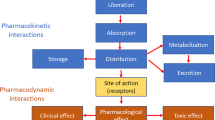
Abstract
There is an increasing interest to administer cytotoxic drugs topatients by the oral route. Quality of life issues, treatmentadvantages and pharmaco-economics are major arguments in favorof oral therapy. However, low or moderate bioavailability incombination with considerable interpatient variability arefrequently observed which may reduce the feasibility of the oralroute for this class of drugs with a generally narrow therapeuticwindow. Until recently, investigators focused on absorptionenhancers which slightly damage the intestinal surface such assalicylates, methylxantines and surfactants to improve the oralbioavailability of drugs. To date, a shift can be seen towardsmore subtle mechanisms to enhance the absorption. This reviewarticle focuses on two important mechanisms that determine theoral bioavailability of cytotoxic drugs. These include thepresence of drug transporters in the intestinal epitheliumpumping drugs into the intestinal lumen, such as MDR1 typeP-glycoproteins, and first-pass elimination by cytochrome P450isoenzymes (e.g. 3A4 and 3A5) or other enzymes in the intestinesand/or liver. Currently preclinical and clinical studies arebeing performed to explore the feasibility of blocking thesetransporters/enzymes in order to achieve higher and less variablesystemic drug levels after oral dosing. This review gives anupdate of the results of these studies. It is concluded however,that further research to unravel the processes involved in oraldrug uptake is warranted to make the oral route a more efficientand consistent way of drug administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Demario MD, Ratain MJ: Oral chemotherapy: Rationale and future directions. J Clin Oncol 16: 2557–2567, 1998
Hoff PM, Pazdur R, Benner SE, Canetta R: UFT and leucovorin: a review of its clinical development and therapeutic potential in the oral treatment of cancer. Anticancer Drugs 9: 479–490, 1998
Shirasaka T, Shimamato Y, Ohshimo H, Yamaguchi M, Kato T, Yonekura K, Fukushima M: Development of a novel form of an oral 5-fluorouracil derivative (S-1) directed to the potentiation of the tumor selective cytotoxicity of 5-fluorouracil by two biochemical modulators. Anticancer Drugs 7: 548–557, 1996
Budman DR, Meropol NJ, Reigner B, Creaven PJ, Lichtman SM, Berghorn E, Behr J, Gordon RJ, Osterwalder B, Griffin T: Preliminary studies of a novel oral fluoropyrimidine carbamate: capecitabine. J Clin Oncol 16: 1795–1802, 1998
McKeage MJ, Mistry P, Ward J, Boxall FE, Loh S, O'Neill C, Ellis P, Kelland LR, Morgan SE, Murrer B, Santabarbara P, Harrap KR, Judson IR: A phase I and pharmacology study of an oral platinum complex, JM216: dose-dependent pharmacokinetics with single-dose administration. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 36: 451–458, 1995
Liu G, Franssen E, Fitch MI, Warner E: Patient preferences for oral versus intravenous palliative chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 15: 110–115, 1997
Kakolyris S, Samonis G, Koukourakis M, Vlachonicolis I, Chalkiadakis G, Kalbakis K, Souglakos I, Agelaki S, Toloudis P, Georgoulias V: Treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer with prolonged oral etoposide. Am J Clin Oncol 21: 505–508, 1998
Gridelli C, Rossi A, Scognamiglio F, Guida C, Fiore F, Gatani T, Scoppa G, Pergola M: Carboplatin plus oral etoposide in elderly patients with advanced non small cell lung cancer. A phase II study. Anticancer Res 17: 4755–4758, 1997
Sullivan SD, Mozaffari E, Johnson ES, Wolitz R, Follansbee SE: An economic evaluation of oral compared with intravenous ganciclovir for maintenance treatment of newly diagnosed cytomegalovirus retinitis in AIDS patients. Clin Ther 18: 546–558, 1996
