Abstract
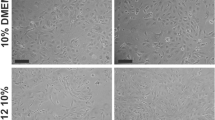
A serum-free medium formulation – TUD-1 – was developed supporting growth of HUVEC in tissue culture. Special features of the basal medium formulation are highly elevated levels of glutamine and serine as well as the inclusion of N-acetylcysteine and phosphoascorbic acid. The cellular mitogenic needs are satisfied by bFGF, VEGF, EGF and liver growth factor. Further hormone supplementation consists of insulin and hydrocortisone. A protocoll for serum-free passage of HUVEC was established for serum-free long-term cultivation of freshly isolated HUVEC for up to 20 cumulative population doublings without significant differences in final cell density compared to controls cultivated with serum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Groot PG, Willems C, Gonsalves MD, van Aken WG and van Mourik JA (1983) The proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells in serum-free medium. Thromb Res 31: 623–634.
Friedl P, Tatje D and Czapla R (1989) An optimized culture medium for human vascualr endothelial cells from umbilical cord veins. Cytotechnology 2: 171–179.
Fujii DK, Cheng J and Gospodarowicz D (1983) Phosphatidyl choline and the growth in serum-free medium of vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cells, and corneal endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol 114: 267–278.
Gimbrone MA, Shefton EJ and Cruise SA (1978) Isolation and primary culture of endothelial cells from human umbilical vessels. Tissue Culture Ass Man 4: 813–817.
Gorfien S, Spector A, DeLuca D and Weiss S (1993) Growth and physiological functions of vascular endothelial cells in a new serum-free medium (SFM). Exp Cell Res 206: 291–301.
Gospodarowicz D, Vlodavsky I and Savion N (1981) The role of fibroblast growth factor and the extracellular matrix in the control of proliferation and differentiation of corneal endothelial cells. Vision Res 21: 87–103.
Hoshi H and McKeehan WL (1984) Brain-and liver cell-derived factors are required for growth of human endothelial cells in serum-free culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 6413–6417.
Jaffe EA, Nachman RL, Becker CG and Minick CR (1973) Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest 52: 2745–2756.
Jäger V, Lehmann J and Friedl P (1988) Serum-free growth medium for the cultivation of a wide spectrum of mammalian cells in a stirred bioreactor. Cytotechnology 1: 319–329.
Knedler A and Ham RG (1987) Optimized medium for clonal growth of human microvascular endothelial cells with minimal serum. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 23: 481–491.
Maciag T, Hoover GA, Stemerman MB and Weinstein R (1981) Serial propagation of human endothelial cells in vitro. J Cell Biol 91: 420–426.
Schrimpf G, Schröder M, Weitnauer E and Friedl P (1994) Metabolic rates of endothelial cells in vitro. Cytotechnology 16: 43–50.
Sunada H, Masuda M and Fujiwara K (1993) Preservation of differentiated phenotypes in cultured aortic endothelial cells by malotilate and phosphoascorbic acid. Eur J Cell Biol 60: 48–56.
Vlodavsky I, Johnson LK, Greenburg G and Gospodarowicz D (1979) Vascular endothelial cells maintained in the absence of fibroblast growth factor undergo structural and functional alterations that are incompatible with their in vivo differentiated properties. J Cell Biol 83: 468–486.
Weiss TL, Selleck SE, Reusch M and Wintroub BU (1990) Serial subculture and relative transport of human endothelial cells in serum-free, defined conditions. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 26: 759–768.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Labitzke, R., Friedl, P. A serum-free medium formulation supporting growth of human umbilical cord vein endothelial cells in long-term cultivation. Cytotechnology 35, 87–92 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017551218007
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017551218007