Abstract
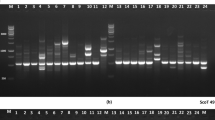
Diversity in 28 accessions representing 12 species of the genus, Cajanus arranged in 6 sections including 5 accessions of the cultivated species, C. cajan, and 4 species of the genus Rhyncosia available in the germplasm collection at ICRISAT was assessed using RFLP with maize mtDNA probes. Cluster analysis of the Southern blot hybridization data with 3 restriction enzymes – 3 probe combinations placed the genus Rhyncosia in a major group well separated from all the species belonging to the genus Cajanus. Within the genus Cajanus, the 4 accessions of C. platycarpus belonging to section Rhynchosoides formed a separate group in contrast to those in other sections of pigeonpea. In the section, Cajanus all the 5 accessions of C. cajan were grouped together and C. cajanifolius belonging to the same section was in a subgroup by itself closer to the main group. The four accessions of C. scarabaeoides, were together and the other species belonging to section Cantharospermum were in different subgroups. The intra-specific variation was seen even within accessions of certain pigeonpea wild species such as C. scarabaeoides, C. platycarpus, C. acutifolius, and even the cultivated species of C. cajan. This study suggests that RFLP of mtDNA can be used for the diversity analysis of pigeonpea and it gives some indications on the maternal lineage among the species. The variations in the mitochondrial DNA hybridization patterns also suggest the extensive rearrangement of the organelle genome among the Cajanus species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, F., P.M. Gur & A.E. Slinkard, 1992. Isozyme polymorphism and phylogenetic interpretations in the genus Cicer L. Theor Appl Genet 83: 620–627.
Close, P.S., R.C. Shoemaker & P. Keim, 1989. Distribution of restriction site polymorphism within the chloroplast genome of the genus Glycine subgenus Soja. Theor Appl Genet 77: 768–776.
Deu, M.P., Hamon, J. Chantereau, P. Dufour, A. D'hont & C. Lanaud, 1995. Mitochondrial DNA diversity in wild and cultivated sorghum. Genome 38: 635–645.
Devos, K.M. & M.D. Gale, 1992. The use of random amplified polymorphic DNA markers in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 84: 567–572.
Dewey, R.E., C.S. Levings III & D.H. Timothy, 1985. Nucleotide sequence of ATPase subunit 6 gene of maize mitochondria. Plant Physiol 79: 914–919.
Ennes R.A., W.T. Sinclair, X-S. Hu & A. Langdon, 1999. Using organelle markers to elucidate the history, ecology and evolution of plant populations. In: P.M. Hollingsworth, R.M. Bateman & R.J. Gornall (Eds.), Molecular Systematics and Plant Evolution, pp. 1–19. Taylor & Francis, London.
Feinburg, A.P. & B. Vogelstein, 1983. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 137: 266–267.
Gawel, N.J., R.L. Jarret & A. Whittemore, 1992. Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP)-based phylogenetic analysis of Musa. Theor Appl Genet 84: 286–290.
Gonzalez, J.M. & E. Ferrer, 1993. Random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis in Hordeum species. Genome 36: 1029–1031.
Grabau, E.A., W.H. Davis, N.D. Phelps & B.G. Gengenbach, 1992. Classification of soybean cultivars based on mitochondrial restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Crop Sci 32: 271–274.
Harris, S.A., 1999. RAPDs in sytematics - a useful methodology? In: P.M. Hollingsworth, R.M. Bateman and R.J. Gornall (Eds.), Molecular Systematics and Plant Evolution, pp. 211–228. Taylor & Francis, London.
Hershkovitz, M.A., E.A. Zimmer & W.J. Hahn, 1999, Ribosomal DNA sequences and angiosperm systematics. In: P.M. Hollingsworth, R.M. Bateman & R.J. Gornall (Eds.), Molecular Systematics and Plant Evolution, pp. 268–326. Taylor & Francis, London.
Hongtrakul, V., G.M. Huestis & S.J. Knap, 1997. Amplified fragment length polymorphisms as tool for DNA fingerprinting sunflower germplasm: genetic diversity among oilseed inbred lines. Theor Appl Genet 95: 400–407.
Isaac, P.G., V.P. Jones & C.J. Leaver, 1985. The maize cytochrome c oxidase subunit I gene: sequence, expression and rearrangement in cytoplasmic male-sterile plants. EMBO J 4: 1617–1623.
Jain, A., S. Bhatia, S.S. Banga, S. Prakash & M. Lakshmikumaran, 1994. Potential use of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) technique to study the genetic diversity in Indian mustard (Brassica juncea) and its relationship to heterosis. Theor Appl Genet: 116–122.
Jarret, R.L., N. Gawel & A. Whittemore, 1992. Phylogenetic relationships of the sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.] J Am Soc Hort Sci 117: 633–637.
Jena, K.K. & G.C. Kochert, 1991. Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of CCDD genome species of the genus Oryza L. Plant Mol Biol 16: 831–839.
Krishna, T.G. & L.J. Reddy, 1982. Species affinities between Cajanus cajan and some Atylosia species based on esterase isozymes. Euphytica 31: 709–713.