Hellriegel ET, Bjornsson TD, Hauck WW: Interpatient variability in bioavailability is related to the extent of absorption: implications for bioavailability and bioequivalence studies. Clin Pharmacol Ther 60: 601–607, 1996
Urquhart J: Patient compliance with crucial drug regimens: implications for prostate cancer. Eur Urol 29: Suppl 2: 124–131, 1996
Davies HA, Lilleyman JS: Compliance with oral chemotherapy in childhood lymphoblastic leukaemia. Cancer Treat Rev 21: 93–103, 1995
Macheras P, Reppas C, Dressman JB: Biopharmaceutics of orally administered drugs. 1st edition, Ellis Horwood, 1995
Rowland M, Tozer TN: Clinical parmacokinetics: Concepts and applications. 3rd edition. Baltimore, Williams and Wilkins, 1995
Kararli TT: Gastro intestinal absorption of drugs. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 6: 39–86, 1989
Rang HP, Dale MM: Pharmacology. 3rd edition. Churchill Livingstone, 1995
Hartman NR, Yarchoan R, Pluda JM, Thomas RV, Wyvill KM, Flora KP, Broder S, Johns DG: Pharmacokinetics of 20,30-dideoxyninosine in patients with severe human immunodeficiency infection. II. The effects of different oral formulations and the presence of other medications. Clin Pharmacol Ther 50: 278–285, 1991
Williams L, Hill DP, Jr., Davis JA, Lowenthal DT: The influence of food on the absorption and metabolism of drugs: an update. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 21: 201–211, 1996
Hoetelmans RM, Meenhorst PL, Mulder JW, Burger DM, Koks CH, Beijnen JH: Clinical pharmacology of HIV protease inhibitors: focus on saquinavir, indinavir, and ritonavir. Pharm World Sci 19: 159–175, 1997
Tsuji A, Tamai I: Carrier-mediated intestinal transport of drugs. Pharm Res 13: 963–977, 1996
Juliano RL, Ling V: A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim Biophys Acta 455: 152–162, 1976
Endicott JA, Ling V: The biochemistry of P-glycoproteinmediated multidrug resistance. Annu Rev Biochem 58: 137–171, 1989
Gottesman MM, Pastan I: Biochemistry of multidrug resistance mediated by the multidrug transporter. Annu Rev Biochem 62: 385–427, 1993
Thiebaut F, Tsuruo T, Hamada H, Gottesman MM, Pastan I, Willingham MC: Cellular localization of the multidrugresistance gene product P-glycoprotein in normal human tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 7735–7738, 1987
Lankas GR, Cartwright ME, Umbenhauer D: P-glycoprotein deficiency in a subpopulation of CF-1 mice enhances avermectin-induced neurotoxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 143: 357–365, 1997
Lankas GR, Wise LD, Cartwright ME, Pippert T, Umbenhauer DR: Placental P-glycoprotein defiency enhances susceptibility to chemically induced birth defects in mice. Reprod Toxicol 12: 457–463, 1998
Schinkel AH, Smit JJM, Van Tellingen O, Beijnen JH, Wagenaar E, van Deemter L, Mol CAAM, van der Valk MA, Robanus-Maandag EC, te Riele HPJ, Berns AJM, Borst P: Disruption of the mouse mdr1a P-glycoprotein gene leads to a deficiency in the blood-brain barrier and to increased sensitivity to drugs. Cell 77: 491–502, 1994
Schinkel AH, Mayer U, Wagenaar E, Mol CAAM, van Deemter L, Smit JJM, van der Valk MA, Voordouw AC, Spits H, Van Tellingen O, Zijlmans JM, Fibbe WE, Borst P: Normal viability and altered pharmacokinetics in mice lacking mdr1-type (drug-transporting) P-glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 4028–4033, 1997
Sparreboom A, van Asperen J, Mayer U, Schinkel AH, Smit JW, Meijer DKF, Borst P, Nooijen WJ, Beijnen JH, van Tellingen O: Limited oral bioavailability and active epithelial excretion of paclitaxel (Taxol) caused by P-glycoprotein in the intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 2031–2035, 1997
Back DJ, Rogers SM: Review: first-pass metabolism by the gastrointestinal mucosa. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1: 339–357, 1987
