Abstract
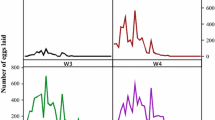
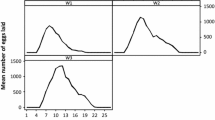
Studies were conducted during the dry period February to May 1986 in River Shelliekha, Bahr El Arab fly belt, Sudan, to obtain baseline data on catch and age compositions, reproductive status and trypanosome infection rates of trapped and fly round samples of Glossina morsitans submorsitans. The objective was to assess the tsetse situation before the establishment of trypanosomiasis treatment stations at the northern limits of the fly belt. Trapped tsetse included significantly higher proportions of tenera) and non-teneral females and a lower male:female ratio. Insemination rates were over 98% in both samples. In any one group, the frequency of pregnancy with egg predominated, followed by the second, first and lastly the third instar larva. There were significant differences between the two groups of females in the proportions of nullipars and pregnancy with any one of the larval instars. Abortion was the predominant reproductive abnormality and no relationship could be found between abortion rate and the sampling method, age or trypanosome infection rate of females. Age compositions were similar in the two samples, save for age categories 0 and 1 for females and two and four for males. Flies were infected with Trypanosoma vivax and T. congolense only, though T. brucei infections could also be diagnosed in livestock.
Résumé
Des études ont été conduites durant la aison séche de Févier à Mai 1986, sur la riviére Shelliekha, dans la ceinture de mouches tsé-tsé de Bahr El Arab au Soudan, en que d’obtenir des données de base sur la capture et la composition en âges, sur la reproductivité et le taux d’infection au trypanosome par les mouches, Glossina morsitans submorsitans, capturées par piégeage et par écrans attractifs. L’objectif du travail était d’estimer la population de la mouche tsé-tsé avant d’installer des stations de traitement de trypanosome dans le nord de la ceinture de mouches. Les mouches tsé-tsé capturées comprenaient un nombré élevé de mouches à jeun et de femelles adultes et une faible proportion mâle: femelle. Les taux d’insémination étaint supérieurs à 98% dans les deux types d’echantillonnage. La fréquence de femelles gravides dans les deux groupes était prédominante, suivis par le second, premier et dernier stades larvaires. Il y avait de différences significatives entre les femelles de deux groupes échantillonés en ce qui concerne le nombre d’individus n’ayant pas pondu les oeufs et les femelles gravides, quels que soient les stades larvaires. L’avortement etait l’anomalie de reproduction prédominante, aucun rapport n’a été trouvé entre le taux d’avortement et la technique d’échantillonnage, l’âge ou le taux d’infection au trypanosome par les femelles. La composition en âges etait identique dans les deux échantillons à l’exception de la categorie d’âge 0 et 1 pour les femelles, et deux quatre pour les mâles. Les mouches tsé-tsé étaient essentiellment infestées avec Trypanosoma vivax et T. congolense bien que l’infection à T. brucei a pu être diagnostiquée chez le bétail.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel El Razig M. T. and Yagi A. I. (1973) The distribution and advance of Glossina morsitans in Southern Darfur District. Bull. Epizoot. Dis. Afr. 21, 253–258.
Allsop R. (1985) Wing fray in Glossina morsitans centralis (Diptera: Glossinidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 75, 1–11.
Buxton P. A. (1955) The Natural History of Tsetse Flies, London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, Memoir No. 10, London, H. K. Lewis & Co. Ltd.
Challier A. (1965) Amelioration de la methode de determination de l’age physiologique des glossines. Etudes faites sur Glossina palpalis gambiense Vanderplank 1949. Bull. Soc. Path. Exot. 58, 250–259.
Challier A. and Laveissiere C. (1973) Un nouveau piege pour la capture des glossines (Glossina: Diptera, Muscidae) description et essais sur le terrain. Cah. ORSTOM Ser. Entomol. Parasitai. 11, 251–260.
Dransfield R. D., Brightwell R., Chaudhury M. F. B., Golder T. K. and Tarimo S. A. R. (1986) The use of odour attractants for sampling Glossina pallidipes Austen (Diptera: Glossinidae) at Nguruman, Kenya. Bull. Entomol. Res. 76, 607–619.
Denlinger D. L. and Ma W. C. (1974) Dynamics of the pregnancy cycle in the tsetse Glossina morsitans. J. Insect Physiol. 20, 1015–1026.
Ford J. and Katondo K. M. (1977) Maps of tsetse flies (Glossina) distribution in Africa, 1973 according to subgeneric groups on scale 1:5,000,000. Bull. Anim. Hlth. Prod. Afr. 25, 188–194.
Glasgow J. P. (1963) The Distribution and A bundance of Tsetse. 241 pp. Pergamon Press, Oxford.
Hall M. J. R., Khier S. M., Rahman A. H. A. and Noga S. (1983) Tsetse and trypanosomiasis survey of Southern Darfur Province I. Bovine trypanosomiasis. Trop. Anim. Hlth. Prod. 15, 191–206.
