Abstract
Purpose : Klinefelter syndrome is the most common chromosomal aberration among azoospermic men. We wanted to compare testicular echogenicity and intratesticular arterial blood in men with this syndrome versus men with normal sperm parameters.
Methods : Testicular sonography including Doppler imaging, was performed as part of the infertility workup in 26 men with Klinefelter syndrome as well as in 26 men with normal sperm parameters.
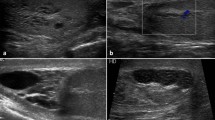
Results : In men with Klinefelter syndrome, sonography of the testicular parenchyma revealed a heterogenous irregular pattern with spread hyper- and hypoechoic foci. Doppler sonography resulted in waveforms of high impedance patterns, reflecting intratesticular blood flow of a high resistance. In men with normal sperm parameters testicular echogenicity was of an almost homogenous regular pattern. In these men, intratesticular blood flow typically exhibited a pattern of low vascular resistance.
Conclusions : The study demonstrates that testicular echogenicity as well as intratesticular blood flow are different in men with Klinefelter syndrome versus men with normal sperm parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Nielsen J, Wohlert M: Chromosome abnormalities found among 34910 newborn children: Results from a 13-year incidence study in Århus, Denmark. Hum Genet 1991;70: 81–83
Guichaoua MR, Delafontaine D, Noel IB, Luciani JM: L'infertilitè masculine d’origine chromosomique. Contracept Fertil Sex 1993;21:113–121
Tournaye H, Staessen C, Liebaers I, Van Assche E, Devroy P, Bonduelle M, Van Steirteghem A: Testicular sperm recovery in nine 47,XXY Klinefelter patients. Hum Reprod 1996;11:1644– 1649
Bader TR, Kammerhuber F, Herneth AM: Testicular blood flow in boys as assessed at color Doppler and power Doppler sonography. Radiology 1997;202:559–564
Foresta C, Garolla A, Bettella A, Ferlin A, Rossato M, Candiani F: Doppler ultrasound of the testis in azoospermic subjects as a parameter of testicular function. Hum Reprod 1998;13:3090–3093
Menkveld R, Kruger TF: (1990) Basic semen analysis. In Human Spermatozoa in Assisted Reproduction, Acosta AA, Kruger TF, Swanson RJ, Van Zyl JA, Ackerman SB, Menkveld R (eds), Baltimore, Williams andWilkins, pp 68–84
World Health Organization: Laboratory Manual for the Examination of Human Semen and Sperm-Cervical Mucus Interaction, 3rd edn, Melbourne, Australia, Cambridge University Press, 1992
Lenz S, Giwercman A, Elsborg A, Cohr KH, Jelnes JE, Carlsen E, Skakkebaek NE: Ultrasonic testicular texture and size in 444 men from the general population: Correlation to semen quality. Eur Urol 1993;24:231–238
Rifkin MD, Kurtz AB, Pasto ME, Goldberg BB: Diagnostic capabilities of high-resolution scrotal ultrasonography: Prospective evaluation. J Ultrasound Med 1985;4:1319
Desai KM, Haworth JM, Gingell JC: Scrotal ultrasound. J R Soc Med 1985;78:710–714
Lenz S: Cancer of the testicle diagnosed by ultrasound and the ultrasonic appearance of the contralateral testicle. Scand J Urol Nephrol 1991;137(Suppl):135–138
Middleton WD, Thorne DA, Melson GL: Color Doppler ultrasound of the normal testis. AJR 1989;152:293–297
Lenz S, Giwercman A, Skakkebæk NE, Bruun E, Frimodt-Moller C: Ultrasound in detection of early neoplasia of the testis. Int J Androl 1987;10:187–190
Swerdlow AJ, Hermon C, Jacobs PA, Alberman E, Beral V, Daker M, Fordyce A, Youings S: Mortality and cancer incidence in persons with numerical sex chromosome abnormalities: A cohort study. Ann Hum Genet 2001;65(Part 2):177– 188
Westlander G, Ekerhovd E, Granberg S, Hanson L, Hanson C, Bergh C: Testicular ultrasonography and extended chromosome analysis in men with nonmosaic Klinefelter syndrome: A prospective study of possible predictive factors for successful sperm recovery. Fertil Steril 2001;75:1102– 1105
Foster RS, Donohue JP: Fertility in testicular cancer patients. AUA Update Series XIV 1995;lesson 19:153–160
London NJM, Smart JG, Kinder RB, Watkin EM, Rees Y, Haley P: Prospective study of routine scrotal ultrasonography in urological practice. Br J Urol 1989;63:416–419
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ekerhovd, E., Westlander, G. Testicular Sonography in Men with Klinefelter Syndrome Shows Irregular Echogenicity and Blood Flow of High Resistance. J Assist Reprod Genet 19, 517–522 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020959818687
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020959818687