Abstract
Purpose: Our purpose was to determine the efficacy of Surfacten, a bovine pulmonary surfactant, on the maturation of in vitro bovine ova.
Methods: We used Surfacten as a supplement to the coculture media both at the onset of coculture and after cleavage in bovine ova had been determined. The controls received no Surfacten.
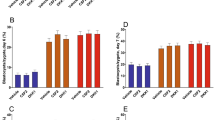
Results: The maturation rate in bovine embryos to the blastocyst stage statistically improved (P < 0.05) in the series in which Surfacten was added to the media at the onset of coculture, compared with the controls and the series in which Surfacten was added after cleavage had been determined.
Conclusions: Surfacten, a commercially available surfactant which is a naturally occurring phospholipid that dramatically increases in the cervical mucus and the ampullaris of the oviduct at or near the time of ovulation, improves the maturation of bovine embryos in vitro by making the coculture medium approach the conditions found in the oviducts.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Osada H, Watanabe Y, Yamada Y, Ueda S, Tsubata K, Takagi S: A histological and electron microscopic evaluation of surfactants in the female genital tract—The structure of SF-phospholipid materials in the normal human fallopian tube. J Clin Electron Microsc 1987;19:665-666
Fujii TK, Osada H, Satoh K: The effects of surfactant in the IVF of cattle. In Proceeding of the 10th World Congress on IVF and Assisted Reproduction, V Gomel, PCK Leung (eds). Bologna, Monduzzi Meditore, 1997, pp 687-690
Bongso A, Hg S-H, Sathananthan H, Lian Ng P, Rauff M, Rahtnam S: Improved quality of human embryos when co-cultured with human ampullary cells. Hum Reprod 1989;4:706-713
Carney EW, Tobback C, Ellington JE, Foote RH: Co-culture of rabbit 2-cell embryos with rabbit oviduct epithelial cells and other somatic cells. Mol Reprod Dev 1990;27:209-215
Yeung WS, Ho PC, Lau EYL, Chan STH: Improved development of human embryos in vitro by a human oviductal cell co-culture system. Hum Reprod 1992;7:1144-1149
Bongso A, Hg S-H, Fong C-Y, Anandakumar C, Marshall B, Edirisinghe R, Rahtnam S: Improved pregnancy rate after transfer of embryos grown in human fallopian tubal cell coculture. Fertil Steril 1992;58:569-574
Eyestone WH, First NL: Co-culture of early cattle embryos to the blastocyst stage with oviductal tissue or in conditioned medium. J Reprod Fertil 1989;85:715-720.
Gandolfi F, Moor M: Stimulation of early embryonic development in sheep by co-culture with oviduct epithelial cells. J Reprod Fertil 1987;81:23-28
Sakkas D, Trounson AO: Co-culture of mouse embryos with oviduct and uterine cells prepared from mice at different days of pseudopregnancy. J Reprod Fertil 1990;90:109-118
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osada, H., Watanabe, Y., Fujii, T.K. et al. Stimulation of Early Embryonic Development in Cattle by Coculture with Surfactant. J Assist Reprod Genet 16, 310–314 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020453932241
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020453932241