Kolars JC, Awni WM, Merion RM, Watkins PB: First-pass metabolism of cyclosporin by the gut. Lancet 338: 1488–1490, 1991
Webber IR, Peters WHM, Back DJ: Cyclosporin metabolism by human gastrointestinal mucosal microsomes. Br J Clin Pharmacol 33: 661–664, 1992
Gomez DY, Wacher VJ, Tomlanovich SJ, Hebert MF, Benet LZ: The effects of ketoconazole on the intestinal metabolism and bioavailability of cyclosporine. Clin Pharmacol Ther 58: 15–19, 1995
Kolars JC, Schmiedlin-Ren P, Schuetz JD, Fang C, Watkins PB: Identification of rifampin-inducible P450IIIA4 (CYP3A4) in human small bowel enterocytes. J Clin Invest 90: 1871–1878, 1992
Kolars JC, Lown KS, Schmiedlin-Ren P, Ghosh M, Fang C, Wrighton SA, Merion RM, Watkins PB: CYP3A gene expression in human gut epithelium. Pharmacogenetics 4: 247–259, 1994
Krishna DR, Klotz U: Extrahepatic metabolism of drugs in humans. Clin Pharmacokinet 26: 144–160, 1994
Paine MF, Khalighi M, Fisher JM, Shen DD, Kunze KL, Marsh CL, Perkins JD, Thummel KE: Characterization of interintestinal and intraintestinal variations in human CYP3Adependent metabolism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283: 1552–1562, 1997
Lown KS, Kolars JC, Thummel KE, Barnett JL, Kunze KL, Wrighton SA, Watkins PB: Interpatient heterogeneity in expression of CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 in small bowel. Lack of prediction by the erythromycin breath test. Drug Metab Dispos 22: 947–955, 1994
Guengerich FP: Characterization of human cytochrome P450 enzymes. FASEB J 6: 745–748, 1992
Wacher VJ, Wu CY, Benet LZ: Overlapping substrate specificities and tissue distribution of cytochrome P450 3A and 239 P-glycoprotein: implications for drug delivery and activity in cancer chemotherapy. Mol Carcinog 13: 129–134, 1995
Zeller FP, Ueda CT, Wulf BG, Meyers DG: Effect of caffeine on the oral absorption and disposition of quinidine. Clin Pharm 3: 72–75, 1984
Nakamura J, Takamura R, Kimura T, Muranishi S, Sezaki H: Enhancement effect of methylxanthines on the intestinal absorption of poorly absorbable dyes from the rat small intestine. Biochem Pharmacol 28: 2957–2960, 1979
Whitmore DA, Brookes LG, Wheeler KP: Relative effects of different surfactants on intestinal absorption and the release of proteins and phospholipids from the tissue. J Pharm Pharmacol 31: 277–283, 1979
Benet LZ, Wu CY, Hebert MF, Wacher VJ: Intestinal drug metabolism and antitransport processes: A potential paradigm shift in oral drug delivery. J Contr Release 39: 139–143, 1996
Berg SL, Tolcher A, O'Shaughnessy JA, Denicoff AM, Noone M, Ognibene FP, Cowan KH, Balis FM: Effect of Rverapamil on the pharmacokinetics of paclitaxel in women with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 13: 2039–2042, 1995
Wishart GC, Bissett D, Paul J, Jodrell D, Harnett A, Habeshaw T, Kerr DJ, Macham MA, Soukop M, Leonard RCF, Knepil J, Kaye SB: Quinidine as a resistance modulator of epirubicin in advanced breast cancer: mature results of a placebo-controlled randomized trial. J Clin Oncol 12: 1771–1777, 1994
Solary E, Caillot D, Chauffert B, Casasnovas RO, Dumas M, Maynadie M, Guy H: Feasibility of using quinine, a potential multidrug resistance-reversing agent, in combination with mitoxantrone and cytarabine for the treatment of acute leukernia. J Clin Oncol 10: 1730–1736, 1992
van der Graaf WTA, de Vries EGE, Uges DRA, Nanninga AG, Meijer C, Vellenga E, Mulder POM, Mulder NH: In vitro and in vivo modulation of multidrug resistance with amiodarone. Int J Cancer 48: 616–622, 1991
Ferry DR, Traunecker H, Kerr DJ: Clinical trials of Pglycoprotein reversal in solid tumours. Eur J Cancer 32A: 1070–1081, 1996
