Abstract
Purpose : To determine the frequency and type of microdeletions on the Y chromosome, and to evaluate cytogenetic findings in unselected ICSI candidates at a Danish Fertility Clinic.
Methods : Genomic DNA was extracted from blood samples, which were collected prospectively from 400 ICSI candidates attending the Fertility Clinic at Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark. Twenty-five sequence tagged sites (STSs) spanning the azoospermia factor (AZF) regions of the Y chromosome were amplified in 5 multiplex sets to investigate Y microdeletions. Semen analysis, karyotype analysis, and histological evaluation of testicular biopsies were also performed.
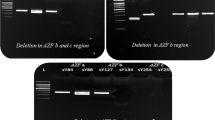
Results : Y microdeletions were detected in 3 (0.75%) of 400 unselected ICSI candidates. The frequency of Y microdeletions was found higher in azoospermic men (2%) than in oligozoospermic men (0.6%). Two patients having oligozoospermia had Y microdeletions in the AZFc region only, whereas the patient having azoospermia had Y microdeletions spanning the AZFb and AZFc regions. No microdeletion was detected in the AZFa region. Chromosomal anomalies were found in 6.1% of azoospermic men and in 2.7% of oligozoospermic men. A high frequency of cytogenetic abnormalities was found in normozoospermic men with fertilization failure (7.4%).
Conclusions : The frequency of Y microdeletions both in the unselected ICSI candidates and subgroups classified as azoospermic and oligozoospermic seems rather low compared to results of previous studies, which have been quite varying. It is possible that in addition to patient selection criteria, ethnical and geographical differences may contribute to these variations. Cytogenetic evaluation of normozoospermic men with fertilization failure seems indicated because of a high frequency of cytogenetic abnormalities.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Najmabadi H, Huang V, Yen P, Subbarao MN, Bhasin D, Banaag L, Naseeruddin S, de Krester DM, Baker HW, McLachlan RI: Substantial prevalence of microdeletions in infertile men with idiopathic azoospermia and oligozoospermia detected by a sequence-tagged site-based mapping strategy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1996;81:1347–1352
Chang PL, Sauer MV, Brown S: Y chromosome microdeletion in a father and his four infertile sons. Hum Reprod 1999;14:2689–2694
Van der Ven K, Montag M, Peschka B, Leygraaf J, Schwanitz G, Haidl G, Krebs D, van der Ven H: Combined cytogenetic and Y chromosome microdeletion screening in males undergoing intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Mol Hum Reprod 1997;3:699–704
Simoni M, Gromoll J, Dworniczak B, Rolf C, Abshagen K, Kamischke A, Carani C, Meshede D, Behre Hm, Horst J, Nieschlah E: Screening for microdeletions of the Y chromosome involving the DAZ (deleted in azoospermia) gene in azoospermia and severe oligozoospermia. Fertil Steril 1997;67:542–547
Kim SW, Kim KD, Paick JS: Microdeletions within the azoospermia factor subregions of the Y chromosome in patients with idiopathic azoospermia. Fertil Steril 1999;72:349– 353
Kent-First M, Muallem A, Shultz J, Pryor J, Roberts K, Nolten W, Meisner L, Chandley A, Gouchy G, Jorgensen L, Havighurst T, Grosch J: Defining regions of theY-chromosome responsible for male infertility and identification of a fourth AZF region (AZFd) by Y-chromosome microdeletion detection. Mol Reprod Dev 1999;53:27–41
Kerr NJ, Zhang J, Sin FY, Benny P, Sin IL: Frequency of microdeletions in the azoospermia factor region of the Y-chromosome of New Zealand men. N Z Med J 2000;10:468– 470
