Abstract
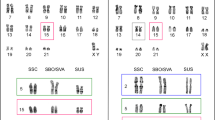
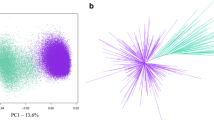
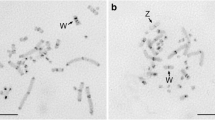
Satellite DNAs (stDNAs) of four Acomys species (spiny-mice), A. cahirinus, A. cineraceus, A. dimidiatus and A. russatus, belong to closely related sequence families. Monomer sizes range from 338 to 364 bp. Between-species sequence identity was from 81.0% to 97.2%. The molecular phylogeny of the sequences helps to clarify the taxonomy of this ‘difficult’ group. The A. dimidiatus genome contains about 60 000 repeats. According to the restriction patterns, repeats are arranged in tandem. The stDNA maps to the centromeric heterochromatin of most autosomes, both acrocentric and metacentric, but appears to be absent in the centromeric region of Y chromosomes. A well-conserved centromere protein B (CENP-B) box is present in the stDNA of A. russatus while it is degenerated in the other species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso S, Minty A, Bourlet Y, Buckingham M (1986) Comparison of three actin-coding sequences in the mouse: evolutionary relationships between the actin genes of warm blooded vertebrates. J Mol Evol 23: 11-22.
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215: 403-10.
Arnason U, Manolova Y, Manolov G, Bregula U, Levan A (1986) Satellite DNA in the three Cbands of an unusual mouse marker chromosome-A model of chromosomal evolution. Exp Cell Res 164: 256-260.
Benson DA, Boguski MS, Lipman DJ, Ostell J, Ouellette BF (1998) GenBank. Nucl Acids Res 26: 1-7.
Choo KHA (1997) The Centromere. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Fry K, Salser W (1977) Nucleotide sequences of Hs-alpha satellite DNA from kangaroo rat, Dipodomys ordii, and characterization of similar sequences in other rodents. Cell 12: 1069-1084.
Gamperl R, Ehmann CH, Bachmann K (1982) Genome size and heterochromatin variation in rodents. Genetica 58: 199-212.
Haaf T, Mater AG, Wienberg J, Ward DC (1995) Presence and abundance of CENP-B box sequences in great ape subsets of primate-specific α-satellite DNA. J Mol Evol 41: 487-491.
Hörz W, Altenburger W (1981) Nucleotide sequence of mouse satellite DNA. Nucl Acids Res 9: 683-696.
Hörz W, Zachau HG (1977) Characterization of distinct segments in mouse satellite DNA by restriction nucleases. Eur J Biochem 73: 383-392.
John B, Miklos GLG (1979) Functional aspects of satellite DNA in heterochromatin. Inter Rev Cytol 58: 1-114.
Kipling D, Mitchell AR, Masumoto H, Wilson HE, Nicol L, Cooke H (1995) CENP-B binds a novel centromeric sequence in the asian mouse Mus caroli. Mol Cell Biol 15: 4009-4020.
Kipling D, Warburton PE (1997) Centromeres, CENP-B and Tigger too. Trends Genet 13: 141-145.
Kunze B, Weichenhan D, Virks P, Traut W, Winking H (1996) Copy numbers of a clustered long-range repeat determine C-band staining. Cytogenet Cell Genet 73: 86-91.
Lima-de-Faria A, Arnason U, Widegren B et al. (1984) Conservation of repetitive DNA sequences in deer species studied by southern blot transfer. J Mol Evol 20: 17-24.
López CC, Edström J-E (1998) Interspersed centromeric element with a CENP-B box-like motif in Chironomus pallidivittatus. Nucl Acids Res 26: 4168-4172.
Masumoto H, Masukata H, Muro Y, Nozaki N, Okazaki T (1989) A human centromere Antigen (CENP-B) interacts with a short specific sequence in alphoid DNA, a human centromeric satellite. J Cell Biol 109: 1963-1973.
Masumoto H, Yoda K, Ikeno M, Kitagawa K, Muro Y, Okazaki T (1993) Properties of CENP-B and its target sequence in a satellite DNA. NATO ASI Ser H 72: 31-43.
Musser GG, Carleton MD (1993) Rodentia: Sciurognathi: Muridae: Murinae. In: Wilson DE, Reeder DAM, eds. Mammalian species of the world — A taxonomic and geographic reference. Washington, UK: Smithsonian Institution Press, pp. 501-755.
Plass C, Weichenhan D, Kunze B et al. (1995) A member of the mouse LRR transcript family with homology to the human Sp100 gene. Hereditas 122: 245-256.
Redi CA, Garagna S, Della Valle G et al. (1990) Differences in the organization and chromosomal allocation of satellite DNA between the European long tailed house mice Mus domesticus and Mus musculus. Chromosoma 99: 11-17.
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4: 406-425.
Schweizer D (1981) Counterstain-enhanced chromosome banding. Hum Genet 57: 1-14.
Singer MF (1982) Highly repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Int Rev Cytol 76: 67-112.
Sumner AT (1972) A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp Cell Res 75: 304-306.
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, positions-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucl Acids Res 22: 4673-4680.
Volobouev VT, Tranier M, Dutrillaux B (1991) Chromosome evolution in the genus Acomys: Chromosome banding analysis of Acomys cf. dimidiatus (Rodentia, Muridae). Bonn Zool Beitr 42: 253-260.
Volobouev V, Vogt N, Viegas-Pequignot E, Malfoy B, Dutrillaux B (1995) Characterization and chromosomal location of two repeated DNAs in three Gerbillus species. Chromosoma 104: 252-259.
Volobouev V, Gautun JC, Sicard B, Trainer M (1996a) The chromosome complement of Acomys spp. (Rodentia, Muridae) from Oursi, Burkina Faso — the ancestral karyotype of the cahirinusdimidiatus group? Chromosome Res 4: 526-530.
Volobouev VT, Guatun JC, Tranier M (1996b) Chromosome evolution in the genus Acomys (Rodentia, Muridae): Chromosome banding analysis of Acomys cahirinus. Mammalia 2: 217-222.
Weichenhan D, Kunze B, Zacker S, Traut W, Winking H (1997) Structure and expression of the murine Sp100 nuclear dot gene. Genomics 43: 298-306.
Wong AKC, Rattner JB (1988) Sequence organization and cytological localization of the minor satellite of mouse. Nucl Acids Res 16: 11645-11661.
Wu Z, Liu WX, Murphy C, Gall J (1990) Satellite 1 DNA sequence from genomic DNA of the giant panda Ailuropoda malanoleuca. Nucl Acids Res 18: 1054.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kunze, B., Traut, W., Garagna, S. et al. Pericentric satellite DNA and molecular phylogeny in Acomys (Rodentia). Chromosome Res 7, 131–142 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009251202340
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009251202340