Ladizinsky, G. & A. Hamel, 1980. Seed protein profiles of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan) and some Atylosia species. Euphytica 29: 313–317.
Levinson, G. & G.A. Gutman, 1987. Slipped-strand mispairing: a major mechanism for DNA sequence evolution. Molec Biol Evol 4: 203–221.
Mackill, D.J., 1995. Classifying Japonica rice cultivars with RAPD markers. Crop Sci 35: 889–894.
McGregor C.E., C.A. Lambert, M.M. Greyling, J.H. Louw & L. Warnich, 2000. A comparative assessment of DNA fingerprinting techniques (RAPD, ISSR, AFLP and SSR) in tetraploid potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) germplasm. Euphytica 113: 135–144.
Miller, J.C. & S.D. Tanksley, 1990. RFLP analysis of phylogenetic relationships and genetic variation in the genus Lycopersicon. Theor Appl Genet 80: 437–448.
Moeykens, C.A., S.A. Mackenzie & R.C. Shoemaker, 1995. Mitochondrial genome diversity in soybean: repeats and rearrangements. Plant Mol Biol 29: 245–254.
Nadimpalli, R.G., R.L. Jarret, S.C. Phatak & G. Kochert, 1993. Phylogenetic relationships of the pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan) based on nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Genome 36: 216–223.
Nei, M & W.H. Li, 1979. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 76: 5269–5273.
Nene, Y.L. & V.K. Sheila, 1990. Pigeonpea: Geography and importance. In: Y.L. Nene, S.D. Hall & V.K. Sheila (Eds.), The Pigeonpea, pp. 1-15. C.A.B. International.
Provan, J., N. Saranzo, N.J. Wison, J.W. McNicol, M. Margante & W. Powel, 1999. The use of uniparentally inherited simple sequence repeat markers in plant population studies and systematics. In: P.M. Hollingsworth, R.M. Bateman & R.J. Gornall (Eds.), Molecular Systematics and Plant Evolution, pp. 35–50. Taylor and Francis, London.
Pundir, R.P.S. & R.B. Singh, 1985. Cytogenetics of F1 hybrids between Cajanus and Atylosia species and its phylogenetic implications. Theor Appl Genet 71: 216–220.
Ratnaparkhe, M.B., V.S. Gupta, M.R. Ven Murthy & P.K. Ranjekar, 1995. Genetic fingerprinting of pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.] and its wild relatives using RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 91: 893–898.
Reddy, L.J. & D.N. De, 1983. Cyto-morphological studies in Cajanus cajan ?Atylosia lineata. Ind J Genet 43: 96–103.
Reddy, L.J., J.M. Green & D. Sharma, 1981. Genetics of Cajanus cajan (L.) Mills sp. ?Atylosia spp. In: Proceedings of the International workshop on Pigeonpeas, 15-19 Dec 1980. ICRISAT Center, Vol 2, pp. 39–50. Patancheru, AP, India.
Singh, A.K., S. Sivaramakrishnan, M.H. Mengesha & C.D. Ramaiah, 1991. Phylogenetic relations in section Arachis based on seed protein profile. Theor Appl Genet 82: 593–597.
Sivaramakrishnan, S., K. Seetha, A. Nageshwar Rao & Laxman Singh, 1997. RFLP analysis of Cytoplasmic male-sterile lines of pigeonpea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.] developed by interspecific crosses. Euphytica 93: 307–312.
Smartt, J., 1990. Grain Legumes: Evolution and Genetic Resources, pp. 278–293. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Svitashev, S., T. Bryngelsson, A. Vershinin, C. Pedersen, T. Sall & R. von Bothmer, 1994. Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Hordeum using repetitive DNA sequences. Theor Appl Genet 89: 801–810.
Tozuka, A., H. Fukushi, T. Hirata, M. Ohara, A. Kanazawa, T. Mikami, J. Abe & Y. Shimamoto, 1998. Composite and clinal distribution of Glycine soja in Japan revealed by RFLP analysis of mitochondrial DNA. Theor Appl Genet 96: 170–176.
van der Maesen, L.J.G., 1986. Cajanus D.C. and Atylosia W. & A. (Leguminosae). Agric. University of Wageningen Papers 85-4 (1985). Agricultural University. Wageningen, The Netherlands, 225 pp.
van der Maesen, L.J.G., 1990. Pigeonpea: origin, history, evolution, and taxonomy. In: Y.L. Nene, S.D. Hall & V.K. Sheila (Eds.), The Pigeonpea, pp. 15-46. C.A.B. International.
Wang, G., R. Mahalingam & H.T. Knap, 1998. (C-A) and (GA) anchored simple sequence repeats (ASSRs) generated polymorphism in soybean, Glycine max (L.) Merr. Theor Appl Genet 96: 1086–1096.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sivaramakrishnan, S., Kannan, S. & Reddy, L. Diversity in selected wild and cultivated species of pigeonpea using RFLP of mtDNA. Euphytica 125, 21–28 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015759318497
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015759318497