Liow SL, Ghadessy FJ, Ng SC, Yong EL: Y chromosome microdeletions, in azoospermic or near-azoospermic subjects, are located in the AZFc (DAZ) subregion. Mol Hum Reprod 1998;4:763–768
Qureshi SJ, Ross AR, Ma K, Cooke HJ, Intyre MA, Chandley AC, Hargreave TB: Polymerase chain reaction screening for Y chromosome microdeletions: A first step towards the diagnosis of genetically-determined spermatogenic failure in men. Mol Hum Reprod 1996;2:775–779
Silber SJ, Alagappan R, Brown LG, Page DC: Y chromosome deletions in azoospermic and severely oligozoospermic men undergoing intracytoplasmic sperm injection after testicular sperm extraction. Hum Reprod 1998;13:3332– 3337
Jiang MC, Lien YR, Chen SU, Ko TM, Ho HN, Yang YS: Transmission of de novo mutations of the deleted in azoospermia genes from a severely oligozoospermic male to a son via intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Fertil Steril 1999;71:1029– 1032
Osterlund C, Segersteen E, Arver S, Pousette A: Low number of Y-chromosome deletions in infertile azoospermic men at a Swedish andrology center. Int J Androl 2000;23:225–229
Friel A, Houghton JA, Maher M, Smith T, Noel S, Nolan A, Egan D, Glennon M: Molecular detection of Y chromosome microdeletios: An Irish study. Int J Androl 2001;24:31–36
Foresta C, Ferlin A, Garolla A, Moro E, Pistorello M, Barbaux S, Rossato M: High frequency of well-defined Y-chromosome deletions in idiopathic Sertoli cell-only syndrome. Hum Reprod 1998;13:302–307
Kremer JA, Tuerlings JH, Meuleman EJ, Schoute F, Mariman E, Smeets DF, Hoefsloot LH, Braat DD, Merkus HM: Microdeletions of the Y chromosome and intracytoplasmic sperm injection: From gene to clinic.Hum Reprod 1997;12: 687–691
Krausz C, Bussani-Mastellone C, Granchi S, McElreavey K, Scarselli G, Forti G: Screening for microdeletions of Y chromosome genes in patients undergoing intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Hum Reprod 1999;14:1717–1721
Van Landuyt L, Lissens W, Stouffs K, Tournaye H, Liebaers I, Van Steirteghem A: Validation of a simple Yq deletion screening programme in an ICSI candidate population. Mol Hum Reprod 2000;6:291–297
Krausz C, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Frydelund-Larsen L, Quintana-Murci L, McElreavey K, Skakkebaek NE: Doubleblind Y chromosome microdeletion analysis in men with known sperm parameters and reproductive hormone profiles: Microdeletions are specific for spermatogenic failure. Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001;86:2638–2642
WHO Laboratory Manual for the Examination of Human Semen and Sperm-Cevical Mucusa Interaction, 3rd edn. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 1992
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF:A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 1988;11:1215
Bor P, Hindkjaer J, Ingerslev HJ, Kolvraa S: Multiplex PCR for screening of microdeletions on the Y chromosome. J Assisted Reprod Gen 2001;18:209–216
Rooney DE, Czepulkowiski BH (eds): Human Cytogenetics— A Practical Approach. Oxford, UK, IRL Press, 1984
Simoni M, Bakker E, Eurlings MCM, Matthijs G, Moro E, Muller CR, Vogt PH: Laboratory guidelines for molecular diagnosis of Y-chromosomal microdeletions. Int J Androl 1999;22:292–299
Pryor JL, Roberts KP: Principles of sequence-tagged site selection in screening for Y deletions. Hum Reprod 1998;13:1768
Ma K, Sharkey A, Kirsch S, Vogt P, Keil R, Hargreave TB, McBeath S, Chandley AC: Towards the molecular localisation of the AZF locus: Mapping of microdeletions in azoospermic men within 14 subintervals of interval 6 of the human Y chromosome. Hum Mol Genet 1992;1:29–33
