, Baker LH, Buroker TR, Horwitz J, Vaitkevicius VK: Pharmacokinetics of 5-fluorouracil administered orally, by rapid intravenous and by slow infusion. Cancer Res 40: 2223–2228, 1980
Meta-analysis Group in Cancer: Efficacy of intravenous continuous infusion of fluorouracil compared with bolus administration in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 16: 301–308, 1998
Bedikian AY, Stroehlein JR, Karlin DA, Bennetts RW, Bodey GP, Valdivieso M: Chemotherapy for colorectal cancer with a combination of PALA and 5-FU. Cancer Treat Rep 65: 747–753, 1981
Weiss GR, Ervin TJ, Meshad MW, Kufe DW: Phase II trial of combination therapy with continuous-infusion PALAand bolusinjection 5-FU. Cancer Treat Rep 66: 299–303, 1982
Ardalan B, Jamin D, Jayaram HN, Presant CA: Phase I study of continuous-infusion PALA and 5-FU. Cancer Treat Rep 68: 531–534, 1984
Erlichman C, Donehower RC, Speyer JL, Klecker R, Chabner BA: Phase I-Phase II trial of N-phosphonacetyl-L-aspartic acid given by intravenous infusion and 5-fluorouracil given by bolus injection. J Natl Cancer Inst 68: 227–231, 1982
Muggia FM, Camacho FJ, Kaplan BH, Green MD, Greenwald ES, Wernz JC, Engstrom PF: Weekly 5-fluorouracil combined with PALA: Toxic and therapeutic effects in colorectal cancer. Cancer Treat Rep 71: 253–256, 1987
Ardalan B, Singh G, Silberman H: A randomized phase I and II study of short-term infusion of high-dose fluorouracil with or without N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartic acid in patients with advanced pancreatic and colorectal cancers. J Clin Oncol 6: 1053–1058, 1988
O'Dwyer PJ, Paul AR, Walczak J, Weiner LM, Litwin S, Comis RL: Phase II study of biochemical modulation of fluorouracil by low-dose PALA in patients with colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 8: 1497–1503, 1990
Leichman CG, Fleming TR, Muggia FM, Tangen CM, Ardalan B, DoroshowJH, Meyers FJ, HolcombeRF, Weiss GR, Mangalik A, Macdonald JS: Phase II study of fluoruracil and its modulation in advanced colorectal cancer: A Southwest Oncology Group Study. J Clin Oncol 13: 1303–1311, 1995
Green S, Weiss GR: Southwest Oncology Group standard response criteria, endpoint definitions and toxicity criteria. Invest New Drugs 10: 239–253, 1992
Kensler TW, Erlichman C, Jayaram HN, Tyagi AK, Ardalan B, Cooney DA: Peripheral leucocytes as indicators of the enzymatic effects of N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartic acid (PALA) on human L-aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase) activity. Cancer Treat Rep 64: 967–973, 1980
Advanced Colorectal Cancer Meta-analysis Project: Metaanalysis of randomized trials testing the biochemical modulation of fluorouracil by methotrexate in metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin Oncol 12: 960–969, 1994
Corfu-A Study Group: Phase III randomized study of two fluorouracil combinations with either interferon alfa-2a or leucovorin for advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 13: 921–928, 1995
Hill M, Norman A, Cunningham D, Findlay M, Nicolson V, Hill A, Iveson A, Evans C, Joffe J, Nicolson M, Hickish T: Royal Marsden phase III trial of fluorouracil with or without interferon alfa-2b in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 13: 1297–1302, 1995
Wolmark N, Bryant J, Smith R, Grem J, Allegra C, Hyams D, Atkins J, Dimitrov N, Oishi R, Prager D, Fehrenbacher L, Romond E, Colangelo L, Fisher B: Adjuvant 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin with or without interferon alfa-2a in colon carcinoma: National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project protocol C-05. J Natl Cancer Inst 90: 1810–1816, 1998
Royce ME, McGarry W, Bready B, Dakhil SR, Belt RJ, Goodwin JW, Gray R, Hoff PM, Winn R, Pazdur R: Sequential biochemical modulation of fluorouracil with folinic acid, N-phosphonacetyl-L-aspartic acid, and interferon alfa-2a in advanvced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 17: 3276–3282, 1999
Edler D, Glimelius B, Hallstrom M, Jakobsen A, Johnston PG, Magnusson I, Ragnhammar P, Blomgren H: Thymidylate synthase expression in colorectal cancer: A prognostic and predictive marker of benefit from adjuvant fluorouracil-based chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 20: 1721–1728, 2002
Johnston PG, Fisher ER, Rockette HE, Fisher B, Wolmark N, Drake JC, Chabner BA, Allegra CJ: The role of thymidylate synthase expression in prognosis and outcome of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with rectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 12: 2640–2647, 1994
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Whitehead, R.P., Benedetti, J.K., Abbruzzese, J.L. et al. A phase II pilot study of high-dose 24-hour continuous infusion of 5-FU and leucovorin and low-dose PALA for patients with colorectal cancer: A Southwest Oncology Group study. Invest New Drugs 22, 467–473 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:DRUG.0000036689.28596.c6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:DRUG.0000036689.28596.c6