Toffoli G, Sorio R, Gigante M, Corona G, Galligioni E, Boiocchi M: Cyclosporin A as a multi drug-resistant modulator in patients with renal cell carcinoma treated with teniposide. Br J Cancer 75: 715–721, 1997
Boesch D, Gaveriaux C, Jachez B, Pourtier-Manzanedo A, Bollinger P, Loor F: In vivo circumvention of P-glycoproteinmediated multidrug resistance of tumor cells with SDZ PSC 833. Cancer Res 51: 4226–4233, 1991
Covelli A: SDZ PSC 833: A new multidrug-resistance modulator. Tumori 83: S21-S24, 1997
Hyafil F, Vergely C, Du Vignaud P, Grand-Perret T: In vitro and in vivo reversal of multidrug resistance by GF120918, an acridonecarboxamide derivative. Cancer Res 53: 4595–4602, 1993
Booth CL, Brouwer KR, Brouwer KLR; Effect of multidrug resistance modulators on the hepatobillary disposition of doxorubicin in the isolated perfused rat liver. Cancer Res 58: 3641–3648, 1998
Dantzig AH, Shepard RL, Cao J, Law KL, Ehlhardt WJ, Baughman TM, Bumol TF, Starling JJ: Reversal of Pglycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance by a potent cyclopropyldibenzosuberane modulator, LY335979. Cancer Res 56: 4171–4179, 1996
Starling JJ, Shepard RL, Cao J, Law KL, Norman BH, Kroin JS, Ehlhardt WJ, Baughman TM, Winter MA, Bell MG, Shih C. Gruber J, Elmquist WF, Dantzig AH: Pharmacological characterization of LY335979: a potent cyclopropyldibenzosuberane modulator of P-glycoprotein. Adv Enzyme Regul 37: 335–347, 1997
Saeki T, Ueda K, Tanigawara Y, Hori R, Komano T: Human P-glycoprotein transports cyclosporin A and FK506. J Biol Chem 268: 6077–6080, 1993
Spoelstra EC, Westerhoff HV, Pinedo HM, Dekker H, Lankelma J: The multidrug-resistance-reverser verapamil interferes with cellular P-glycoprotein-mediated pumping of daunorubicin as a non-competing substrate. Eur J Biochem 221: 363–373, 1994
Archinal-Mattheis A, Rzepka RW, Watanabe T, Kokubu N, Itoh Y, Combates NJ, Bair KW, Cohen D: Analysis of the interactions of SDZ PSC 833 ([30-keto-Bmt1]Val2]-cyclosporine), a multidrug resistance modulator, with Pglycoprotein. Oncol Res 7: 603–610, 1995
Twentyman PR, Bleehen NM: Resistance modification by PSC-833, a novel non-immunosuppressive cyclosporin. Eur J Cancer 27: 1639–1642, 1991
Smith AJ, Mayer U, Schinkel AH, Borst P: Availability of PSC833, a substrate and inhibitor of P-glycoproteins, in various concentrations of serum. J Nat Cancer Inst 90: 1161–1166, 1998
Jette L, Murphy GF, Beliveau R: Drug binding to Pglycoprotein is inhibited in normal tissues following SDZPSC 833 treatment. Int J Cancer 76: 729–737, 1998
van Asperen J, van Tellingen O, Sparreboom A, Schinkel AH, Borst P, Nooijen WJ, Beijnen JH: Enhanced oral bioavailability of paclitaxel in mice treated with the Pglycoprotein blocker SDZ PSC 833. Br J Cancer 76: 1181–1183, 1997
van Asperen J, van Tellingen O, van der Valk MA, Rozenhart M, Beijnen JH: Enhanced oral absorption and decreased elimination of paclitaxel in mice with cyclosporin A. Clin Cancer Res 4: 2293–2297, 1998
Harris JW, Rahman A, Kim BR, Guengerich FP, Collins JM: Metabolism of taxol by human hepatic microsomes and liver slices: participation of cytochrome P450 3A4 and an unknown P450 enzyme. Cancer Res 54: 4026–4035, 1994
Meerum Terwogt JM, Beijnen JH, ten Bokkel Huinink WW, Rosing H, Schellens JHM: Co-administration of cyclosporin enables oral therapy with paclitaxel. Lancet 352: 285, 1998
Malingré MM, Schellens JHM, Duchin K, Rosing H, Beijnen JH: Oral paclitaxel in a twice daily dose regimen. Br J Clin Pharmacol 47: 463P, 1999
Malingré MM, Meerum Terwogt JM, Beijnen JH, Rosing H, Koopman FJ, van Tellingen O, ten Bokkel Huinink WW, Swart M, Duchin K, Schellens JHM: Clinical pharmacology of oral paclitaxel in a dose escalating study. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 18: 166a, 1999
