Abstract
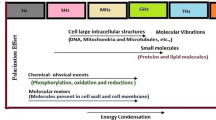
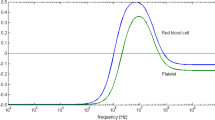
Dielectrophoresis is a well established and effective means for the manipulation of viable cells. However, its effectiveness greatly depends upon the utilization of very low electrical conductivity media. High conductivity media, as in the case of cell culture media, result only in the induction of weaker repulsive forces (negative dielectrophoresis) and excessive medium heating. A dielectrophoresis-based cell separation device (DEP-filter) has been recently developed for perfusion cultures that successfully overcomes these obstacles and provides a very high degree of viable cell separation while most of the nonviable cells are removed from the bioreactor by the effluent stream. The latter results in high viabilities throughout the culture period and minimization of lysed cell proteases in the bioreactor. However, an important question that remains to be answered is whether we have any adverse effects by exposing the cultured cells to high frequency electric fields for extended periods of time. A special chamber was constructed to quantitate the effect under several operational conditions. Cell growth, glucose uptake, lactate and monoclonal antibody production data suggest that there is no appreciable effect and hence, operation over long periods of time of the DEP-filter should not have any adverse effect on the cultured cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidor IG and Sowers AE (1992) Kinetics and mechanism of cell membrane electrofusion. J Biophys 61: 1557-1569.
Archer GP, Render MC, Betts WB and Sancho M (1993) Dielectrophoretic concentration of micro-organisms using grid electrodes. Microbios 76: 237-244.
Avgerinos GC, Drapeau D, Socolow J, Mao JI, Hsiao K and Broeze RJ (1990) Spin filter perfusion system for high density cell culture: production of recombinant urinary type plasminogen activator in CHO cells. Bio/Technol 8: 54-58.
Berthold W and Kempken R (1994) Interactions of cell culture with downstream purification: a case study. Cytotechnol 15: 229-242.
Cantoni O, Sestili P, Fiorani M and Dachà M (1995) The effect of 50 Hz sinusoidal electric and/or magnetic fields on the rate of repair of DNA single/double strand breaks in oxidatively injured cells. Biochem Molec Biol Int 37: 681-689.
Cantoni O, Sestili P, Fiorani M and Dachà M (1996) Effect of 50 Hz sinusoidal electric and/or magnetic fields on the rate of repair of DNA single/double strand breaks in cultured mammalian cells exposed to three different carcinogens: methylmethane, sulphonate, chromate and 254 nm UV. Biochem Molec Biol Int 38: 527-538.
Caron AW, Tom RL, Kamen AA and Massie B (1994) Baculovirus expression system scaleup by perfusion of high-density Sf-9 cell cultures. Biotechnol Bioeng 43: 881-891.
Cotter TG and Al-Rubeai M (1995) Cell death (apoptosis) in culture systems. Tibtech 13: 150-155.
Deo YM, Mahadevan MD and Fuchs R (1996) Practical considerations in operation and scale-up of spin filter based bioreactors for monoclonal antibody production. Biotechnol Prog 12: 57-64.
Doblhoff-Dier O, Gaida T, Katinger H, Burger W, Gröschl M and Benes E (1994) A novel ultrasonic resonance field device for the retention of animal cells. Biotechnol Prog 10: 428-432.
Docoslis A, Kalogerakis N, Behie LA and Kaler KVIS (1997) A novel dielectrophoresis-based device for the selective retention of viable cells in cell culture media. Biotechnol Bioeng 54: 239-250.
Esclade LRJ, Carrel S and Péringer P (1991) Influence of the screen material on the fouling of spin filters. Biotechnol Bioeng 38: 159-168.
Forestell SP (1992) Optimization of microcarrier cultures used in human vaccine production, Ph.D. thesis, University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
Fuhr G, Glasser H, Müller T and Schnelle T (1994) Cell manipulation and cultivation under AC electric field influence in highly conductive media. Biochim Biophys Acta 1201: 353-360.
Gaida Th, Doblhoff-Dier O, Strutzenberger K, Katinger H, Burger W, Gröschl M, Handl B and Benes E (1996) Selective retention of viable cells in ultrasonic resonance field devices. Biotechnol Prog 12: 73-76.
Gascoyne PRC, Becker FF and Wang X-B (1995) Membrane changes accompanying the induced differentiation of Friend murine erythroleukemia cells studied by dielectrophoresis. Bioelectrochem Bioenerget 36: 115-125.
Gimsa J, Marszalek P, Loewe U and Tsong TY (1991) Dielectrophoresis and electrorotation of neurospora slime and murine myeloma cells. Biophys J 60: 749-760.
Grosse C and Schwan HP (1992) Cellular membrane potentials induced by alternating fields. Biophysical J 63: 1632-1642.
