Abstract
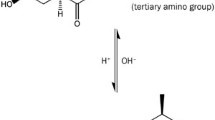
Purpose. To investigate the relation between intestinal effective permeability (Peff) and surface activity of fluvastatin and verapamil.
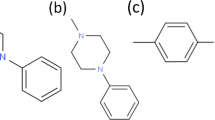
Methods. Peff values were determined for fluvastatin, antipyrine and D-glucose following colon perfusions in the rat in situ. The perfusion solutions differed regarding concentrations of fluvastatin (0-2500 μM) and surface tension (58.9-43.7 mN/m). A cellulose derivative, ethyl-(hydroxyethyl) cellulose (EHEC), was added to lower the surface tension of one of the perfusion solutions. The surface tension of perfusion solutions containing R/S-verapamil (8-814 μM) and R/S-verapamil + chlorpromazine (814 μM + 10 mM) were related to the corresponding Peff values from the literature.
Results. The Peff of fluvastatin correlated inversely (r2 = 0.985, p < 0.05) with the surface tension of the perfusion solutions below the critical micelle concentration (CMC, 1 mM). Decreasing the surface tension with EHEC increased the Peff of fluvastatin by 36% (p < 0.001), but not to the extent anticipated from the correlation between the Peff and the surface tension. EHEC also increased the Peff of antipyrine by 49% (p < 0.01) but not for D-glucose. The Peff of R/S-verapamil correlated inversely with the surface tension (r2 = 0.980, p < 0.001).
Conclusions. The ability of fluvastatin to decrease the surface tension at the membrane surface can partly explain the concentration dependent colonic Peff of fluvastatin. This study shows that the surface activity of the drug molecule itself is an important physicochemical factor that should be taken into consideration when evaluating drug absorption studies performed in vitro or in situ.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. Lindahl, R. Sandström, A.-L. Ungell, and H. Lennernäs. Concentration-and region-dependent intestinal permeability of fluvastatin in the rat. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 50:737–744 (1998).
V. D. Makhey and P. J. Sinko. Regional functional expression of multidrug resistance efflux pumps, Pgp and MRP, in human and rat intestine. Pharm. Res. 14:S–646 (1997).
B. H. Stewart, E. L. Reyner, R. Stern, E. A. Zegarac, R. Boyd, and L. R. Whitfield. Atorvastatin inhibits the P-glycoprotein-mediated secretion of 3H-digoxin in Caco-2 cell monolayers. Pharm. Res. 14:S–671 (1997).
J. Dimitroulakos and H. Yeger. HMG-CoA reductase mediates the biological effects of retinoic acid on human neuroblastoma cells: lovastatin specifically targets P-glycoprotein-expressing cells. Nat. Med. 2:326–33 (1996).
M. Holmberg, C. Sandberg, P. Nygren, and R. Larsson. Effects of lovastatin on a human myeloma cell line: increased sensitivity of a multidrug-resistant subline that expresses the 170 kDa P-glycoprotein. Anticancer Drugs. 5:598–600 (1994).
A. T. Florence. Surfactant interactions with biomembranes and drug absorption. Pure & Appl. Chem. 53:2057–2068 (1981).
E. K. Anderberg, C. Nystrom, and P. Artursson. Epithelial transport of drugs in cell culture. VII: Effects of pharmaceutical surfactant excipients and bile acids on transepithelial permeability in monolayers of human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cells. J. Pharm. Sci. 81:879–87 (1992).
B. J. Aungst, H. Saitoh, D. L. Burcham, S.-M. Huang, S. A. Mousa, and M. A. Hussain. Enhancement of the intestinal absorption of peptides and non-peptides. J. Contr. Rel. 41:19–31 (1996).
T. Lindmark, T. Nikkila, and P. Artursson. Mechanisms of absorption enhancement by medium chain fatty acids in intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cell monolayers. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 275: 958–64 (1995).
T. Lindmark, Y. Kimura, and P. Artursson. Absorption enhancement through intracellular regulation of tight junction permeability by medium chain fatty acids in Caco-2 cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 284:362–9 (1998).