Meerum Terwogt JM, Malingré MM, Beijnen JH, van Tellingen O, Rosing H, Koopman FJ, ten Bokkel Huinink WW, Swart M, Duchin K, Schellens JHM: Mass balance of paclitaxel (Paxene) in humans after both intravenous and oral administration. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 18: 190a, 1999
Wils P, Phung-Ba V, Warnery A, Lechardeur D, Racissi S, Hidalgo IJ, Scherman D: Polarized transport of docetaxel and vinblastine mediated by P-glycoprotcin in human intestinal epithelial cell monolayers. Biochem Pharmacol 48: 1528–1530, 1994
Richel DJ, Malingré MM, ten Bokkel Huinink WW, Rosing H. van Tellingen O, Swart M, Beijnen JH, Schellens JHM: Cyclosporin A strongly enhances the oral bioavallability of docetaxel in cancer patients. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 18: 201a, 1999
D'Incalci M, Farina P, Sessa C, Mangioni C, Conter V, Masera G, Rocchetti M, Pisoni MB, Piazza E, Beer M, Cavalli F: Pharmacokinetics of VP 16–213 given by different administration methods. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 7: 141–145, 1982
Smyth RD, Pfeffer M, Scalzo A, Comis RL: Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of etoposide (VP-16). Semin Oncol 12, Suppl 2: 48–51, 1985
Harvey VJ, Slevin ML, Joel SP, Smythe MM, Johnston A, Wrigley PFM: Variable bioavailability following repeated oral doses of etoposide. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol 21: 1315–1319, 1985
Desoize B, Woirin V, Legros M, Coninx P. Reduced oral etoposide bioavailability in patients with advanced cancer of the head and neck. J Natl Cancer Inst 84: 348–350, 1992
Nguyen L, Chatelut E, Chevreau C, Tranchand B, Lochon I, Bachaud JM, Pujol A, Houin G, Bugat R, Canal P: Population pharmacokinetics of total and unbound etoposide. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 41: 125–132, 1998
Harvey VJ, Slevin NIL, Joel SP, Johnston A, Wrigley PFM: The effect of dose on the bioavailability of oral etoposide. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 16: 178–181, 1986
Slevin ML, Joel SP, Whomsley R, Devenport K, Harvey VJ, Osborne RJ, Wrigley PFM: The effect of dose on the bioavailability of oral etoposide: confirmation of a clinically relevant observation. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 24: 329–331, 1989
Hande KR, Krozely MG, Greco FA, Hainsworth JD, Johnson DH: Bioavailability of low-dose oral etoposide. J Clin Oncol 11: 374–377, 1993
Greco FA: Chronic etoposide administration: overview of clinical experience. Cancer Treat Rev 19, Suppl C: 35–45, 1993
Lum BL, Kaubisch S, Yahanda AM, Adler KM, Jew L, Ehsan MN, Brophy NA, Halsey J, Gosland MP, Sikic BI: Alteration of etoposide pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics by cyclosporine in a phase I trial to modulate multidrug resistance. J Clin Oncol 10: 1635–1642, 1992
Keller RP, Altermatt HJ, Donatsch P, Zihlmann H, Laissue JA, Hiestand PC: Pharmacologic interactions between the resistance-modifying cyclosporine SDZ PSC 833 and etoposide (VP 16–213) enhance in vivo cytostatic activity and toxicity. Int J Cancer 51: 433–438, 1992
Leu BL, Huang JD: Inhibition of intestinal P-glycoprotein and effects on etoposide absorption. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 35: 432–436, 1995
Kobayashi K, Ratain MJ, Fleming GF, Vogelzang NJ, Cooper N, Sun BL: A phase I study of CYP3A4 modulation of oral etoposide with ketoconazoleconazol in patients with advanced cancer. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 15: 471, 1996
Shepard DR, Kobayashi K, Wang C, Ratain MJ: Population pharmacokinetic determination of the modulation of oral etoposide (VP-16) elimination by ketoconazole. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 17: 190a, 1998
Siegsmund MJ, Cardarelli C, Aksentijevich I, Sugimoto Y, Pastan I, Gottesman MM: Ketoconazole effectively reverses multidrug resistance in highly resistant KB cells. J Urol 151: 485–491, 1994