Hall M. J. R., Khier S. M., Rahman A. H. A. and Noga S. (1984) Tsetse and trypanosomiasis survey of Southern Darfur Province II. Entomological aspects. Trop. Anim. Hlth. Prod. 16, 127–140.
Hargrove J. W. (1977) Some advances in trapping of tsetse (Glossina spp.) and other files. Ecol. Entomol. 2, 123–137.
Harley J. M. B. (1967a) Further studies on age and trypanosome infection rates of Glossina pallidipes Aust., G. palpalis fuscipes Newst. and G. brevipalpis Newst. in Uganda. Bull. Entomol. Res. 57, 459–477.
Harley J. M. B. (1967b) The influence of sampling method on the trypanosome infection rate of catches of Glossina pallidipes Aust., G. palpalis fuscipes Newst., and G. brevipalpis Newst. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 10, 240–252.
Jackson C. H. N. (1946) An artificially isolated generation of tsetse flies (Diptera). Bull. Entomol. Res. 37, 291–299.
Jordan A. M. (1974) Recent developments in the ecology and methods of control of tsetse flies Glossina spp. (Diptera: Glossinidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 63, 361–399.
Katondo K. M. (1984) Revision of second edition of tsetse distribution maps. An interim report. Insect Sci. Applic. 5, 381–388.
Langley P. A. and Hall M. J. R. (1984) Aspects of the regulation of the mating behaviour in tsetse. Insect Sci. Applic. 5, 351–356.
Lloyd L. L. and Johnson W. B. (1924) The trypanosome infection of tsetse flies in Northern Nigeria and a new method of estimation. Bull. Entomol. Res. 14, 265–288.
Madubunyi L. C. (1978) Relative frequency of reproductive abnormalities in a natural population of Glossina morsitans morsitans (Diptera: Glossinidae) in Zambia. Bull. Entomol. Res. 68, 437–442.
Mohammed-Ahmed M. M., and Dairri M. F. (1987) Trypanosome infection rate of Glossina pallidipes during wet and dry seasons in Somalia. Trop. Anim. Hlth. Prod. 19, 11–20.
Mohamed-Ahmed M. M., Abdel Karim E. I. and Rahman A. H. A. (1988) Field multiple drug-resistant bovine trypanosomes and recommendations for a new drug policy in South Darfur Province, Sudan. Veterinary Research Administration Report. Soba. Khartoum, Sudan.
Mohamed-Ahmed M. M., Ahmed A. I. and Ishag A. (1989) Trypanosome infection rate of Glossina morsitans submorsitans in Bahr El Arab, South Darfur Province Sudan. Trop. Anim. Hlth. Prod. 21, 229–244.
Okiwelu S. N. (1977) Insemination, pregnancy and suspected abortion rates in a natural population of Glossina morsitans morsitans (Diptera: Glossinidae) in the Republic of Zambia. J. Med. Entomol. 14, 19–23.
Otieno L. H. (1983) Inadequacy of the dissection method for estimation of the trypanosome infection rates. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 77, 329–330.
Randolf S. E. and Rogers D. J. (1981) Physiological correlates of the availability of Glossina morsitans centralis Machado to different sampling methods. Ecol. Entomol. 6, 63–77.
Rogers D.J. (1978) Metabolic strategies of male and female tsetse (Diptera: Glossinidae) in the field. Bull. Entomol. Res. 68, 639–654.
Ryan L. and Molyneux D. H. (1982) Reproductive statistics of a natural population of Glossina morsitans centralis Vand. (Diptera:Glossinidae). Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 76, 215–218.
Saunders D. S. (1962) Age determination for female tsetse flies and the age compositions of samples of G. pallidipes, G. p.fuscipes and G. brevipalpis. Bull. Entomol. Res. 53, 221–238.
Snow W. F. (1977) The Malaise trap as a method for sampling Glossina morsitans submorsitans Newstead: a primary note. Proc. Int. Sci. Comm. Tryp. Res. 15th Meeting Banjul, The Gambia, Publication No. 110, pp. 329–333.
Takken W. (1984) Studies on the biconical trap as a sampling device for tsetse (Diptera: Glossinidae) in Mozambique. Insect Sci. Applic. 5, 357–361.
Turner D. A. (1987) The population ecology of Glossina pallidipes Austen (Diptera:Glossinidae) in the Lambwe Valley, Kenya I. Feeding behaviour and activity patterns. Bull. Entomol. Res. 77, 317–333.
Turner D. A. and Snow W. F. (1984) Reproductive abnormality and loss in natural populations of Glossina pallidipes Austen (Diptera: Glossi nidae) in Kenya. Bull. Entomol. Res. 74, 299–309.
Vale G. A. (1980) Field studies of responses of tsetse flies (Glossinidae) and other Diptera to carbon dioxide, acetone and other chemicals. Bull. Entomol. Res. 70, 563–570.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohamed-Ahmed, M.M., Abdel Karim, E.I. & Rahman, A.H.A. Reproductive Status, Catch and Age Compositions of a Natural Population of Glossina Morsitans Submorsitans in Bahr El Arab Fly Belt, Sudan. Int J Trop Insect Sci 14, 445–453 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400014119
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758400014119