Abstract
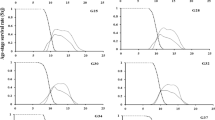
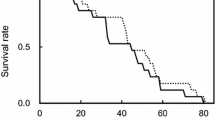
Life-fertility tables were described for Bracon hebetor Say (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) developing on the millet head caterpillar (MHC), Heliocheilus albipunctella de Joannis (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Mated B. hebetor females lived an average of 24.7 days, oviposited ca. 22 days, and produced 173.7 adult progeny with a 1:1 sex ratio. The estimated innate capacity of increase (rc) and net reproductive rate (R0) were 0.26 and 86.5, respectively. The mean generation time was 17 days.
Résumé
Les tables de vie et fécondité ont été décrites pour Bracon hebetor Say (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) se développant sur la mineuse de l’épi du mil, Heliocheilus albipunctella de Joannis (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). En moyenne, les femelles fécondées de B. hebetor vécurent 24,7 jours, ont pondu pour une durée de 22 jours, et ont produit une progéniture de 173,7 adultes avec un sexe ratio de 1:1. Le taux d’accroissement (rc) de la population et le taux reproductif net (R0) étaient de 0,26 et 86,5, respectivement. La durée moyenne d’une génération était de 17 jours.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benson J. F. (1973) Intraspecific competition in the population dynamics of Bracon hebetor Say (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). J. Anim. Ecol. 42: 105–124.
Bhatnagar V. S. (1987) Conservation and encouragement of natural enemies of insect pests in dry land subsistence farming: problems, progress and prospects in the Sahelian zone. Insect Sci. Applic. 8, 791–795.
Clark A. M. (1963) The influence of diet upon the adult life span of two species of Bracon. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 56, 616–619.
Gahukar R. T., Guevremont H., Bhatnagar V. S., Doumbia Y. O., N’doye M. and Pierrard G. (1986) A review of the pest status of the millet spike worm Raghuva albipunctella) (Noctuidae: Lepidoptera) and its management in the Sahel. Insect Sci. Applic. 7, 457–463.
Gerling D. (1969) The parasites of Spodoptera littoralis Boisd (Lep.: Noctuidae) eggs and larvae in Israel. Israel J. Entomol. 4, 73–81.
Girling D. (1971) Occurrence, abundance and efficiency of some local parasites attacking Spodoptera littoralis (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in selected cotton fields in Israel. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 64, 1373–1376.
Guevremont H. (1982) Etude de la mineuse de l’épi et autres insects du mil. Rapport Annuel de Recherches Pour l’Année 1981. Centre National de Recherches Agronomiques (CNRA); Tarna (Maradi), Niger.
Guevremont H. (1983) Recherches sur l’entomofaune du mil. Rapport Annuel de Recherches Pour l’Année 1982. Centre National de Recherches Agronomiques (CNRA); Tarna (Maradi), Niger.
Hagstrum D. W. and Smittle B. J. (1977) Host finding ability of Bracon hebetor and its influence upon adult parasite survival and fecundity. Environ. Entomol. 6, 437–439.
Harakly F. A. (1968) Biological studies of the cabbage web-worm, Hellula undalis F. (Lepidoptera: Crambidae: Pyraustinae). Bull. Soc. Entomol. Egypte 52, 294–298.
Payne N. M. (1933) The differential effect of environmental factors upon Microbracon hebetor Say (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) and its host Ephestia kuhniella Zeller (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Biol. Bull. 2, 187–205.
Rawat R. R., Rathore Y. S. and Saxena D. K. (1968) Bionomics of Hellula undalis Fb., the cabbage borer (Pyralidae: Lepidoptera) at Jabalpur. Indian J. Entomol. 30, 235–237.
Reinert J. A. and King E. W. (1971) Action of Bracon hebetor Say as a parasite of Plodia interpunctella at controlled densities. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 64, 1335–1340.
Richards O. W. and Thomson W. S. (1932) A contribution to the study of the genera Ephestia Gn. (including Strimax Dyar), and Plodia Gn. (Lepidoptera: Ptfycitidae) with notes on the parasites of the larvae. Trans. R. Entomol. Soc. Lond. 80, 169–250.
Rotary N. and Gerling D. (1973) The influence of some external factors upon sex ratio of Bracon hebetor Say (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). En viron. Entomol. 2, 134–138.
Southwood T. R. E. (1978) Ecological methods, with particular reference to the study of insect populations. Chapman and Hall, New York.
Wyett G. C. (1943) Some aspects of parasitism in field populations of Plutella maculipennis Curt. J. Entomol. Soc. Sth. Afr. 6, 65–80.
Ullyett G. C. (1945) Distribution of progeny by Microbracon hebetor Say, J. Entomol. Soc. Sth. Afr. 8, 123–131.
Youm O. (1990) Evaluation of natural enemies associated with the millet stalk borer, Haimbachia ignefusalis (Hampson) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) in Niger. Ph.D. dissertation, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Youm, O., Gilstrap, F.E. Life-Fertility Tables of Bracon Hebetor Say (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) Reared On Heliocheilus Albipunctella De Joannis (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Int J Trop Insect Sci 14, 455–459 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400014120
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400014120
Key Words
- Life-fertility tables
- Bracon hebetor
- millet head caterpillar
- Heliocheilus albipunctella
- West Africa
- Niger