Foresta C, Ferlin A, Garolla A, Rossato M, Barbaux S, De Bortoli A: Y-chromosome deletions in idiopathic severe testiculopathies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997;82:1075–1080
Fujisawa M, Shirakawa T, Kanzaki M, Okada H, Arakawa S, Kamidono S: Y-chromosome microdeletion and phenotype in cytogenetically normalmenwith idiopathic azoospermia. Fertil Steril 2001;76:491–495
Kato H, Komori S, Nakata Y, Sakata K, Kanazawa R, Handa M, Kobayashi S, Koyama K, Isojima S: Screening for deletions in interval D16-22 of the Y chromosome in azoospermic and oligozoospermic Japanese men. J Hum Genet 2001;46:110–114
Ferlin A, Moro E, Garolla A, Foresta C: Human male infertility and Y chromosome deletions: Role of the AZF-candidate genes DAZ, RBM and DFFRY. Hum Reprod 1999;14:1710– 1716
Stuppia L, Gatta V, Calabrese G, Guanciali Franchi P, Morizio E, Bombieri C, Mingarelli R, Sforza V, Frajese G, Tenaglia R, Palka G: A quarter of men with idiopathic oligo-azoospermia display chromosomal abnormalities and microdeletions of different types in interval 6 of Yq11. Hum Genet 1998;102:566–570
Grimaldi P, Scarponi C, Rossi P, March MR, Fabbri A, Isidori A, Spera G, Krausz C, Geremia R: Analysis of Yq microdeletions in infertile males by PCR and DNA hybridization techniques. Mol Hum Reprod 1998;4:1116–1121
Rejio R, Lee TY, Salo P, Alagappan R, Brown LG, Rosenberg M, Rozen S, Jaffe T, Straus D, Hovatta O, Chapelle A, Silber S, Page DC: Diverse spermatogenetic defects in human caused by Y chromosome deletions encompassing a novel RNA-binding protein gene. Nature Genet 1995;10:383–393
Affara N, Bishop C, Brown W, Cooke H, Davey P, Ellis N, Graves JM, Mitchell M, Rappold G, Tyler-Smith C, Yen P, Lau YF: Report of the Second InternationalWorkshop on Y Chromosome Mapping 1995. Cytogenet Cell Genet 1996;73:33–76
Vogt PH, Edelmann A, Kirsch S, Henegariu O, Hirschmann P, Kiesewette F, Kohn FM, Schill WB, Farah S, Meschede D, Behra HM, Castel A, Nieschlag E, Weidner W, Grone HJ, Jung A, Engel W, Haidl G: Human Y chromosome azoospermia factors (AZF) mapped different subregions in Yq11. Hum Mol Genet 1996;5:933–943
Vollrath D, Foote S, Hilton A, Brown LG, Beer-Romero P, Bogan JS, Page DC: The human Y chromosome: A 43-interval map based on naturally occurring deletions. Science 1992;258:52–59
Foote S, Vollrath D, Hilton A, Page DC: The human Y chromosome: Overlapping DNA clones spanning the euchromatic region. Science 1992;2:60–66
Yen PH: A long-range restriction map of deletion interval 6 of the human Y chromosome: A region frequently deleted in azoospermic males. Genomics 1998;54:5–12
Krausz C, Qintana-Murci L, Barbaux S, Siffori JP, Rouba H, Delafontaine D, Souleyreau-Therville N, Arvis G, Antoine JM, Erdei E, Taar JP, Tar A, Jeandidier E, Plessis G, Bourgeron T, Dadoune JP, Fellous M, McElreavey K: A high frequency of Y chromosome Deletions in males with nonidiopathic infertility. J Endoc Metab 1999;84;3606–3612
Retief A, Van Zyl J, Menkveld M: Chromsome studies in 496 infertile males with a sperm count below 10 million per ml. Hum Genet 1984;66:162–164
Gekas J, Thepot F, Turleau C, Siffroi JP, Dadoune JP, Wasels R, Benzacken B: Chromosomal factors of infertility in candidate couples for ICSI: An equal risk of constitutional aberrations in women and men. Hum Reprod 2001;16: 82–90
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bor, P., Hindkjær, J., Kølvraa, S. et al. Y-Chromosome Microdeletions and Cytogenetic Findings in Unselected ICSI Candidates at a Danish Fertility Clinic. J Assist Reprod Genet 19, 224–231 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015358802577
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015358802577