M. Tomita, M. Hayashi, T. Horie, T. Ishizawa, and S. Awazu. Enhancement of colonic drug absorption by the transcellular permeation route. Pharm. Res. 5:786–9 (1988).
M. Shima, K. Yohdoh, M. Yamaguchi, Y. Kimura, S. Adachi, and R. Matsuno. Effects of medium-chain fatty acids and their acylglycerols on the transport of penicillin V across Caco-2 cell monolayers. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 61:1150–5 (1997).
B. Persson, S. Nilsson, and L.-O. Sundelöf. On the characterization principles of some technically important water-soluble nonionic cellulose derivatives. Part II: Surface tension and interaction with a surfactant. Carbohydr. Polym. 29:119–127 (1996).
P. D. Lundin, B. R. Westrom, N. Pantzar, and B. W. Karlsson. Bidirectional small intestinal permeability changes to differentsized molecules after HCl-induced injury in the rat. Dig. Dis. Sci. 42:677–83 (1997).
R. Sandström, A. Karlsson, and H. Lennernäs. The lack of stereoselective P-glycoprotein mediated transport of R/S-verapamil across the rat jejunum. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. In Press (1998).
H. Toreson and B. M. Eriksson. Determination of fluvastatin enantiomers and the racemate in human blood plasma by liquid chromatography and fluorometric detection. J. Chromatogr. A. 729:13–18 (1996).
H. Lennernäs, Ö. Ahrenstedt, R. Hällgren, L. Knutson, M. Ryde, and L. K. Paalzow. Regional jejunal perfusion, a new in vivo approach to study oral drug absorption in man. Pharm. Res. 9:1243–1251 (1992).
I. Komiya, J. Y. Park, A. Kamani, N. F. H. Ho, and W. I. Higuchi. Quantitative mechanistic studies in simultaneous fluid flow and intestinal absorption using steroids as model solutes. Int. J. Pharmaceutics. 4:249–262 (1980).
A. T. Florence and D. Attwood, Physicochemical principles of pharmacy, Macmillan, London, 2nd ed., 1993.
P. M. Seeman and H. S. Bialy. The surface activity of tranquilizers. Biochem. Pharmacol. 12:1181–1191 (1963).
G. S. Retzinger, L. Cohen, S. H. Lau, and F. J. Kezdy. Ionization and surface properties of verapamil and several verapamil analogues. J. Pharm. Sci. 75:976–82 (1986).
J. A. Marqusee and K. A. Dill. Solute partitioning into chain molecule interphases: Monolayers, bilayer membranes, and micelles. J. Chem. Phys. 85:434–444 (1986).
D. M. Woodcock, M. E. Linsenmeyer, G. Chojnowski, A. B. Kriegler, V. Nink, L. K. Webster, and W. H. Sawyer. Reversal of multidrug resistance by surfactants. Br. J. Cancer. 66:62–8 (1992).
S. Drori, G. D. Eytan, and Y. G. Assaraf. Potentiation of anticancer-drug cytotoxicity by multidrug-resistance chemosensitizers involves alterations in membrane fluidity leading to increased membrane permeability. Eur. J. Biochem. 228:1020–9 (1995).
A. Helenius and K. Simons. Solubilization of membranes by detergents. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 415:29–79 (1975).
G. W. Gullikson, W. S. Cline, V. Lorenzsonn, L. Benz, W. A. Olsen, and P. Bass. Effects of anionic surfactants on hamster small intestinal membrane structure and function: relationship to surface activity. Gastroenterology. 73:501–11 (1977).
A. Lindahl, R. Sandström, A.-L. Ungell, B. Abrahamsson, T. W. Knutson, L. Knutson, and H. Lennernäs. Jejunal permeability and hepatic extraction of fluvastatin in humans. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 60:493–503 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindahl, A., Persson, B., Ungell, AL. et al. Surface Activity and Concentration Dependent Intestinal Permeability in the Rat. Pharm Res 16, 97–102 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018879014281
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018879014281