Stewart DJ, Grewaal D, Green RM, Verma S, Maroun JA, Redmond D, Robillard L, Gupta S: Bioavailability and pharmacology of oral idarubecin. Cancer Chermother Pharmacol 27: 308–314, 1991
Schleyer E, Kuhn S, Ruhrs H, Unterhalt M, Kaufmann CC, Kern W, Braess J, Straubel G, Hiddemann W: Oral idarubicin pharmacokinetics-correlation of trough level with idarubicin area under curve. Leukemia 10: 707–712, 1996
Damiani D, Michieli M, Michelutti A, Pea F, Baraldo M, Fanin R, Russo D, Furlanut M, Baccarani M: P170-related multidrug resistance. Enhancement of idarubicin content in leukemic cells with cyclosporin in vivo: a report of two cases. Leukemia 9: 1792–1795, 1995
Tolomeo M, Gancitano RA, Musso M, Porretto F, Perricone R, Abbadessa V, Cajozzo A: Comparative activity of idarubicin and idarubicinol in combination with cyclosporin A in multidrug-resistant leukemia cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 39: 157–161, 1996
Tidefelt U, Prenkert M, Paul C: Comparison of idarubicin and daunorubicin and their main metabolites regarding intracellular uptake and effect on sensitive and multidrugresistant HL60 cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 38: 476–480, 1996
Hegewisch-Becker S: MDR1 reversal: criteria for clinical trials designed to overcome the multidrug resistance phenotype. Leukemia 10, Suppl 3: S32-S38, 1996
Armand JP, Marty M: Navelbine: a new step in cancer therapy? Semin Oncol 2: 41–45, 1989
Zhou XJ, Bore P, Monjanel S, Sahnoun Z, Favre R, Durand A, Rahinani R: Pharmacokinctics of navelbine after oral administration in cancer patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 29: 66–70, 1991
Ueda K, Cardarelli C, Gottesman MM, Pastan I: Expression of full-length DNA for the human MDR1 gene confers resistance to colchicine, doxorubicin and vinblastine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 3004–3008, 1987
Meyers MB, Scotto KW, Sirotnak FM: P-glycoprotein content and mediation of vincristine efflux: correlation with the level of differentiation in luminal epithelium of mouse small intestine. Cancer Commun 3: 159–165, 1991
Zhou XJ, Zhou-Pan XR, Favre R, Rahmani R: Relative bioavailability of two oral formulations of navelbine in cancer patients. Biopharm Drug Dispos 15: 577–586, 1994
Lucas S, Donehower RC, Rowinsky EK, Trump DL, Weiner E,WarginWA, Hohneker JA: Absolute bioavailability (ABA) and pharmacokinetics of weekly navelbine (NVB) liquid filled soft gelatin capsules at full therapeutic doses in patients (pts) with solid tumors. Proc 7th NIC-EORTC Symposium on New Drugs in Cancer Therapy abstract 264, March 17–20, 1992
van Tellingen O, Sips JHM, Beijnen JH, Bult A, Nooijen WJ: Pharmacology, bioanalysis and pharmacokinetics of the vinca alkaloids and semi-synthetic derivatives. Anticancer Res 12: 1699–1716, 1992
Schellens JHM, Creemers GJ, Beijnen JH, Rosing H, de Boer-Dennert M, McDonald M, Davies B, Verweij J: Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of oral topotecan: a new topoisomerase I inhibitor. Br J Cancer 731: 1268–1271, 1996
Herben VMM, Schellens JH, ten Bokkel Huinink WW, Rosing H, van Zomeren DM, Batchelor FB, Beusenberg FB, Beijnen JH: The effect of food co-administration on the pharmacokinetics of topotecan gelatin capsules. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 17: 1999
Hendricks CB, Rowinsky EK, Grochow LB, Donehower RC, Kaufmann SH: Effect of P-glycoprotein expression on the accumulation and cytotoxicity of topotecan (SK&F 104864), a new camptothecin analogue. Cancer Res 52: 2268–2278, 1992
Hoki Y, Fujimori A, Pommier Y: Differential cytotoxicity of clinically important camptothecin derivatives in Pglycoprotein-overexpressing cell lines. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 40: 433–438, 1997