Hansen HA, Damgaard B and Emborg C (1993) Enhanced antibody production associated with altered amino acid metabolism in a hybridoma high-density perfusion culture established by gravity separation. Cytotechnol 11: 155-166.
Hawrylik SJ, Wasiko DJ, Pillar JS, Cheng JB and Lee ES (1994) Vortex flow filtration of mammalian and insect cells. Cytotechnol 15: 253-258.
Holian O, Astumian RD, Lee RC, Reyes HM, Attar BM and Walter RJ (1996) Protein kinase C activity is altered in HL60 cells exposed to 60 Hz AC electric fields. Bioelectromagnetics 17: 504-509.
Huang Y, Wang X-B, Tame JA and Pethig R (1993) Electrokinetic behavior of colloidal particles in traveling electric fields: studies using yeast cells. J Phys D Appl Phys 26: 1528-1535.
Hülscher M, Scheibler U and Onken U (1991) Selective recycle of viable animal cells by coupling of airlift reactor and cell settler. Biotechnol Bioeng 39: 442-446.
Kaler KVIS and Jones TB (1990) Dielectrophoretic spectra of single cells determined by feedback-controlled levitation. Biophys J 57: 173-182.
Kaler KVIS, Xie JP, Jones TB and Paul R (1992) Dual-frequency dielectrophoretic levitation of Canola protoplasts. Biophys J 63: 58-69.
Knedlitschek G, Noszvai-Nagy M, Meyer-Waarden H, Schinnelpfeng J, Weibezahn KF and Dertinger H (1994) Cyclic AMP response in cells exposed to electric fields of different frequencies and intensities. Radiat Environ Biophys 33: 141-147.
Krishna GG, Anwar AKW, Mohan DR and Ahmad A (1989) Dielectrophoretic study of human erythrocytes. J Biomed Eng 11: 375-380.
Lee SM (1989) The primary stages of protein recovery. J Biotechnol 11: 103-118.
Loscher W and Mevissen M (1994) Animal studies on the role of 50/60 Hz magnetic fields in carcinogenesis. Life Science 54: 1531-1543.
Mahar JT (1993) Scale-up and validation of sedimentation centrifuges. Part I: Scale-up. Biopharm (September), 42-51.
Markx GH, Talary MS and Pethig, R (1994) Separation of viable and non-viable yeast using dielectrophoresis. J Biotechnol 32: 29-37.
Neil GA and Zimmermann U (1993) Electroinjection. Methods Enzymol 221: 339-361.
Neumann E, Sowers AE and Jordan CA (1989) Electroporation and Electrofusion in Cell Biology. Plenum Press, New York-London.
Oh DJ, Choi SK and Chang HN (1994) High-density continuous cultures of hybridoma cells in a depth filter perfusion system. Biotechnol Bioeng 44: 895-901.
Pohl HA (1977) In: Catsimpoolas N (ed) Methods of Cell Separation. Vol. 1 (pp. 67-169) Plenum Press, New York.
Sagan LA (1992) Epidemiological and laboratory studies of power frequency electric and magnetic fields. JAMA 268: 625-629.
Schwan HP (1983) Biophysics of the interaction of electromagnetic energy with cells and membranes. In: Grandolfo M, Michaelson SM and Rindi A (eds) Biological Effects and Dosimetry of Nonionizing Radiation. (pp. 213-231) Plenum Press, New York.
Searles JA, Todd P and Kompala DS (1994) Viable cell recycle with an inclined settler in the perfusion culture of suspended recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biotechnol Prog 10: 198-206.
Sukhorukov VL, Arnold WM and Zimmermann U (1993) Hypotonically induced changes in the plasma membrane of cultured mammalian cells. J Membrane Biol 132: 27-40.
Trampler F, Sonderhoff SA, Pui PWS, Kilburn DG and Piret JM (1994) Acoustic cell filter for high density perfusion culture of hybridoma cells. Bio/Technol 12: 281-284.
Trombi L, Petrini M, Manara G, Mese ED and Revoltella RP (1993) Effects of repeated exposure to high-voltage electric discharges and low-frequency electromagnetic fields on cultured mouse P3x63Ag8 plasmocytoma cells. Electro-and Magnetobiology 12: 125-134.
Whitson GL, Carrier WL, Francis AA, Shih CC, Georghiou S and Regan JD (1986) Effects of extremely low frequency electric fields on cell growth and DNA repair in human skin fibroblasts. Cell Tissue Kinetics 19: 39-47.
Zimmermann U (1986) Electrical breakdown, electropermeabilization and electrofusion. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 105: 176-256.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Docoslis, A., Kalogerakis, N. & Behie, L.A. Dielectrophoretic forces can be safely used to retain viable cells in perfusion cultures of animal cells. Cytotechnology 30, 133–142 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008050809217
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008050809217