Sugiyarna Y, Kato Y, Chu XY: Multiplicity of biliary excretion mechanisms for the camptothecin derivative irinotecan (CPT-11), its metabolite SN-38, and its glucuronide: role of canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter and P-glycoprotein. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 42, Suppl: S44–9, 1998
Jansen WJM, Hulscher TM, van Ark-Otte J, Giaccone G, Pinedo HM, Boven E: CPT-11 sensitivity in relation to the expression of P170-glycoprotein and multidrug resistanceassociated protein. Br J Cancer 77: 359–365, 1998
Diasio RB, Harris BE: Clinical pharmacology of 5-fluorouracil. Clin Pharmacokinet 16: 215–237, 1989
Finch RE, Bending MR, Lant AF: Plasma levels of 5-fluorouracil after oral and intravenous administration in cancer patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol 7: 613–617, 1979
Cohen JL, Irwin LE, Marshall GJ, Darvey H, Bateman JR: Clinical pharmacology of oral and intravenous 5-fluorouracil (NSC-19893). Cancer Chemother Rep 58: 723–731, 1974
Chirstophidis N, Vajda FJ, Lucas I, Drummer O, Moon WJ, Louis WJ: Fluorouracil therapy in patients with carcinoma of the large bowel: a pharmacokinetic comparison of various rates and routes of administration. Clin Pharmacokinet 3: 330–336, 1978
Naguib FN, el Kouni MH, Cha S: Enzymes of uracil catabolism in normal and neoplastic human tissues. Cancer Res 45: 5405–5412, 1985
Harris BE, Song R, Soong SJ, Diasio RB: Relationship between dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase activity and plasma 5-fluorouracil levels with evidence for circadian variation of enzyme activity and plasma drug levels in cancer patients receiving 5-fluorouracil by protracted continuous infusion. Cancer Res 50: 197–201, 1990
Spector T, Harrington JA, Porter DJ: 5-Ethynyluracil (776C85): inactivation of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol 46: 2243–2248, 1993
Baccanari DP, Davis ST, Knick VC, Spector T: 5-Ethynyluracil (776C85): a potent modulator of the pharmacokinetics and antitumor efficacy of 5-fluorouracil. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 11064–11068, 1993
Baker SD, Khor SP, Adjei AA, Doucette M, Spector T, Donehower RC, Grochow LB, Sartorius SE, Noe DA, Hohneker JA, Rowinsky EK: Pharmacokinetic, oral bioavailability, and safety study of fluorouracil in patients treated with 776C85, an inactivator of dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase. J Clin Oncol 14: 3085–3096, 1996
Pazdur R, Hoff PM, Medgyesy D, Royce M, Brito R: The oral fluorouracil prodrugs. Oncology (Huntingt) 12, Suppl 7: 48–51, 1998
Anttila MI, Sotaniemi EA, Kairaluoma MI, Mokka RE, Sundquist HT: Pharmacokinetics of ftorafur after intravenous and oral administration. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 10: 150–153, 1983
Fukushima M, Shimamoto Y, Kato T, Uchida J, Yonekura R, Ohshimo H, Shirasaka T: Anticancer activity and toxicity of S-1, an oral combination of tegafur and two biochemical modulators, compared with continuous i.v. infusion of 5-fluorouracil. Anticancer Drugs 9: 817–823, 1998
Kono A, Hara Y, Sugata S, Karube Y, Matsushima Y, Ishitsuka H: Activation of 50deoxy-5-fluorouridine by thymidine phosphorylase in human tumors. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 31: 175–178, 1983
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bardelmeijer, H.A., van Tellingen, O., Schellens, J.H. et al. The Oral Route for the Administration of Cytotoxic Drugs: Strategies to Increase the Efficiency and Consistency of Drug Delivery. Invest New Drugs 18, 231–241 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006469621561
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006469621561